Current research favors chondroitin as a way to combat the negative consequences of cartilage loss.
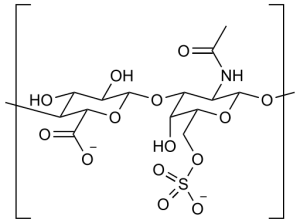
Chondroitin sulfate is a crucial structural component of cartilage. It is believed to aid joint health through:
- Minimizing cartilage loss. Chondroitin seems to reduce the rate of cartilage breakdown, helping relieve pain from arthritis.
- Improving mobility and comfort. Chondroitin seems to improve joint movement, elasticity, and strength while also reducing pain.
Overview
Chondroitin, more accurately known as chondroitin sulfate (CS), is a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) compound known to be the main structural component of cartilage – the resilient, cushion-like tissue between joints.
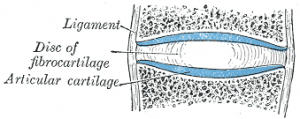
In addition, chondroitin also seems to aid joint health by absorbing excess fluid and blocking enzymes that break down cartilage.
In decades past medical practitioners mistakenly believed that chondroitin was capable of healing joint damage similar to the way deer antler is reported to. However, current research leans more toward its ability to minimize the consequences of joint wear and tear, including inflammation, cellular breakdown, and an excess of fluids.
How Chondroitin May Help With Joint Health
As a joint health ingredient, chondroitin may protect cartilage via two potential mechanisms:
Reducing inflammation
Chondroitin seems capable of decreasing the production of several key inflammatory molecules, including nuclear factor-kB (NF-κB), Erk1/2, and abrogated p38MAPK.2 Decreasing inflammatory damage around joints may be beneficial for their overall health.
Diminishing the availability of cartilage-destroying cells
Chondroitin seems to increase the expression ratio of osteoprotegerin (OPG) to receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL).3 In turn, this effect may:
- Reduce the amount of cellular damage that NF-κB can inflict.
- Reduce the availability of osteoclasts, which break down bone and cartilage.
Enhancing joint mobility
Although the precise mechanism is currently unknown, some medical researchers believe that chondroitin may also improve joint elasticity and movement by absorbing excess water around joints.
Chondroitin Benefits & Uses for Joint Health
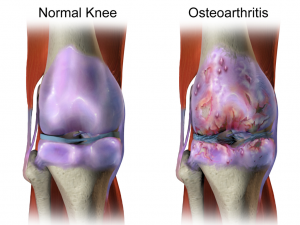
Most people take chondroitin supplements for helping with joint pain and arthritis in particular. And although chondroitin may not be as effective as previously though, recent research suggests that it can still aid joint health by:
- Reducing cartilage loss. Chondroitin seems to slow the deterioration of cartilage and bones as a result of joint conditions such as osteoarthritis.4
- Reducing joint pain secondary to slowing down cartilage loss.
- Enhancing joint mobility. Chondroitin has potential to improve movement and elasticity of knee and hip joints.
Research
Animal Research
According to animal studies, chondroitin may benefit joint health by:
- Reducing inflammation and cartilage breakdown. Chondroitin was shown to reduce the expression of inflammatory markers and enzymes that break down cartilage in bovine joints.6
Human Research
Current clinical studies have found that chondroitin sulfate reduces joint pain and improves joint function, particularly in cases of osteoarthritis.
Chondroitin (800 mg) may decrease hand pain and improve hand function in people with osteoarthritis
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind investigation, 162 patients with hand osteoarthritis (OA) were given either a placebo or 800 mg of chondroitin sulfate (CS) once a day for 6 months. Compared to the placebo, there was significantly decreased hand pain as shown by decreases in visual analog scores (VAS), improved hand function, and reduced morning stiffness.
- The study concluded that “CS improves hand pain and function in patients with symptomatic OA of the hand and shows a good safety profile.”7
Chondroitin (800 mg) may decrease knee pain and improve knee function in people with osteoarthritis
In this randomized, placebo-controlled investigation, 120 patients with osteoarthritis were given either placebo or 800 mg of chondroitin sulfate (CS) every day for a 3-month period, twice in the same year. The decrease in knee function due to osteoarthritis (OA) was reduced by 36% in the CS group compared to only 23% in the placebo group. In addition, pain and cartilage reduction were alleviated alongside improvement of walking time in the CS group.
- The study concluded that “oral CS decreased pain and improved knee function…with symptom-modifying agents for OA. The inhibitory effect of CS on the radiological progression of the medial femoro-tibial joint space narrowing could suggest further evidence of its structure-modifying properties in knee OA.”8
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 130 patients with osteoarthritis (OA) were given placebo or 1 gram of chondroitin sulfate (CS) daily for 3 months. Researchers identified a trend toward greater improvement in the CS compared to the placebo group, including reduced pain and improved function.
- The study concluded that there was “a trend towards efficacy of CS 1 g/day compared to placebo with good tolerability after 3 month treatment, and persistent efficacy one month posttreatment.”9
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study, 42 patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) were given placebo or 800 mg of chondroitin sulfate (CS) every day for 1 year. CS significantly reduced pain, increased overall mobility, and stabilized the medial femoro-tibial joint width compared to placebo.
- The study concluded that “oral chondroitin 4- and 6-sulfate is an effective and safe symptomatic slow-acting drug for the treatment of knee OA. In addition, CS might be able to stabilize the joint space width and to modulate bone and joint metabolism.”10
Dosage for Joint Health
- Research studies generally use between 800 and 1000 mg of chondroitin sulfate per day
- Typical supplemental capsules range from 1000 – 1200 mg, daily
- Chondroitin is frequently combined with glucosamine and MSM, other supplements with proposed joint health benefits
Supplements in Review Says
- Chondroitin 1000 – 1200 mg daily for joint health.
Chondroitin may support joint mobility and reduce cartilage loss. We recommend chondroitin as a supplement for cartilage loss, especially in cases of osteoarthritis.
1000 – 1200 mg seems to be the ideal dose. We recommend taking chondroitin in 1000 – 1200 mg daily doses until research clarifies the optimal dosage.
Leave a Reply