White kidney bean extract may help fat-burning regimens by blocking the absorption of dietary starches.

Customarily consumed as a reliable source of fiber and protein, the white kidney bean has reputed advantages for general healthy living, as well as weight management. When combined with exercise and a hearty diet, the white kidney bean extract may benefit fat burning by:
- Reducing digestion and absorption of starches. White kidney beans contain alpha-amylase inhibitors (AI).
- Maintaining stable blood sugar levels. The beans reportedly help lower plasma glucose.
- Enhancing satiety. Studies indicate decreased food intake after ingesting white kidney bean extract.
Overview
The white kidney bean, phaseolis vulgaris, hails from Central America and is so named due to its kidney-like appearance, along with the other members of the kidney bean family. Aficionados of the legume praise it as a superfood due its high content of fiber, essential minerals, vitamins, and proteins. One cup (177 grams) of the goods carries roughly 15 g of protein and an impressive 11 g of fiber, which equates to nearly half of our daily fiber needs. Additional components favorable to our health and in abundant supply include antioxidants, vitamin B9 (folic acid), and molybdenum (sulfite oxidase).
One of the conspicuous downsides to eating an exaggerated amount of these beans is the elevated amount of carbohydrates it musters at about 40 g per serving, or just about 70% of your daily need. Despite the ostensible drawback, numerous research studies advocate the bean as a potential weight loss supplement, particularly in conjunction with low-carbohydrate diets.
![By Flickr user CharlesLam . Photo uploaded to commons by user ltshears (Flickr here) [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Megacopta_cribraria-300x225.jpg)
- A number of legume seeds, including that of the white kidney bean, have developed alpha-amylase inhibitors as a self-defense mechanism to ward away unwanted insect invaders.1
Now taking the same concept of inhibiting starch, or carbohydrate, digestion specifically in the context of dieting, researchers have attempted to exploit this effect and correspondingly apply it to weight loss.
How White Kidney Beans May Help Fat Burning
Block absorption of carbohydrates
White kidney beans contain substantial quantities of alpha-amylase inhibitor (AI), which prevents the breakdown of complex carbohydrates into simple, digestible sugars in the small intestine.2 Known as “carbohydrate blocking,” this process may reduce our carbohydrate caloric intake, which could prompt less fat accumulation.
Amylase in action. By BQmUB2012134 (Own work) [CC0], via Wikimedia Commons
Oxidize lipids through bacterial fermentation
Similarly, when resistant starches enter the colon undigested, they enable the kind of bacterial fermentation that promotes lipid oxidation. The breakdown and release of fat from the body could decrease long-term fat accumulation.3
Balance blood sugar levels
As a carb-blocker, the alpha-amylase inhibitor found in white kidney beans may delay early absorption of starch and sucrose in order to fortify overall well-being.4
White Kidney Bean Popular Uses
Proponents of the white kidney bean refer to the bean as a starch blocker for its purported ability to minimize how much starch we actually absorb when eating typical carbohydrates. Such claims have led to the development of branded white kidney bean supplements, most notably Phase 2®. Studies have suggested that using white kidney bean extracts may augment dieting because it cuts body fat — with particularly heightened outcomes when taken during periods of exercise — although more statistically significant evidence demonstrating its direct ability to burn fat is wanting.6
Onward to the research. After this awesome bean image.
![Phaseolus Vulgaris. By Rasbak (Own work) [GFDL or CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Snijboon_peulen_Phaseolus_vulgaris-1.jpg)
Research
Animal Research
Research indicates that alpha-amylase inhibitors drawn from a variety of starches, including white kidney beans, appear to assist fat burning in a similar fashion, such as:
- Delaying carbohydrate digestion and lowering plasma glucose levels. A wheat amylase inhibitor may delay carbohydrate digestion and absorption, and subsequently lower plasma glucose levels.7
- Increasing satiety. Heightened satiety and corresponding reductions in weight gain in rats may be induced by a wheat amylase inhibitor.8
- Reducing weight gain. A white kidney bean amylase inhibitor may reduce weight gain and blood glucose levels.9
Human Research
White kidney bean extract (445 mg) may reduce body fat in overweight adults
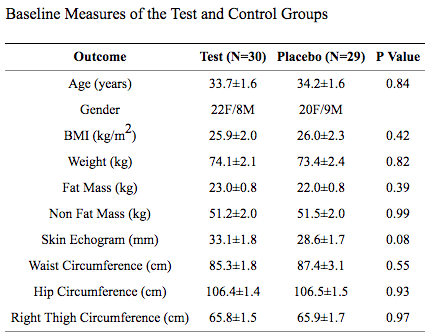
In this investigation, 445 mg of white kidney bean extract was given to 60 slightly overweight adults in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for 30 consecutive days just before a meal. Significant reductions in body weight (-2.93 ± 1.16), fat mass (-2.4± 0.67), BMI, adipose tissue thickness, and waist/hip/thigh circumferences were reported.
