Calming neurotransmitter GABA lowers anxiety and induces relaxation.
- Reduction of anxiety. Similar to the GABA naturally found in the brain, GABA supplements seem to reduce anxiety and stress.
- Potential improvement of mood. Poor GABA activity may be involved in depression and other mood disorders.
Overview
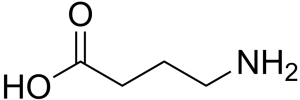
Gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a naturally occurring amino acid produced in the brain. As the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA’s function is to bind to neurons and reduce their activity, working as a natural calming agent. This effect results in the reduction of anxiety and promotes relaxation.
As such, it’s not surprising that a wide range of medications aimed at reducing anxiety and seizures – including both natural supplements and pharmaceuticals such as benzodiazepines – work mainly by interacting with GABA or its receptors.
GABA itself can also be supplemented as a way to reduce anxiety and promote sleep, and possibly even boost growth hormone levels. However, GABA supplementation remains a controversial topic because of the long-standing belief that it has difficulty crossing the blood-brain barrier.
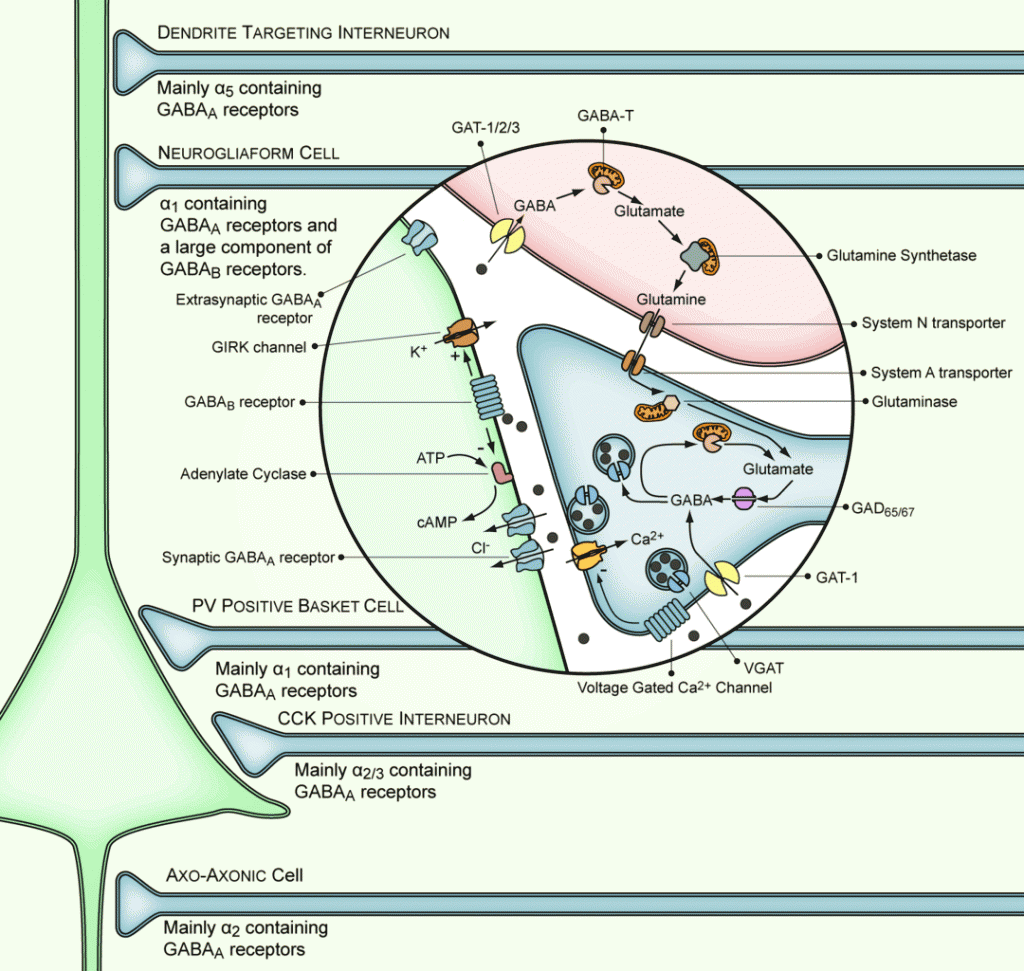
How GABA Might Help the Brain
Reducing neuron activity
GABA’s Nootropic Uses & Benefits
GABA is a popular dietary supplement used to reduce anxiety and stress, promote relaxation, and prepare the body for sleep. Although these uses are backed by science, GABA supplements have difficulty crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBP), which has put their usefulness up to continued debate. Some argue that supplementation can still have an effect by affecting other parts of the body or areas of the brain not protected by the BBB.
Research
Human Research
What little clinical research exists suggests that GABA supplements may be able to reduce anxiety and stress.
GABA (100 mg) may reduce anxiety and promote relaxation
In this placebo-controlled study, 13 adults took water, L-theanine, or GABA, and had their brain function examined by electroencephalograms (EEG) 1 hour after supplementation. EEG findings showed that GABA induced relaxation and reduced anxiety.
- The study concluded that “GABA could work effectively as a natural relaxant and its effects could be seen within 1 hour of its administration to induce relaxation and diminish anxiety.”4
GABA (100 mg) may alleviate stress from mental tasks
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial, 63 adults were given placebo or 100 mg GABA tablets 30 minutes after completing a challenging mental task. The results of a subsequent EEG showed that GABA led to decreases in alpha and beta band brain waves, which indicate a reduction of stress.
- The study concluded that “GABA might have alleviated the stress induced by the mental tasks.”5
GABA (28 mg) in chocolate seems to reduce stress
Participants in this double-blind study were administered chocolate infused with 28 mg of GABA 15 minutes before taking a stressful arithmetic test. EEG measurements were taken before and 15 minutes after the test. Heart Rate Variable measurements determined by EEG analysis showed rapid recovery from the stressful state induced by the test to a normal state in those who consumed GABA-infused chocolate.
- The researchers concluded that “GABA chocolate was considered to have a psychological stress-reducing effect.” 6
Nootropic Dosage
- Research suggests that GABA doses of 28 – 100 mg are effective for reducing anxiety
- GABA supplements provide doses of 200 – 1000 mg daily
Supplements in Review Says
- GABA 700 – 800 mg as a nootropic.
GABA has some nootropic value as an anxiety-reducer. GABA’s ability to relieve anxiety promote relaxation is well documented, and it’s possible that low GABA may be linked to depression. Having said, the effectiveness of GABA supplements remains contested.
700 – 800 mg should be sufficient. If you do take GABA, a total dose of 700 – 800 mg daily seem to be effective.