
The skincare industry offers many different options for keeping your skin young and healthy. You can use creams, gels, lotions, go to a spa, get dermal fillers, chemical peels, laser treatments, and even plastic surgery. But these treatments can be expensive, harmful, and often ineffective. One alternative solution that is rapidly growing in popularity is dietary supplements. These supplements boost your skin from the inside out, and in many cases can be taken in topical forms.
But how do skin supplements work? What is the best way to take them? Are they backed by research? In this skin supplements guide, we are going to answer these and other questions by looking at the science and medical research behind skin supplementation.
Skin Basics
The skin is the body’s largest organ. As you probably guessed, the skin’s major role is to form a protective barrier that separates the rest of your body from the outside environment. The skin helps prevent dehydration, defends against harmful microbes and substances, protects against the sun, helps control your temperature, protects the bones, muscles, and organs from damage, and alerts you about heat, cold, and other physical sensations to keep you safe. It also acts as a storage area for water and nutrients and produces vitamin D.
In addition, the skin is one of the most important indicators of overall health and age. Because of this, most people are as equally concerned about the appearance of their skin as its overall health. Indeed, the desire to keep your skin looking as youthful as possible drives a multi-billion dollar skincare industry.
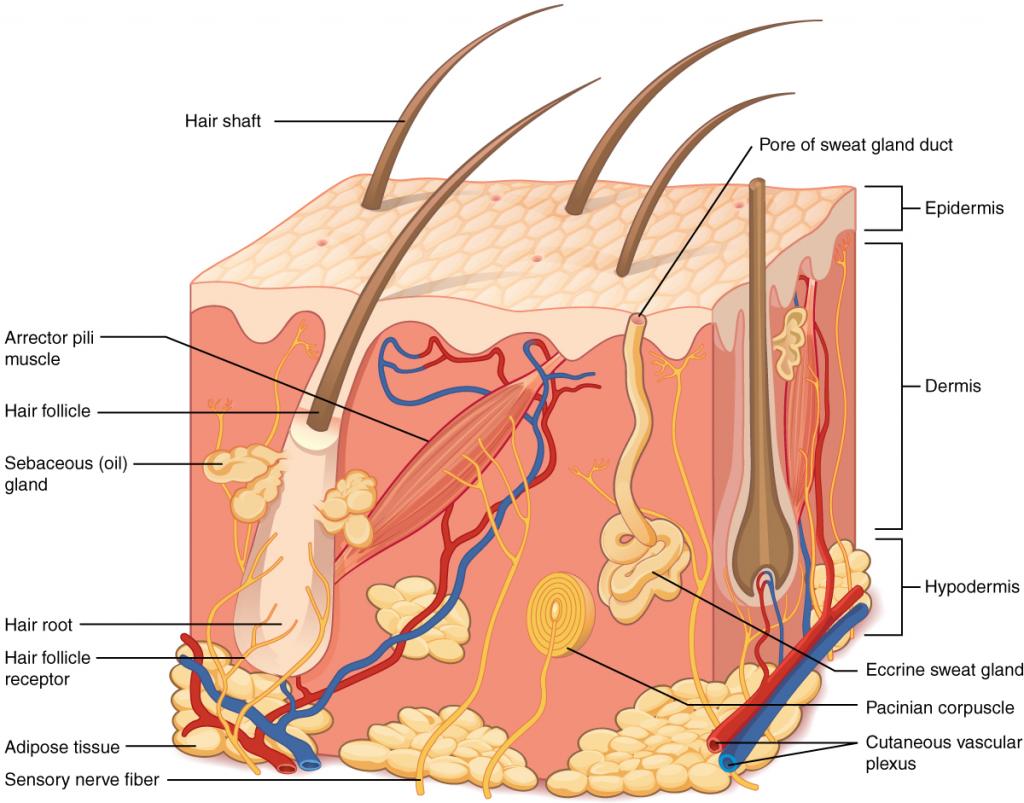
The skin has three levels – the outer epidermis, the middle dermis, and the innermost subcutis (hypodermis). The epidermis is primarily composed of dead skin cells called keratinocytes that are firmly held together in a lipid (fat) matrix to form a protective barrier. Skin supplements typically target the epidermis since it is the only layer of skin that is visible.
Skin Aging
Our skin ages in two ways: intrinsic (natural aging caused by internal physiological factors), and extrinsic (caused by preventable outside factors).
The skin naturally begins to lose its youthful appearance starting at about 25 years old. Wrinkles, age spots, dryness, and other signs of aging gradually develop, and the skin become thinner and loses its volume and plumpness. These effects can be accelerated by extrinsic factors such as sun (ultraviolet light) exposure, smoking, drinking, air pollution, sleep deprivation, and an unhealthy diet.

