Vitamin D is a key component of multivitamins for its critical role in the upkeep of bone health and immunity.
- Bone health. Vitamin D helps the body use and absorb calcium and phosphorus needed for healthy bones.
- Immunity. Similar to vitamin C, vitamin D is critical to healthy immune system function.
Overview
Identified in the early 20th century as a way to counter brittle bones, vitamin D has since been classified as a collection of fat-soluble compounds with two main forms relevant to human health: vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).
Once vitamin D enters the body, it needs to be converted into calcidiol in the liver and then into calcitriol in the kidneys, after which it is able to play a major part in sustaining the health and function of bones, the immune system, the process of cell differentiation, and other vital functions. More on vitamin D and immunity.
Although fatty fish such as salmon and tuna and fish liver oil contain high concentrations of vitamin D, as a whole not many foods contain this essential vitamin. As such, it is often added to milk and breakfast cereals.1 In addition, unlike most vitamins, it can also be made naturally in the skin via sun exposure.
Recent years have marked a surge in interest in vitamin D supplementation in no small part due to the discovery that many people don’t get enough. One national study found that 70% of Americans have an intake below the recommended requirement of vitamin D,2while another suggested the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency to be 41.6%, with rates as high as 82.1% in Blacks and 69.2% in Hispanics.3
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Vitamin D
| Age | Males | Females |
| 0 – 12 months | 10 µg | 10 µg |
| 1 – 8 years | 15 µg | 15 µg |
| 9 – 13 years | 15 µg | 15 µg |
| 14 – 18 years | 15 µg | 15 µg |
| 19 – 70 years | 15 µg | 15 µg |
| 71+ years | 20 µg | 20 µg |
Foods High in Vitamin D
| Food | Serving Size | Amount per serving (µg) |
| Salmon (canned) | 3 ounces | 11.6 |
| Sardines (canned) | 3 ounces | 4.1 |
| Instant oatmeal (Quaker) | 1 packet | 3.9 |
| Milk (fortified) | 8 ounces | 2.5 |
| Cereal (fortified) | 1 cup | 1.3 |
| Egg yolk | 1 large | 0.9 |

How Vitamin D Supports General Health
Supporting bone development and health
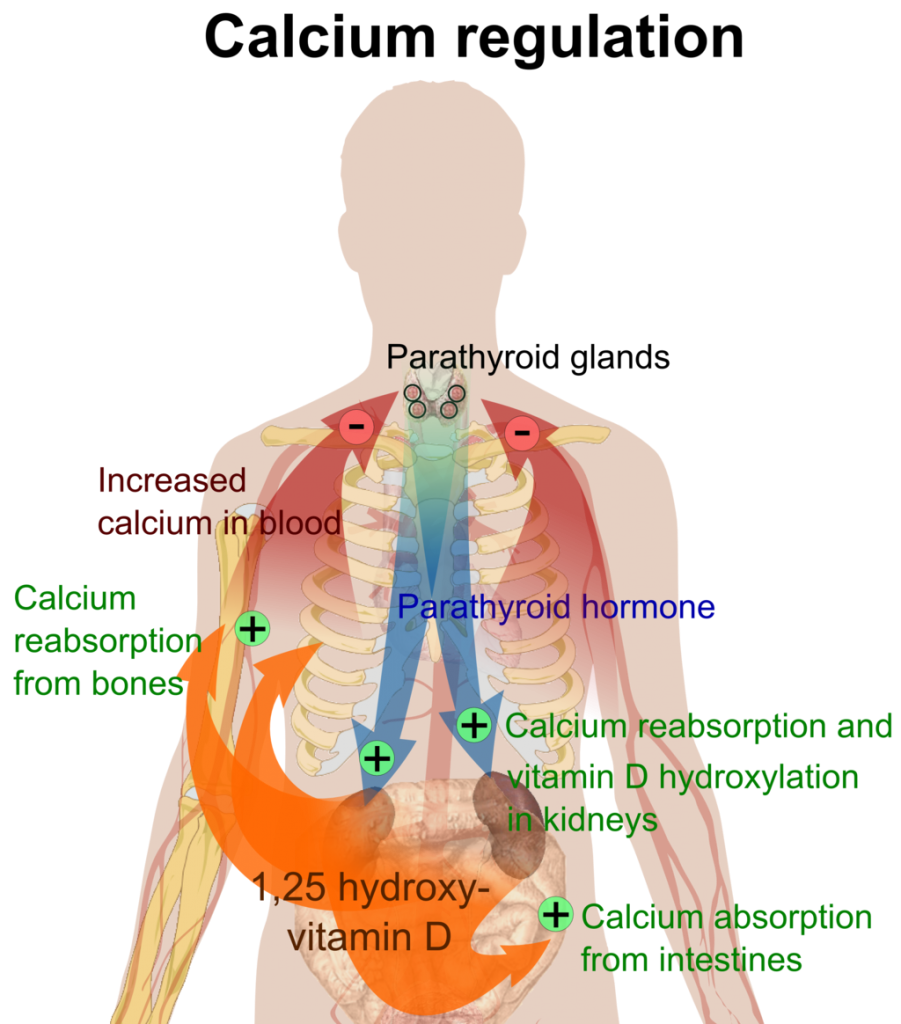
Vitamin D is vital not only for bone growth and development but also for maintaining bone strength.4 Vitamin D’s bone-maintaining function can be divided into two parts.
First, vitamin D is required for the effective use of calcium by:
- Enhancing the absorption of calcium from food
- Increasing the amount of calcium reabsorbed after being filtered by the kidneys
- Acquiring calcium from bone when calcium levels in the blood are low
Second, vitamin D is crucial for phosphorus balance by:
- Enhancing the absorption of phosphorus
- Stabilizing phosphorus levels
Vitamin D balances calcium and phosphorus levels and thus enables bones to mineralize and stabilize.5
Regulating cell differentiation
Cell differentiation describes the process of cells being given specific identities and roles. By regulating cell differentiation, vitamin D helps cells find their place while limiting the proliferation of new cells, which could otherwise lead to serious health concerns.6
Enhancing the immune system
Vitamin D has been demonstrated to play a key role in the proper functioning of the immune system by aiding the work of immune cells such as T-cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and monocytes, as well as by inhibiting autoimmunity, in which the body destroys its own healthy cells.7 8 9
Vitamin D’s Benefits as a Multivitamin
Given the widespread deficiency and insufficiency of vitamin D, taking a multivitamin that contains this vital nutrient is a good way to bring your intake up to recommended levels, ensuring that you support its roles in bone health and immunity.
In addition, low vitamin D status has also been associated with serious autoimmune health issues, such as type I diabetes, multiple sclerosis, arthritis, and lupus.
Multivitamin Dosage
- Multivitamins typically provide 10 – 20 µg of vitamin D
- Health professionals have set the upper tolerable limit at 100 µg of vitamin D per day.
Supplements in Review Says
- Vitamin D 2000 IU (50 µg) as part of a multivitamin.
Vitamin D is essential for healthy bones, immunity, and cell differentiation. Whether consumed through food and supplements or made naturally in the body, vitamin D is a core part of bone growth and maintenance, immune function, and cell differentiation.
Take 2000 IU of vitamin D. We recommend supplementing with 2000 IU of vitamin D, especially for those over 50 years old.
Leave a Reply