Fundamental energy molecule CoQ10 may reduce chronic fatigue and improve exercise capacity in untrained individuals.
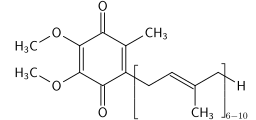
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a complex nutrient that is essential for the generation of energy in humans and animals. It may be able to enhance energy levels through its role in:
- Energy metabolism. CoQ10 is involved in the set of cellular reactions that generate the body’s energy.
Overview
First isolated in 1957, coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), otherwise known as ubiquinone, is a vitamin-like molecule that is naturally present throughout the body with notably high quantities in heart cells. Its central role lies in helping generate the body’s principal energy source (ATP) via the essential process known as aerobic cellular respiration.1
As a medication, CoQ10 has two major uses:
- Treating heart and blood vessel conditions, such as congestive heart failure (CHF), chest pain, and high blood pressure.
- Reducing oxidative stress. CoQ10 also acts as an antioxidant.
In recent years, CoQ10’s well-known association with energy production has led to speculations that it might be able to boost energy levels during exercise or challenging mental activities. In addition, the tendency of CoQ10 to naturally decrease as we age has made it a popular anti-aging drug.
How CoQ10 May Help With Energy
Energy metabolism
CoQ10’s levels are highest in the mitochondria – the cell’s “power plant”. Here, it plays a key role in the body’s energy metabolism by participating in cellular respiration – the series of chemical reactions that generate some 95% of the body’s energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).3
CoQ10 Benefits & Uses for Energy
Research
Human Research
Researchers generally agree that CoQ10 is capable of increasing energy in people experiencing chronic fatigue. Meanwhile, in terms of exercise performance in healthy individuals, it’s benefits seem to be restricted to untrained individuals, whereas experienced trainees see no effect.
CoQ10 may improve chronic fatigue
In this prospective observational investigation, 155 people experiencing fatigue tried a number of treatments, including coenzyme Q10, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), ginseng, magnesium, and yoga. Fatigue improvement was found to be greatest for CoQ10 (69%) and DHEA (65%).
- The study concluded that “the percentage of users who found a treatment helpful was greatest for coenzyme Q10 (69% of 13 subjects)…[in] fatigue improvement.”5
CoQ10 (200 mg) may enhance muscle performance and delay onset of exhaustion
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation, 20 athletes took either placebo or 200 mg of CoQ10 daily for 6 weeks. The average improvement in time to exhaustion (AT) during exercise was significantly improved with CoQ10 (40.26 sec). Muscle strength and performance also improved with CoQ10 based on leg extension exercises.
- The study concluded that “it did improve muscle performance as measured by time to AT and leg strength (quadriceps muscle reps). Many other measures of mitochondrial function also tended to improve during CoQ10 treatment.”6
CoQ10 (300 mg) may improve fatigue perception during exercise
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation, 17 volunteers were given placebo, 100 mg, or 300 mg of CoQ10 every day over the course of 8 days while biking on an ergometer. The increase in maximum velocity was greater in the 300 mg CoQ10 group than in the placebo group. In addition, subjective feelings of fatigue post-exercise were alleviated more in the 300 mg CoQ10 group than in the placebo group.
- The study concluded that “administration of coenzyme Q10 improved subjective fatigue sensation and physical performance during fatigue-inducing workload trials and might prevent unfavorable conditions as a result of physical fatigue.”7
CoQ10 (300 mg) might not improve exercise performance in trained individuals
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover investigation, 15 trained adults received placebo or 300 mg of CoQ10 daily for 4 weeks before performing an exercise treadmill test and a repeated cycle sprint test. CoQ10 was found to improve exercise performance in a few, but not the majority, of participants.
- The study concluded that “treatment with CoQ10 in healthy, exercise-trained subjects increases total and reduced blood CoQ10, but this increase does not translate into improved exercise performance or decreased oxidative stress.”8
CoQ10 (120 mg) does not seem to enhance exercise performance in trained men
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation, 19 trained men were given either placebo or 120 mg of CoQ10 every day for 6 weeks. There were no significant differences between groups in terms of time to exercise exhaustion or other measures.
- The study concluded that “ubiquinone was ineffective as an ergogenic aid in both the young and older, trained men.”9
CoQ10 (100 mg) may slightly improve exercise performance and fatigue in untrained men
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover investigation, 15 men took either placebo or 100 mg of CoQ10 daily for two 8-week periods. Compared to the placebo, CoQ10 resulted in increased average power in the last of the 5 cycling tests as well as decreased fatigue indexes.
- The study concluded that “CoQ10 may show performance-enhancing effects during the repeated bouts of supramaximal exercises and CoQ10 might be used as ergogenic aid.”10
Dosage for Energy
- Research studies tend to support the use of 100 – 200 mg doses of CoQ10 daily
- Typical supplemental capsules contain 100 mg of CoQ10
Supplements in Review Says
- CoQ10 100 mg for energy.
CoQ10 may decrease chronic fatigue and elevate exercise capacity in untrained individuals. If you’re experience chronic fatigue or looking to start working out, then CoQ10 might be able to help.
Specialized CoQ10 supplements may have optimal efficacy. CoQ10 not decrease with age, but also becomes increasingly more difficult for the body to absorb. As such, we recommend trying 100 mg of CoQ10 in an enhanced-absorption form, such as ubiquinol, colloidal-Q10 (CoQsource®), or CoQ10 with BioPerine black pepper extract.11
Leave a Reply