An adaptogenic herb that helps erectile strength and male sex drive… but it’s not really a T-booster.
![By H. Zell (Own work) [GFDL or CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Tribulus_terrestris_as-a-t-booster-225x300.jpg)
- Possible influence on luteinizing hormone (LH), which plays a role in testosterone production.
- May increase sensitivity to androgens (male hormones), which could explain its well-documented sex drive benefits for men.
Other Benefits for Men
Tribulus appears to improve erectile function, especially in men with androgen deficiency or low sperm count. This aphrodisiac quality may extend to help overall sexual health, including libido and male performance.
Overview
Tribulus terrestris is a Mediterranean plant native to warm and temperate parts of southern Europe, Asia, Africa and Australia. A hardy vine, Tribulus can thrive even in arid, poor-soil conditions. It’s commonly called puncture vine because its thorny nuts are so sharp they can flatten bicycle tires.
![By Zeynel Cebeci (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Tribulus-spikes.jpg)
Today, the bodybuilding industry touts Tribulus as a T-booster that can increase strength and lean muscle mass in men. However, clinical studies have cast doubt on Tribulus’s T-boosting abilities.
How we think Tribulus might work
Tribulus supplies a primary active ingredient called protodioscin, which belongs to a class of compounds called steroidal saponins.
Protodioscin (and the other saponins in Tribulus) has some potent benefits for male health that might influence T, but absolutely will promote the feeling of masculine health–particularly sexual prowess–that’s associated with robust testosterone levels.
In particular, Tribulus’s “active compound” Protodioscin is believed to:
- Act as a precursor used in the formation of testosterone
- Stimulate production of DHEA, another T precursor
- Increase luteinizing hormone, which may assist T production
- Increase the body’s sensitivity to T and other male hormones
Our take: Tribulus is not a direct T booster. It does, however, seem to play a role in the body’s production and utilization of male sex hormones.
What about Tribulus for Sports Nutrition?
Tribulus is aggressively marketed as an herb for enhancing athletic capacity, strength, endurance, and overall performance at the gym. But sorry athletes… one recent journal article says there’s no evidence that Tribulus helps muscle mass, strength, or T levels, either alone or when combined with strength training.
The authors of this review attributed Tribulus’s popularity among athletes to “a temporary placebo effect,” and went on to conclude that “The published data concerning TT do not provide strong evidence for either usefulness or safe usage in sport.“1
Research
Animal Research
Some early research suggests that Tribulus works as an aphrodisiac in rats with low levels of male hormones.2. Additional research has suggested that Tribulus seems to improve erectile function in both animal tissues and live rabbits after 1 month of oral treatment.3.
Tribulus’s effects on male hormones are less clear. One study found that oral doses of Tribulus improved LH levels in rats with low male hormone levels. However, LH only increased slightly in healthy control animals, and the studies didn’t reveal any increases in testosterone at all.4.
A Tribulus extract given by injection to rhesus monkeys, rabbits, and rats showed increases in blood T levels for all three species. However, another study showed no increase in blood T levels in rats that were fed a Tribulus extract for 28 days.5
Human Research
Research on Tribulus’s possible androgen benefits seems to create even more conflict. While there’s no solid evidence that Tribulus boosts T or other male hormones in men, there are a few studies that suggest it may help men with erectile dysfunction, low sex drive, and other masculine concerns.
Tribulus may improve sexual health in men with low sperm count
An Indian study gave Tribulus to men complaining of low sperm count and infertility, then asked them to answer a questionnaire about their symptoms. The results seemed to suggest that Tribulus may improve sexual health in men with a low sperm count. However, further testing found no evidence that Tribulus increases sperm count.
