Leucine may be a potent pre-workout supplement when standard sources of protein are unavailable.
![Leucine. By Sten André (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Leucine_simple-295x300.png)
- Promoting muscle development. From basic protein synthesis and expansion to restoration, leucine is a critical component of all-around muscle growth.
- Enhancing strength and endurance. Leucine is a science backed supplement for athletic performance, working by decreasing protein degradation rates and elevating oxygen levels.
Overview
Leucine is an essential α-amino acid that humans need to consume from other sources for successful protein synthesis and restoration to take place. Fortunately, the special amino acid is extensively available in more or less all foods that carry protein. Common sources of leucine dietary consumption include:
| Food | Leucine per 100 g serving (grams) |
| Soybeans | 3.23 |
| Red Meats (Beef) | 3.17 |
| Poultry (Chicken) | 2.65 |
| Pork Cuts (Sirloin) | 2.56 |
| Fish (Tuna) | 2.29 |
| Seeds & Nuts (Pumpkin) | 2.42 |
Among the BCAAs, leucine appears to lead the charge in protein synthesis and is thus hailed as one of the most vital ingredients in muscle formation. The key role of leucine in helping to build muscle makes it a highly demanded workout and exercise supplement; it is a favorite among fitness buffs and bodybuilders.
![Soybeans are one of the best sources of leucine. By Scott Bauer (USDA Image Number K5267-7) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Soybeanvarieties.jpg)
How Leucine Might Help With pre workout Formulas
Preserving muscle
When taken at high concentrations, leucine may be capable of restoring muscle protein and limiting its breakdown. Cases of low protein intake, excessive bed rest, and intense workout routines consequence in the degradation of muscles. Leucine is reportedly able to inhibit skeletal muscle protein degradation and impart anti-atrophy effects by challenging proteolysis.1 Skeletal muscle recovery after exercise is also facilitated through leucine supplementation.2
Increasing metabolic response to protein
The deterioration of muscle mass in certain situations is a consequence of a decrease in the metabolic response to leucine, such is the case with sarcopenia. Using higher portions of leucine specifically seems to hinder muscle breakdown and boost protein synthesis in scenarios of reduced metabolic response, like in the elderly.34
Improving muscle formation
Leucine stimulates muscle protein synthesis (MPS) by activating the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and eventually inducing a eukaryotic initiation factor (eIR4E) for protein translation. Read: It helps to build muscle.5 Leucine takes a particular fancy to the mTORc1 subset of mTORs, which is a nifty protein complex that regulates cellular signaling. A more detailed explanation of leucine’s role in MPS follows below.
Leucine and the mTOR Pathway
The overarching mechanism of leucine’s impact on protein synthesis follows the pathway:
- SHP-2 → Calcium mobilized → hVPS34 binds to calmodulin → mTORc1 activated → S6K1 activated → muscle protein synthesized
![Muscle protein synthesis cascades. By Brook MS, et al. [CC BY 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Muscle_protein_synthesis_signaling_cascades.jpg)
Although the overall process looks complex, leucine’s role is quite simple. Leucine takes action by pumping up intracellular calcium levels. More available calcium results in more calmodulin binding to hVPS34, which in turn induces mTORc1 activation.6
Simply put, leucine makes calcium available, which turns on mTOR for protein synthesis. A similar operation takes effect when muscles are contracted.
Leucine Proposed Benefits & Uses
Leucine’s pre workout potential lies in the duality of elevating muscle protein synthesis while minimizing muscle protein breakdown. Higher portions seem to be required for the latter to come into play. Leucine attacks both fronts via the mTOR pathway.
While the importance of leucine is little contested, the relevance of leucine supplementation may be questioned due to its relatively easy access in many foods.
Most people, especially those engaged in routine exercise or training programs, tend to consume sufficient amounts of leucine in their normal diet.
![Combine soy milk and low-fat yogurt rich in whey protein. By Peggy Greb, USDA ARS [Public domain or Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Soy-whey-protein-diet-1.jpg)
Research
Animal Research
Leucine reportedly has positive effects on muscle building. Research indicates that leucine is capable of:
- Stimulating muscle protein synthesis. Leucine intake was necessary to build healthy skeletal muscle in rats.8
- Improving muscle function. Mice given a dose of leucine infused whey protein showed decreased muscle fatigue and improved muscle power and grip strength.9
Human Research
To little surprise, leucine studies consistently demonstrate its potential use as a protein building supplement. Some research goes so far as to conclude leucine supplementation may enhance workout performance. Let’s look at some of the human science:
Leucine (4 g) may enhance power output in untrained adult males
In this double-blind investigation, 26 untrained adult males participating in a resistance training program were given 4 grams of leucine daily at 50 mg per kg over the course of 12 weeks. Average power output increased from 31% to 40.8% and significantly higher gains in total repetition maximums (5-RM) without negatively affecting body mass.
