Ornithine may prompt an acute although fleeting boost to growth hormones
- Increasing growth hormone levels. Ornithine is purported to increase growth hormone (GH) levels.
- Reducing stress. The amino acid may benefit sleep by diminishing overall stress.
- Stimulating energy levels. By increasing energy levels, ornithine seems to reduce fatigue associated with workouts.
Overview
Not to be confused with ornithine ketoglutarate, ornithine is one of a collection of amino acids categorized as non-proteinogenic since it does not function as a precursor to proteins. Instead, ornithine serves as a critical intermediate and rate-limiting step in the urea cycle. One of the primary functions of ornithine is to breakdown ammonia into urea so that it can be properly released from the body.
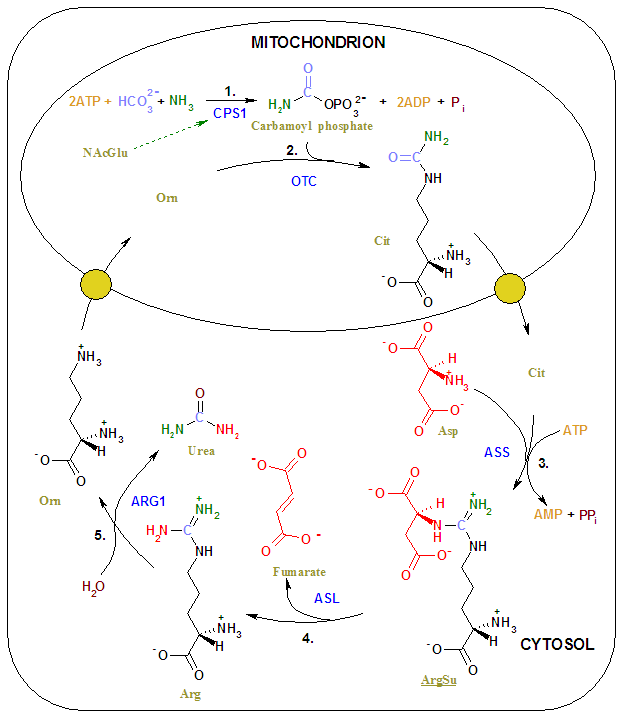
The relationship between ornithine and ammonia breakdown makes ornithine a likely candidate for facilitating recovery in scenarios of excess ammonia buildup, such as in hepatic encephalopathy or extensive cardiovascular workouts.
On top of being used as one of several potential remedies for liver issues, ornithine has been used to combat post-exercise fatigue and even mitigate stress in general.
Hoping to identify other uses for ornithine, researchers discovered that it may – in some cases – have a hand in triggering growth hormone (GH) secretion, which various health groups have taken as justification for its supplementation in enhancing workouts, developing muscles, and improving sleep.
How Ornithine May Help With Growth Hormones
Supporting hypothalamic hormone secretion
Ornithine elevates the serum concentration not only of growth hormone (GH), but other pituitary hormones as well, including cortisol and ACTH, which hints at a complementary association between ornithine and the hypothalamus. It’s possible that ornithine triggers hypothalamic functioning in general and causes it to crank up the secretion of a wide variety of hormones rather than exclusively pumping up GH levels.1
Precisely how ornithine triggers growth hormone secretion, and whether or not subsequent elevation in GH levels has meaningful benefits, still needs to be elucidated through continued research.
Ornithine Benefits & Uses for Growth Hormones
For the most part, the research favors the likelihood of ornithine supplements boosting growth hormone (GH) levels, which has positive implications for health. Ornithine may offer such natural benefits as:
- Stimulating energy levels and decreasing fatigue.
- Reducing stress.
- Aiding sleep.
- Supporting a healthy immune system by assisting the development of vital organs, including the thyroid.2
Unlike other growth hormone stimuli, such as 5-HTP and L-DOPA, however, ornithine seems to impart only a short-term influence on growth hormones. Some medical research collectives go so far as to claim that even though ornithine may promote growth hormones, the resulting increase in GH levels doesn’t leave much of a mark when it comes to muscle mass or general strength.3
Ornithine supplementation seems to be a safe bet for growth hormones but whether or not it’s definitively advantageous for athletic or mainstream use is still up in the air.
Research
Human Research
Clinical studies are conflicting: whereas some studies demonstrate the capacity of ornithine to increase growth hormone (GH) levels, such evidence is lacking in others. In addition, the surge in GH seems to be temporary, which reveals its weak potential to make lasting impacts.
In this placebo-controlled, double-blind investigation, 17 strength-trained male athletes were given either a placebo or 3000 mg of arginine (arg) and 2000 mg ornithine (orn) supplement twice daily while conducting heavy resistance exercise 3 times a day for a period of 3 weeks. Significant elevations in growth hormone (GH) and IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1) were noted 2 minutes and 1 hour after exercise completion.
