Non-intoxicating cannabis compound CBD seems to help with arthritis.

CBD is one of the main therapeutic compounds found in cannabis plants. It may aid joint health by:
- Reducing inflammation and pain. CBD has been shown to interact with nervous system receptors that control inflammation and pain.
- Immunosuppression. CBD can reduce overactive immune system activity, which is helpful for autoimmune (rheumatoid) arthritis.
Overview
CBD (cannabidiol) is one of the most abundant cannabinoids – natural compounds that are largely responsible for the medicinal and psychoactive properties of cannabis plants, also known as marijuana. CBD has multiple health benefits, the most recognized of which are:
- Reduction of inflammation and pain
- Reduction of anxiety and stress
Moreover, unlike THC – the cannabinoid most associated with cannabis – CBD does not have any intoxicating effects. Because of this, it has experienced a large surge in popularity as more and more people seek to reap the health benefits of cannabis without the mind-altering effects.
CBD is now being used to help with a large range of conditions, including anxiety disorders, sleep problems, and arthritis. Early research suggests that much like THC, CBD can help reduce the inflammation and pain associated with this joint disorder.
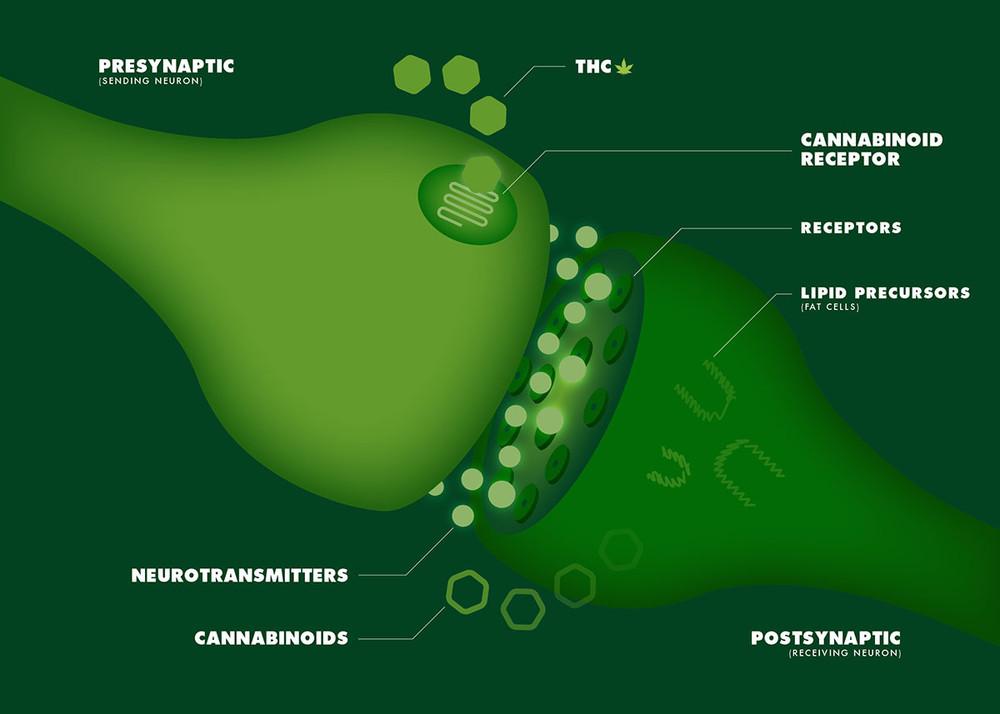
How CBD Might Help With Joint Health
Cannabidiol is known to work via multiple mechanisms of action, many of which remain unknown or poorly understood.
Interacting with receptors that control pain and inflammation
At the most basic level, CBD appears to either block or activate several receptors that control inflammation, the sensation of pain, and immune system function. More specifically, CBD seems to:
- Activate the TRPV1 (vanilloid) receptor which controls inflammation and sensitivity to pain 2
- Block the GPR55 receptor, which controls nociception – the response of the nervous system to potentially harmful stimuli 3
Increasing levels of anandamide and adenosine
CBD has been shown to reduce the uptake and breakdown of anandamide – a neurotransmitter and the main endocannabinoid that is produced inside the body. [Deutsch DG. A Personal Retrospective: Elevating Anandamide (AEA) by Targeting Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) and the Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (FABPs). Front Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 13;7:370. eCollection 2016.] This effect increases the levels of anandamide, which may result in reduction of inflammation and pain through increased activation of the body’s endocannabinoid system.