What are Skin Supplements?
Skin supplements are natural compounds used to support the skin’s health and appearance by slowing down and protecting against both intrinsic and extrinsic aging. Most skin supplements are either compounds already present in the skin – such as collagen – or herbs & nutrients that can enhance its health.
Some supplements – such as vitamin E – can also be applied topically in the form of ointments, gels, creams, lotions, solutions, suspensions, foams, and serums. The skin supplement industry is growing rapidly as a cheaper, safer, natural alternative to other skincare products and treatments.
Skin Supplement Benefits
Most people take skin supplements to counteract marks of aging and sun exposure such as wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, hyperpigmentation, dryness, and loss of elasticity.
The second major reason to take skin supplements is to ward off skin disorders. Common skin conditions include acne, atopic dermatitis (eczema), rosacea, psoriasis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
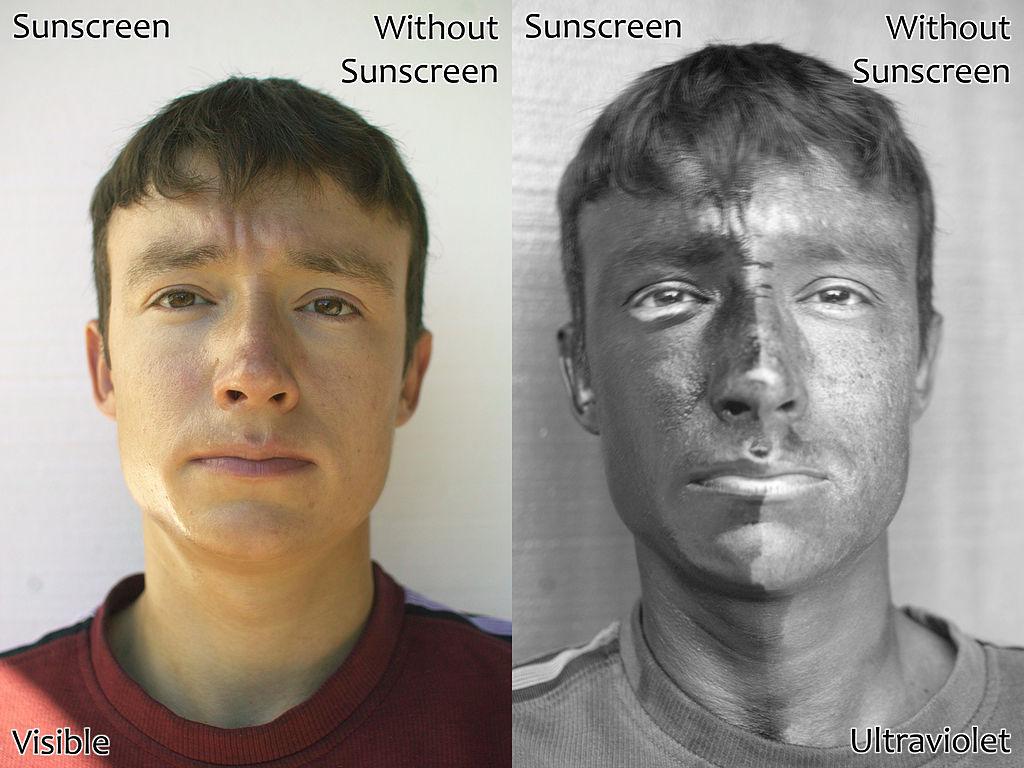
The third major reason for skin supplementation is to provide photoprotection (sunscreen) – protection against ultraviolet light damage caused by sun exposure. UV radiation damage is the leading preventable cause of premature skin aging.
Finally, some people also take skin supplements to fade scars and improve other skin injuries.
How to take Skin Supplements
Skin supplements can be taken orally (by mouth) or topically (directly on the skin). These two routes have different considerations to keep in mind.
Oral