- The study concluded that “significant increases (p < 0.05) were observed in both GH and IGF-1 serum levels after arg and orn supplementation.”5
Ornithine (170 mg / kg) may increase growth hormone release in bodybuilding
In this randomized investigation, 12 adult bodybuilders were given ornithine at 40, 100, or 170 mg / kg body weight over three consecutive Saturdays. Serum growth hormone levels increased in those who took the highest dosage of 170 mg/kg but not in those who took 40 or 100 mg/kg.
- The study concluded that “only at the highest dosage did ornithine elicit a predictable rise in serum growth hormone level.”6
Ornithine (2 g) might not increase human growth hormone levels in competitive weightlifters
In this double-blind, crossover investigation, 11 weightlifters between the ages of 19 and 35 years were supplemented with a combination of amino acids arginine, ornithine, and lysine at 2 grams daily, divided into 2 doses, for a period of 4 days. High daily peaks of human growth hormone (hGH) and insulin were noted but the physiological variation of hGH and insulin was not affected.
- The study concluded that “the ergogenic value of low-dose oral amino acid supplementation in increasing hGH or insulin secretion seems questionable.”7
In this randomized, placebo-controlled investigation, 7 male bodybuilders were given either a placebo, 2.4 grams of arginine-lysine, 1.85 grams of ornithine-tyrosine, or a 20-g BovrilR drink after 8 hours of fasting. According to serum samples drawn every 30 minutes for 3 hours, serum GH levels were not significantly affected.
- The study concluded that “serum GH concentrations were not altered consistently in healthy young males following the ingestion of the amino acid supplements in the quantities recommended by the manufacturers.”8
Ornithine (400 mg) may relieve stress, improve sleep quality, and reduce fatigue in healthy adults
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 52 healthy Japanese adults consumed either a placebo or 400 mg of L-ornithine every day for 8 weeks. Blood levels were analyzed for cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone-sulphate (DHEA-S) levels. Perceived mood and quality of sleep were measured by the Profile of Mood States (POMS), Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS), and Ogri-Shirakawa-Azumi sleep inventory MA version (OSA-MA). L-ornithine was found to decrease the cortisol/DHEA-S ratio, reduce anger, and improved perceived sleep quality.
- The study concluded that “L-ornithine supplementation had a favourable effect on the cortisol response as an objective stress marker and improved perceived mood and sleep quality related to fatigue as well as subjective feelings derived from stress.”9
Ornithine (2000 mg) may reduce fatigue by increasing the efficiency of energy consumption
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2-way crossover investigation, 17 healthy adults were give either a placebo or 2000 mg daily for 1 week and then 6000 mg for 1 day. The volunteers performed a fatigue-inducing physical task for 2 hours 2 times a day over an 8 day period while taking ornithine. Ornithine supplementation was observed to significantly attenuate subjective feelings of fatigue according to visual analog scale at postrecovery and promote lipid metabolism by increasing the efficiency of energy consumption.
- The study concluded that “it is difficult to obtain amounts of L-ornithine from ordinary meals that would be sufficient to promote the antifatigue effect. We recommend L-ornithine intake as a nutritional supplement in cases of physical fatigue.”10
In this placebo-controlled, crossover investigation, 14 healthy adults who trained on a consistent basis participated in exhaustive ergometer bicycle exercises after supplementation with either a placebo or 100 mg / kg body weight of ornithine. Although exercise time of the ergometer exercise, exercise intensity at exhaustion, maximal oxygen uptake, and maximal heart rate showed no significant differences, ammonia metabolism was improved with ornithine.
- The study concluded that “although the ingestion of L-ornithine hydrochloride before the exercise cannot be expected to improve performance, it does increase the ability to buffer ammonia, both during and after exercise.”11
Dosage for Growth Hormone
Ornithine may be taken as:
- A supplemental tablet, 500 – 1000 mg, daily
- In clinical studies: l-ornithine hydrochloride, 78% ornithine, 50 – 170 mg / kg body weight
Supplements in Review Says
- Ornithine, 1000 mg
Ornithine may temporarily benefit growth hormone. We recommend ornithine as a safe means of triggering growth hormone (GH) secretion for short stints. Elevated GH levels from ornithine may stimulate energy, reduce stress and fatigue, and support the immune system but seem to have minimal lasting impact on workout performance and muscle growth.
Take ornithine as a standardized tablet in 1000 mg doses. Doses of approximately 1 gram per day seem sufficient enough to efficiently increase growth hormone levels in most cases. Higher levels of ornithine appear to have more consistent results but increased risk of bowel irritation.
Leave a Reply