Phosphatidylserine (PS) supports healthy brain cell membranes — “turning back the clock” on memory & mental clarity.
![By Pudelek (Marcin Szala) (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/512px-Sunflower_from_Silesia-300x225.jpg)
- Supporting neuron membranes. As a critical component of brain cell membranes, PS has been shown to fight cognitive decline, improve memory, and other aspects of cognition.
Overview
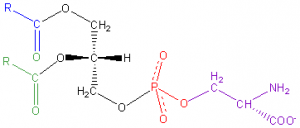
Phosphatidylserine (PS) is categorized as a phospholipid – a fat compound that acts as a key component of cell membranes.1 PS is found throughout the body, but is most concentrated in the brain, where it makes up 15% of the total phospholipid pool.2 Given this, its not surprising that PS is vital to optimal brain health and has been associated with nootropic effects.
Brain cell membranes: More dynamic than you might think.
More than serving as a static barrier, brain cell membranes perform a wide range of important activities, including:
- Helping synthesize neurotransmitters
- Sending & receiving electrical impulses
- Allowing nutrients & oxygen into brain cells
- Blocking toxins from entering brain cells
- Communicating with the immune system
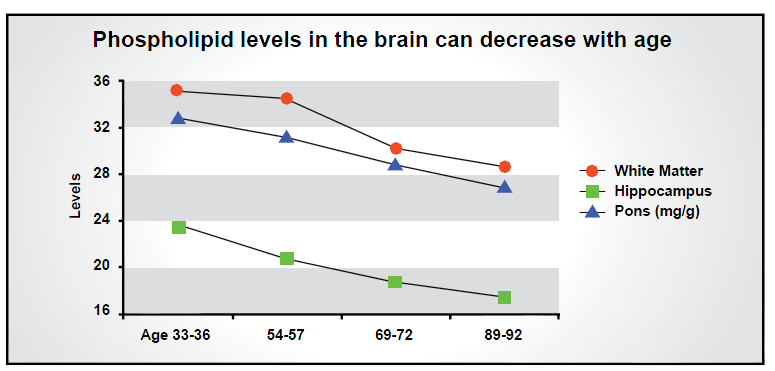
Phospholipid-depleted brain cell membranes can misfire, become stiff and thick, and undergo other types of dysfunction. In turn, this can lead to brain problems such as: 3
- Alzheimer’s4
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
- Age-Associated Memory Impairment (AAMI)
- Early signs of Age-Related Cognitive Decline (ARCD)
How PS Might Help the Brain
As a major component of brain cell membranes, phosphatidylserine has been demonstrated to:
Support brain energy metabolism
PS has shown a capacity to boost brain energy metabolism by enhancing the inflow of glucose and oxygen molecules.5
Optimizing neural communication
Brain processes require effective communication between neurons through the exchange of electrical impulses from neuron to neuron.6 PS stimulates brain chemicals that boost these neural impulses.7
Signaling for brain “clean-up”
In damaged neurons, PS helps bring in immune cells to engulf the cell before its death unleashes harmful toxins.8 9 10
Promoting brain cell survival
Evidence suggests that PS works in concert with Omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to protect brain cells from damaging factors, which may prolong neuron survival.11
PS Potential Nootropic Benefits & Uses
And while most research has focused on its benefits for the elderly, there is also some evidence that it may boost cognition in individuals of all ages, including children with ADHD.
Research
Human Research
Clinical studies have demonstrated on multiple occasions that phosphatidylserine has favorable effects on cognitive function, with particularly notable improvements in memory.
This study administered either 100 mg of PS or placebo to 51 patients aged 55-75 believed to have Alzheimer’s for a span of 12 weeks. At the study’s end, researchers found that patients who took PS showed improvement across several measures of cognitive performance when compared with placebo. The most significant improvements were found in patients with the mildest cognitive impairment.
- The researchers concluded that phosphatidylserine “may be a promising candidate for study in the early stages of Alzheimer’s.”13
Phosphatidylserine (100 mg) appears to help with Age-Associated Memory Impairment
Researchers investigated how PS supplementation of 100 mg daily (or placebo) for 12 weeks might help 149 age-associated memory impairment (AAMI) patients between the ages of 50 and 75. After the supplementation period was complete, investigators found that, relative to those who took placebo, patients who took PS performed better on tests of learning and day-to-day memory. Participants who had the worst cognitive function were found to be most likely to benefit from PS supplementation.
- The researchers concluded that “the compound may be a promising candidate for treating memory loss later in life.”14
Phosphatidylserine (300 mg) seems to improve cognitive function in elderly women with depression
In this small study, 10 elderly women with depression were given a placebo for 15 days followed by 300 mg PS daily for 30 days. Patients were then evaluated with a series of four tests for measuring mood, memory, and overall cognition. PS was found to improve depression and several parameters of cognitive function.
