Hyaluronic acid may enhance skin health and appearance by supporting optimal hydration.
- Improving hydration. HA supplementation can directly increase HA levels in the skin, helping it retain water.
- Stimulating fibroblasts. These cells produce HA, collagen, and other compounds crucial to optimal skin health and appearance.
Overview
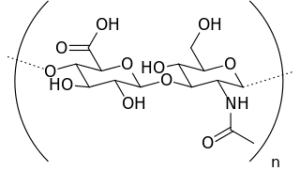
Also known as hyaluronan, hyaluronic acid (HA) is a natural gel-like compound found in the skin, eyes, joints, and other tissues. HA is a major component of the extracellular matrix that provides biological “scaffolding” for cells and maintains tissue structure.
Research suggests that HA’s main role is to retain water, helping keep skin, joints, and other tissues hydrated. Much like collagen, HA naturally decreases from aging, sun damage, and other factors. In fact, the HA skin levels of a 75-year-old are less than 25% of those found in a 19-year-old person.
Hyaluronic acid has many different uses. In medicine, HA is applied topically to the skin to promote wound healing and used in some eye surgeries. It can also be found in eye drops and functional food products. More importantly, hyaluronic acid is one of the most popular skincare ingredients. For example, dermatologists commonly use HA injections (e.g. fillers such as Restylane) to reduce wrinkles, fine lines, and other visual signs of aging.
As a supplement, hyaluronic acid is most commonly used to alleviate arthritis, especially in combination with other joint-supportive nutrients such as collagen and chondroitin. In addition, both HA supplements and topical products (e.g. serums) are increasingly popular as a way to keep the skin hydrated, plump, and youthful.
How Hyaluronic Acid Might Help With Skin Health
Improving skin hydration
Research suggests that when taken orally, some of the hyaluronic acid is absorbed and migrates into the skin and other tissues. 1In this sense, taking HA supplements can directly increase HA levels in the skin and help support optimal hydration.
Stimulating fibroblasts
HA has also been demonstrated to improve the activity and growth of fibroblast cells in the skin, increasing their own production of HA and collagen, which play an important role in maintaining skin health and appearance. 2
Hyaluronic Acid Uses & Benefits for the Skin
Hyaluronic acid is growing increasingly popular both as a supplement and topical treatment (cream, serum, lotion, etc.) for supporting skin health and appearance. HA preparations are believed to improve skin hydration and moisture, which can diminish wrinkles and other visible signs of aging, making the skin appear more youthful.
Clinical research of oral hyaluronic acid supplementation and topical application has been overwhelmingly positive, confirming that HA products can have a variety of skin benefits. Specific findings indicate that HA preparations can improve skin elasticity and hydration, and reduce wrinkles, dryness, and eczema.
Having said that, researchers stress the need for further, high-quality studies to conclusively confirm HA’s skin health benefits.
Read more: Skin Supplements Guide
Research
Human Research
Human studies of hyaluronic acid in the form of oral supplements and topical products demonstrate that it can improve skin hydration & elasticity, as well as reduce wrinkles, dryness, and eczema.
Nano-hyaluronic acid cream may improve wrinkles, skin elasticity, and hydration
This study examined the effects of a special low molecular nano-hyaluronic acid on skin health and appearance. A total of 33 women (average age 45) used an HA lotion, serum, or cream daily for 8 weeks. After 8 weeks, the women improved in measurements of skin roughness, elasticity, and hydration, and had reduced depth of wrinkles.
- The researchers concluded that “After 2,4, and 8 weeks of treatment, the skin was significantly more hydrated than the untreated skin.” 4
Topical hyaluronic acid products appear to improve skin hydration and elasticity
This randomized, placebo-controlled study evaluated the skin benefits of hyaluronic acid creams. A total of 76 women (aged 30-60) used a placebo cream on one part of the face, and 0.1% HA creams of various molecular weights on a different part of the skin. The results showed that all HA creams improved skin hydration and elasticity when compared to placebo. In addition, the lowest molecular weight creams also resulted in improved wrinkle depth.
- The researchers concluded that “Topical application of all 0.1% HA formulations used in this study led to significant improvement in skin hydration and elasticity.” 5
Hyaluronic acid-based foam appears to improve eczema
This randomized, double-blind study evaluated the effects of a hyaluronic acid-based foam product on atopic dermatitis (eczema). Twenty people with mild to moderate eczema used a ceramide cream on one side of the body and an HA-based foam on the other side for 4 weeks. Although both products improved the signs and symptoms of eczema, only the HA foam improved eczema severity. In addition, the study participants favored the foam in terms of convenience and ease of use.
- The researchers concluded that “A prescription hyaluronic acid based foam device offers an aesthetic formulation with excellent efficacy in patients requiring an environment for barrier repair with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.” 6
Hyaluronic acid supplementation (120 mg) appears to improve wrinkles
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluated the effects of oral HA supplementation. A total of 60 adults (aged 22-59) with crow’s feet wrinkles were given placebo or 120 mg of HA (either 2 k or 300 k molecule weight) daily for 12 weeks. Compared to placebo, both HA groups showed improvements in wrinkles, with the 300 k group having better results.
- The researchers concluded that “The results suggest that oral HA (both HA 2 k and HA 300 k) inhibits skin wrinkles and improves skin condition.” 7
Hyaluronic acid supplementation (120-240 mg) appears to moisturize the skin and reduce dryness
This review paper discussed the results of four randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Japanese studies of HA supplementation for improving dry skin. The studies included a total of 138 people taking placebo or oral HA supplements (120-240 mg) daily for 4-6 weeks. All of the studies reported improvements in skin moisture and skin dryness.
- The researchers concluded that “Although there were limitations in the studies presented here, consuming HA moisturizes the skin.” 8
Dosage for Skin
- Research studies use 120-240 mg HA supplement dosages
- Standalone hyaluronic acid supplements typically provide 100-200 mg capsule dosages
- Most HA products are applied topically, and as such do not have an accurate dosage
Available Forms
- Both supplements and topical products use the sodium hyaluronate form.
- HA is most widely used in the form of topical serums, lotions, and creams. These products contain either 100% pure HA (serums) or combine HA with other ingredients at varying concentrations (lotions, creams).
- HA can also be taken internally in supplement form (e.g. capsules).
- BioCell Collagen®. This is a branded supplement which combines hyaluronic acid with collagen and chondroitin, and has been shown to improve the visual signs of aging in a clinical study.
Supplements in Review Recommendation
- Hyaluronic acid for skin health, as a topical product (e.g. serum) or supplement.
We recommend hyaluronic acid for skin health. Available research suggests that both topical and oral hyaluronic acid preparations can promote skin hydration and elasticity. However, we’d like to see more clinical research before a conclusive recommendation.
You can use HA topically or orally. You can apply HA topically or take it as a supplement. However, there is currently more evidence for the topical application of HA (e.g. serum). If you do want to take an HA supplement, we recommend dosages of 120-240 mg.
Leave a Reply