- The study concluded that white kidney bean extract “produced significant decreases in body fat while essentially maintaining lean body mass,” and so it “appears to be a safe and effective aid to consider in weight loss/maintenance programs.”11
Phase 2® may promote weight loss but not to a degree of statistical significance
The branded white kidney bean extract, Phase 2® (1500 mg), was given to 27 adults in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for a period of 8 weeks. Those taking the extract lost a total of approximately 3.79 pounds, which was 129% more than the placebo group. Triglycerides levels were also reduced 300% more than the placebo at an average of 26.3 mg/dL.
- The study concluded that white kidney bean extract as a Phase 2® tablet fosters “weight loss and a decrease in triglycerides, although statistical significance was not reached.”12
White kidney bean extract (4 g – 6 g) may stabilize plasma glucose in type II diabetics
In this research study, 3 type II diabetics were given amylase inhibitors (4-6 g) for 3 weeks. Glucose, hormones, and lactic acid were analyzed through blood samples, and total carbohydrate absorption was monitored by breath samples. On average, plasma glucose was reduced by 34% after breakfast, 11% after lunch, and 25% after supper; and carbohydrate malabsorption increased by 4.0 + 1.5%.
- The study concluded that taking white kidney bean extract “significantly (p less than 0.05) reduced postprandial plasma glucose, C-peptide, insulin, and gastric inhibitory polypeptide concentrations…and caused carbohydrate malabsorption.”13
White kidney bean extract (4 g) may reduce plasma glucose by delaying starch absorption
In this investigation, 3 diabetic and 5 non-diabetic adults were given white kidney extract (4 g) with each meal in order to gauge the impact of amylase inhibitor on blocking starch absorption. Starch absorption was slowed with a measuring of carbohydrate malabsorption at 20%.The plasma glucose levels were reduced by a mean of 78% in non-diabetic and 58% in diabetic subjects.
- The study concluded that adequate doses of white kidney bean extract “delayed digestion and uptake of dietary starch and significantly decreased postprandial plasma concentrations of glucose and insulin.”14
The research overall suggests that white kidney bean extracts may contribute to fat burning through alpha-amylase inhibition, which may reinforce weight loss by inhibiting carbohydrate digestion, and ultimately, decreased fat absorption. Inconsistencies among the various research studies, however, remind us of the necessity of continued enquiries concerning the spot-on relationship between white kidney beans and weight loss.
Dosage for Fat Burning
Before commencing any routine weight loss program or supplementation, consider consulting a health care professional. White kidney bean extract may be taken as:
- 500 mg – 1000 mg capsules or tablet with water during a starchy meal
- The amount necessary to inhibit alpha-amylase may vary individually
When to Take White Kidney Bean Extract
Maximal carb-blocking effects of the white kidney bean extract seem to occur when the supplement is taken with a meal, preferably at first bite.
Supplements in Review Recommendation
- White kidney bean extract, 500 mg – 1000 mg
White kidney bean extract may assist in fat burning through diet management. Blocking intestinal carbohydrate absorption per alpha-amylase inhibition is a propitious indication of the dietary benefits of white kidney bean extract. While research does not demonstrate a direct correlation between the extract and fat burning as of yet, taking it as a supplement may inhibit carbohydrate absorption and is assuredly a step in the right direction.
Go with Phase 2®. Taking phase 2®, a non-stimulant extract of the white kidney bean, at 500 mg to 1000 mg of the extract is an effective range for carbohydrate blocking, with variation according to individual metabolic biochemistry. An established product like Phase 2® may serve to bolster healthy weight management, whereas poor quality extracts render excess phytohaemagglutin (PHA), which may reduce effectiveness.
References
![Amylase in action. By BQmUB2012134 (Own work) [CC0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Amylase_reaction.png)
Leave a Reply