- The researchers concluded that PS “induced consistent improvement of depressive symptoms, memory and behavior.”15
Phosphatidylserine (300 mg) may alleviate cognitive decline in the elderly
In this double-blind study, researchers gave 300 mg of PS or placebo to 494 geriatric patients with moderate-to-severe cognitive decline for 6 months. Patients were tested for behavior and cognition at the study’s start, three-month, and six-month marks. At the study’s end, researchers reported that PS was tied to significant improvements across cognition — including learning, awareness, behavior, motivation and memory — and that the supplement was well-tolerated.
- The researchers concluded that “statistically significant improvements in the phosphatidylserine-treated group compared to placebo were observed both in terms of behavioral and cognitive parameters.”16
Soy phosphatidylserine (100, 300 mg) may improve memory function in the elderly
In this double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study, 78 Japanese seniors were given a placebo or either 100 or 300 mg of soybean-derived phosphatidylserine (Soy-PS) every day for 6 months. Although neuropsychological test scores increased in all groups, the memory scores were significantly increased in people with low baseline scores only in the PS treated groups.
- The researchers concluded that “Soy-PS used in this study is considered as safety food ingredient and 6 months of Soy-PS supplementation could improve the memory functions of the elderly with memory complaints.”17
Phosphatidylserine (200 mg) may improve mental function in children with ADHD
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined the use of PS in children with ADHD. A total of 36 children were given placebo or PS (200 mg) daily for 2 months. PS supplementation was found to memory, attention, and impulsivity.
- The researchers concluded that “PS supplementation might be a safe and natural nutritional strategy for improving mental performance in young children suffering from ADHD.”18
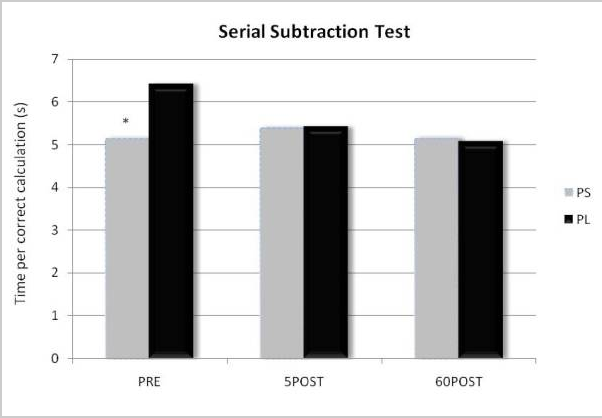
Soy-phosphatidylserine (400 mg) may improve cognitive function before exercise
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 18 resistance-trained male college students took either a placebo or a PS supplement containing 400 mg of soy-derived PS every day for 14 days. PS was found to significantly reduce the time required to correctly calculate subtraction problems by 20% (approximately 1.27 sec per calculation), reduced the total number of errors by 39%, and increased the number of correct calculations by 13% before undergoing resistance training.
- The researchers concluded that “PS supplementation significantly increased cognitive function prior to exercise.”19
Phosphatidylserine’s FDA-qualified health claim. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) allows supplement manufacturers to make the following health claim for PS in the context of dementia and cognitive dysfunction:
“Very limited and preliminary scientific research suggests phosphatidylserine may reduce the risk of dementia and cognitive dysfunction in the elderly.”
Such qualification typically suggests that there is strong evidence for the supplement’s effectiveness.
Nootropic Dosage
- In clinical studies, 100 – 800 mg of PS daily has been associated with cognitive benefits.
- Typical retail supplement dosages range from 100 – 500 mg per day.
Available Forms
- Cow-based phosphatidylserine. Phosphatidylserine was originally sourced from cows’ brains, but safety concerns led to development of vegetarian PS.
- Soy-based phosphatidylserine. Made from soy lecithin, this form is the most widely one used in supplements.
- SerinAid®. This is a branded form of PS made from soy lecithin. It is available in liquid and powder formulations, but has no apparent proprietary advantages over plain PS, despite its higher cost.
- Sharp PS® GREEN. This trademarked form of PS undergoes special processing that sources PS from non-GMO sunflower instead of soy, so it is free of all soy allergens. This form of PS is also noted for its environmentally-friendly manufacturing practices.
Supplements in Review Says
- Phosphatidylserine 100 mg as a nootropic.
Phosphatidylserine is one of the most studied neuronutrients. The brain needs PS to function properly, and taking it seems to enhance cognition in multiple ways, especially in terms of memory. Though PS is mostly used for age-related cognitive decline, its beneficial bio-activities are likely to help the brain across all age groups.
Take 100 mg of PS per day. Starting at 100 mg, PS has shown cognitive benefits in numerous clinical studies.
Leave a Reply