- The study concluded that “L-leucine supplementation may be used as a nutritional supplement to enhance strength performance.”10
In this investigation, untrained adults were given a combination of leucine and whey protein at 3.4 grams and 16.6 grams respectively, during leg resistance training. Muscle anabolism peaked between 1 to 2 hours after ingestion and was consistently greater in those who took leucine than in those who took the placebo. The results of the leucine & whey protein mix, however, were no better than the results of whey protein alone.
- The study concluded that “whey protein plus leucine in healthy young volunteers results in an anabolic response in muscle that is not greater than the previously reported response to whey protein alone.”11
Leucine (3.5 g) may increase muscle protein synthesis and decrease protein breakdown in young adults
In this investigation, 14 young adults were given leucine at either 1.8 grams or 3.5 grams. 180 minutes after ingestion, muscle biopsies found that net muscle protein balance and skeletal muscle protein synthesis similarly improved at both leucine concentrations, although muscle protein breakdown only decreased in the higher leucine concentration.
- The study concluded that “the leucine content typical of high quality proteins (~1.8 g) is sufficient to induce a maximal skeletal muscle protein anabolic response.”12
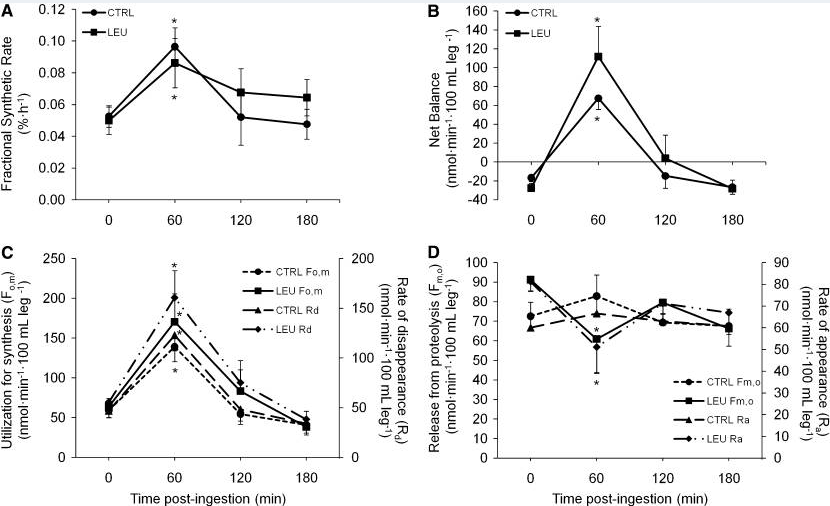
Leucine (0.21 g/kg) may improve lean tissue mass and functional performance in the elderly
In this double-blind, placebo controlled investigation, 25 seniors between the ages of 65 and 75 years in good health were given essential amino acid capsules containing either 0%, 20%, or 40% leucine two times a day at 0.21 grams per kg of body weight for 12 weeks. Lean tissue mass (LTM) and functional performance (FP) were tested through arm curls, chair stands, and walk tests. Significant improvements were noted in lean tissue mass and test performance in seniors who took leucine.
- The study concluded that “twice-daily supplementation of EAAs containing 20% or 40% L-Leucine improved aspects of functional status and at the higher level improved LTM.”13
Leucine (10 g) may increase isometric leg muscle strength and functional performance in the elderly
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind parallel investigation, 30 older adults were given either a total of 10 grams of leucine per day or a placebo while completing resistance training for 12 weeks. Significant results were identified in isometric leg strength, and seniors who took leucine outperformed the control for both chair stands and the timed up and go tests.
- The study concluded that leucine supplementation caused “moderate changes in isometric leg muscle strength and certain components of functional status.”14
Leucine certainly appears to display results that favor its use as a pre workout, especially in bodybuilding applications. Few studies, however, distinguish whether leucine supplementation has more dominant effects than its standard protein food counterpart.
Dosage for Pre-Workout
Leucine may be taken:
- as a pre workout ready-to-drink shake supplement, 5 grams
- as part of a pre workout bulk protein powder matrix designed to help buld muscle, 5 grams
- in a serving of everyday proteins, 3 grams, at ~17.7 mg / lb body weight
- an additional intra-workout dose of 5 grams may be beneficial
Supplemental leucine in a standalone product should be taken in a pure form either when fasting or on a low-protein diet so as to prevent excessive leucine intake.
Supplements in Review Says
- Leucine, 5 grams
Leucine is recommended as a pre workout for muscle activation and development. We recommend leucine, as well as other BCAA’s, as a keen muscle-building pre workout supplement. It is also sometimes used in post workout supplements.
Supplemental leucine is recommended specifically when on a low-protein diet. Leucine is found in plentiful supply in numerous protein foods. While it certainly is capable of boosting muscle formation and workout performance, taking the supplement when also regularly eating normal leucine-containing proteins is not only superfluous, but also potentially harmful and not recommended.
References
Leave a Reply