- Researchers reported that Tribulus seemed to bring significant benefits for erectile strength & rigidity, premature ejaculation, and achievement of orgasm… but in terms of male hormones, Tribulus was associated with “a statistically insignificant difference” that trended towards higher LH and lower T levels.6
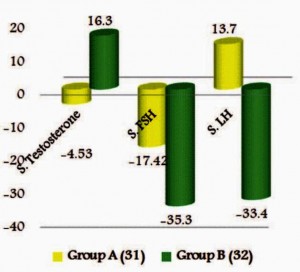
Tribulus may boost certain male hormones in men who are deficient
A pilot study gave 750 mg of Tribulus once a day for 3 months to 30 men complaining of androgen deficiency. During treatment, the men answered a questionnaire measuring their erectile function and had their T and LH levels monitored. At the end of three months, the patients experienced an increase in total and free T levels, but not in levels of LH. The higher T levels were associated with an increase in the quality of erections.
- Researchers concluded that these results “….showed a statistically significant difference in the level of testosterone (total and free) and IIEF-5 (a measure of erectile function), but no statistically significant difference in the level of LH before and after treatment.”7.
It’s hard to base much on the Roaiah study: Its results conflict with evidence suggesting Tribulus boosts LH, and the T benefits it shows for androgen-deficient men may not translate to men who already have healthy T levels.
Tribulus fails to influence androgens in young male subjects
Another study on two experimental groups of healthy young men given 10 mg and 20 mg of Tribulus per kilogram of bodyweight found that Tribulus didn’t increase T production at all when compared to a healthy control group.
- Researchers in this study concluded that “The findings in the current study anticipate that Tribulus terrestris steroid saponins possess neither direct nor indirect androgen-increasing properties.”8
Tribulus has no effect on T in young, healthy athletes
A study on healthy athletes tested the hypothesis that Tribulus raises T in urine samples. The studies found no significant changes in T/E ratio after either short-term or long-term use (up to 5 weeks) of a Tribulus supplement.
- Researchers concluded that Tribulus made no difference in testosterone levels, and further reported that “T. terrestris did not produce the large gains in strength or lean muscle mass that many manufacturers claim can be experienced within 5-28 days.“9
Another (very small 2-subject) study echoed these findings, with researchers concluding that “T. terrestris showed no impact on the endogenous testosterone metabolism.”10.
Will Tribulus make me test positive for banned steroids?
No. Tribulus does not increase T levels beyond the cutoff T/E ratio of 4:1 set by the World Anti-Doping League. The World Anti-Doping League tests for use of illegal steroids using a 4:1 ratio of testosterone to epitestosterone. A T/E ratio over 4:1 indicates the use of anabolic steroids, which boost T production in the body. This fact seems to further verify that Tribulus just doesn’t do much for testosterone.
Dosage Notes
The human body seems to tolerate Tribulus well. Doses of up to 6 grams of the plain fruit powder have been traditionally used with no ill effects. The dose range for most Tribulus supplements is between 250 and 750 mg of dried herb. A dose between 200 and 450 mg is typically used to boost libido and sexual performance in men.
Side Effects
Side effects from Tribulus are also mild. The most common side effects are trouble sleeping and upset stomach (which may be improved by taking Tribulus with food).
Available Forms of Tribulus
Tribulus is usually sold in capsules or as a loose powder that can be made into a tea or added to a beverage.
Standardized Tribulus Extract: A Tribulus extract standardized to contain 40-60% saponins. A standardized Tribulus extract is your best bet: Although the saponins in Tribulus don’t seem to directly increase T, they may have other benefits for male sexual health.
Full-Spectrum Extract: An extract that contains the full range of Tribulus’ plant chemicals. Not standardized for saponin content.
Plain Fruit Powder: This is the plain powdered form of Tribulus and requires larger doses to be effective (up to 6 grams in humans).
Supplements in Review Recommendation
- Tribulus standardized to 40%+ saponins, 500 mg daily
Tribulus is great for masculine health… but benefits appear to be limited to male libido and sexual performance. Despite its reputation, tribulus falls short as a testosterone booster (and as a sports nutrient)–simply because any clinical evidence appears to be weak and conflicted.
By all means, take Tribulus for sexual health. A 500 mg+ saponin-standardized Tribulus supplement will supply guaranteed potency that gives you the best chance of experiencing this herb’s legendary bedroom benefits. We’re not talking quality of sleep, either.
Leave a Reply