Generally speaking, oral skin supplementation has more clinical evidence than topical application. However, the major issue with oral skin supplements is whether they remain intact and active after going through the digestive tract.
For example, some health experts are concerned that oral collagen supplements may be broken down before reaching the blood, making them little more than a glorified protein supplement. However, if the supplement is able to remain intact until it reaches the bloodstream, some of it is incorporated into the skin.
Topical
 At first glance, it seems logical that topical application should be superior to oral supplementation. After all, you’re applying the product directly on where it needs to go – the skin. However, the major issue with topical application is that most substances need to be absorbed into the skin to have an effect.
At first glance, it seems logical that topical application should be superior to oral supplementation. After all, you’re applying the product directly on where it needs to go – the skin. However, the major issue with topical application is that most substances need to be absorbed into the skin to have an effect.
Unless the compound involved has a small molecular weight, it will have trouble penetrating the skin’s outer layer. This is the reason why topical collagen products (e.g. creams and serums) do not penetrate the skin and are essentially useless. Another thing to keep in mind with topical skincare supplements is that they have less research evidence than oral forms.
How do Skin Supplements Work?
Skin health supplements typically work in the three following ways:
Boosting skin components
Some skin supplements work by boosting the levels of the skin’s natural components. This can be done either directly or indirectly. For example, hyaluronic acid and phytoceramide supplements reach the skin through the bloodstream and directly increase the skin’s hyaluronic acid and ceramide levels. 2
On the other hand, some supplements increase the levels of collagen and other skin compounds indirectly. For example, collagen supplements stimulate fibroblast cells to produce their own collagen, while pine bark extract reduces the activity of enzymes that break down collagen. 3
Protecting against oxidative stress
Oxidative stress caused by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defenses plays a central role in the aging of skin, particularly when it is related to sun exposure. This increased stress causes damage to skin cells, accelerating their aging and speeding up the formation of wrinkles and other visual signs of aging. Many skin supplements are potent antioxidants that accumulate in the skin where they help neutralize this oxidative damage. 4
Protecting against inflammation
Inflammation is often tied together with oxidative stress as another major component of aging and exposure to ultraviolet light. One common example of inflammation is sunburn – the red, painful area on skin exposed to the sun for too long. Inflammation also plays a role in many common skin disorders, such as psoriasis.
Many skin health supplements have anti-inflammatory effects that help with both inflammation caused by sun exposure, and the inflammation involved in skin disorders.
Skin Supplement Ingredients
Skin supplements can be divided into several categories:
Skin Constituents
Some of the most popular skin supplements are compounds that are already naturally present in the skin. The best example of this is collagen – a structural protein that helps the skin and other connective tissues maintain their structure. Other examples include hyaluronic acid and ceramides.
Vitamins & Minerals
The most popular vitamins used as skin supplements are vitamin C, D, E, and B7 (biotin). These vitamins can be sold by themselves, or together with other ingredients. One thing to keep in mind with vitamins is that some of them don’t have a lot of research evidence. Most notably, biotin is unlikely to do anything in the absence of deficiency, whereas vitamin E has little to no studies backing its skin uses. In addition, you can get enough vitamins and minerals from a healthy, balanced diet.
However, there is some evidence for using certain vitamins topically, such as vitamin A for improving wrinkles and other signs of aging, and the combination of vitamins C & E as a type of sunscreen.
Carotenoids

Beta-carotene is the best known carotenoid, found in common vegetables such as carrots and kale. Other common carotenoids are lutein and zeaxanthin.
Herbs
Medicinal plant preparations are another common ingredient in skin health supplements. For example, pine bark extract is frequently used to support skin health, thanks to studies showing photoprotection against ultraviolet light and improved hydration, elasticity, and overall skin appearance.

Do Skin Supplements Work?
We’ve discussed the biological mechanisms through which supplements can aid the skin. But is there evidence that they actually work? After all – unlike prescription pharmaceutical medications – supplements do not have to be proven to be effective before they are available to the public.
As it stands, the research evidence backing most skin supplements is positive. However, the issue is that too few studies have been done to date, making it difficult to conclusively recommend most skin ingredients. For more information on the research behind specific skin supplements, check out our skin supplements list and individual supplement posts.
Who Takes Skin Supplements?
Skin supplements are taken by many different people, but the two most common groups are:
- Adults who want to keep their skin looking youthful
- Individuals with skin conditions, such as acne or hyperpigmentation
- People who spend a lot of time out in the sun
Do Skin Supplements have Side Effects?
Skin supplements do not have any serious side effects. However, they may cause minor issues such as digestive discomfort or skin inflammation. Biotin in particular is known to cause acne in some people when taken at high (5,000-10,0000 mcg) doses.
Skin Supplements vs Prescription Medications & Treatments
On the other hand, invasive skincare treatments such as fillers or cosmetic surgery will give you more noticeable results than supplements. However, these treatments also have several downsides: they’re expensive, carry some risks, and only improve the skin’s appearance rather than its actual health. By contrast, skin supplements are affordable, easy to take, and address skin health and appearance simultaneously.
What is the Best Skin Supplement?
Best Individual Skin Supplement
If you could only try one skin supplement, we recommend going with either collagen or hyaluronic acid. These two ingredients are notable in that they are already present in the skin where they contribute to its health and function and are backed by a decent amount of research. In the case of collagen, oral supplements have more research evidence, where for hyaluronic acid most of the successful studies used a topical form.
Best Multi-ingredient Skin Supplement
If you’re looking for the most effective multi-ingredient skin supplement, look for products that contain collagen, hyaluronic acid, and phytoceramides as the main ingredients. All three of these compounds are naturally found in the skin and have research-backed benefits such as improved skin hydration, elasticity, and overall appearance.
Skin Supplements Guide Conclusion

Skin supplements can be an effective way to enhance not just the appearance, but also the underlying health of your skin. They can help protect you from UV light damage, and guard against or even improve the visual signs of aging such as wrinkles and dryness.
Having said that, the effects of skin supplements are fairly small. And if you smoke regularly, don’t get enough sleep, eat poorly, stay out in the sun for too long, or have other unhealthy lifestyle choices, supplements will not be enough to counteract the negative effects on your skin.
In this sense, skin supplements should be considered an addition to a healthy lifestyle as a way to keep your skin as young as possible.