In addition, CBD also reduces the uptake – and therefore increases the levels – of adenosine, another neurotransmitter that seems to suppress inflammation and immune system function. This effect may explain how CBD inhibits the overactive immune response seen in rheumatoid arthritis. 4
CBD Benefits & Uses for Joint Health
CBD is growing increasingly popular as a way to reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling, and improve overall joint function seen in the two main types of arthritis: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid (autoimmune) arthritis. Although clinical trials to back these uses of CBD are only just beginning, these effects are supported by an increasing number of research studies in animals.
Research
Animal Research
Numerous investigations in rodents have shown both the positive effects and mechanisms by which CBD reduces joint pain, swelling, and inflammation seen in arthritis.
CBD gel seems to improve arthritis pain and inflammation
This study tested the use of transdermal (directly on the skin) CBD in a rat model of arthritis. CBD gel (0.6, 3.1, 6.2, or 62.3 mg) was applied daily for 4 days on the affected knee joints. CBD gel was found to reduce joint swelling, pain, and pro-inflammatory biomarker molecules in a dose-dependant manner, with the 6.2 and 62.3 mg doses having the strongest effect.
- The researchers concluded that “topical CBD application has therapeutic potential for relief of arthritis pain-related behaviours and inflammation without evident side-effects.” 5
CBD appears to improve rheumatoid arthritis and stop its progression
For this investigation, arthritic mice were given CBD by injection or orally. CBD was found to influence the immune system, with effects such as reduced release of tumor necrosis factor alpha, a pro-inflammatory molecule. Consequently, CBD was found to stop the progression of arthritis, with optimal effect at doses of 5 mg/kg by injection and 25 mg/kg orally.
- The researchers concluded that “CBD, through its combined immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory actions, has a potent anti-arthritic effect…” 6
CBD appears to reduce inflammation and pain in rheumatoid arthritis
This study examined the use of CBD in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Rats were treated with CBD (5 – 40 mg/kg) for 3 days after the onset of arthritic inflammation. CBD was found to reduce edema (swelling) and pain sensitivity.
- The researchers concluded that “oral cannabidiol has a beneficial action on two symptoms of established inflammation: edema and hyperalgesia.” 7
Human Research
CBD is still a novel area of research, which explains the lack of human trials.
CBD plus THC-based medication appears to ameliorate rheumatoid arthritis
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined the effectiveness of Sativex – a cannabis-based medicine containing THC and CBD – in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A total of 58 people were given Sativex or placebo daily for 5 weeks. The treatment group saw significant improvement of pain, sleep quality, and overall RA activity.
- The researchers concluded that “In the first ever controlled trial of a CBM in RA, a significant analgesic effect was observed and disease activity was significantly suppressed following Sativex treatment.” 8
Dosage for Joint Health
- There is no standard CBD dose for arthritis because of the lack of clinical research
- CBD supplements typically suggest 20 – 25 mg doses of CBD, taken as hemp oil or extract capsules
Available Forms
- CBD oil. The most popular form of CBD, oil tinctures offer ease of use alongside long duration and fast onset.
- CBD capsules/edibles. Although convenient and long-lasting, capsules and edibles have lower efficacy because of low bioavailability.
- CBD vape oil. Vaping CBD provides the fastest relief and strong effects, but has the shortest duration.
- Topical CBD. Topical CBD is applied to the skin as a cream, balm, or ointment, which is an effective option for arthritis and other types of musculoskeletal pain.
- CBD Isolate. 99%+ pure CBD in crystal/powder form.
Supplements in Review Says
- CBD cream or oil 20+ mg for joint health.
CBD seems to be a promising way to help with arthritis. Although clinical trials are just beginning, existing research evidence – coupled with the lack of side effects – make CBD a promising option for ameliorating arthritis.
There is no established dosage of CBD for joint health. It’s best to start with the dosages recommended by the given CBD supplement, which are usually in the 20 – 25 mg range. You can then try increasing the dosage until you see the desired effect.
have started with 5mg cbd increased to 25 mg I am feeling some pain relief. increasing to 50 mg today l in fingers and less pain in hips joints. Will let you know if 50 mg gives me better results.
I have had my right hip replaced ,and now my left hip joint is very painful. Would CBD oil help with my pain . ?
Anyone with chronic pain from arthritis knows often that pain and stiffness is worse in the morning. So when I tried vaping CBD oil for chronic pain relief, that was one of my major concerns. I was skeptical at first. I tried it in the morning. I always get up before the kids anyway so they aren’t exposed too much to Zombie Mom. It usually takes nearly 2 hours for the morning aches to work their way to a manageable level. The first morning, within a half hour I was up and moving. I still (and probably always will) have some pain and stiffness in my hands and feet due to the permanant damage but I would say the water soluble BioCBDplus helps bring the pain in those areas down from an 8 to a 2, something that has never happened with any of my prescription NSAIDs. – Leanne