MCT oil may protect the brain from age-related decline, but claims of improved cognitive performance in healthy adults are untested.
- Neuroprotection. Research suggests that MCTs can help protect the brain from Alzheimer’s and other forms of cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration.
- Enhanced cognition. MCT oil may potentially improve mental energy & focus in healthy individuals, but this claim remains untested by research.
Overview
MCT oil is a supplement made from coconut or palm kernel oil. It is composed of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) – fat molecules that are metabolized differently by the body compared to other types of fats.
In comparison to the more common long-chain triglycerides (LCTs), MCTs are less likely to be stored as fat because they are quickly and easily absorbed, being sent straight to the liver without requiring any modification. Here, they are used to produce ketones (also known as ketone bodies) – a type of molecule that the body can utilize as an alternative energy source to carbohydrates (glucose).
MCTs are used by doctors to help with conditions characterized by food malabsorption, such as diarrhea, steatorrhea, and celiac disease. In addition, they are also used to treat epilepsy.
However, MCT oil is far more popular as a supplement because it is believed to promote weight loss and increase energy levels, benefits that are particularly sought after by athletes. The use of MCT oil is common in the low-carbohydrate, high-fat ketogenic (keto) diet that is meant to switch the body’s primary energy source from glucose to ketones.
Although not a nootropic per se, MCT oil has been suggested to protect neurons from degeneration seen in both natural aging and conditions such as Alzheimer’s. In addition, many people claim to have improved cognitive performance from taking MCT oil.

Not all MCTs are the Same
The four main medium-chain triglycerides are caproic acid, caprylic acid, capric acid, and lauric acid, alternatively known as hexanoic, octanoic, decanoic, and dodecanic acids, with the prefix denoting how many carbon atoms they contain (e.g. “hexa” for 6). Generally speaking, the shorter this carbon chain, the easier it is for the body to utilize the MCT. But even though caproic acid has the shortest carbon chain (6), it is rarely included in MCT oil supplements because of its strong taste and smell.
As such, the next two MCTs by carbon chain length – caprylic (8) and capric (10) acid – are seen as the best options for supplementation. Lauric acid is generally considered the least effective MCT because it has the longest carbon chain (12) and is only one carbon atom away from being a long-chain triglyceride. The majority of MCT supplements are composed of a mixture of caprylic and capric acid with or without lauric acid.
How MCT Oil Might Help With Brain Health
Improving brain energy metabolism
Enhanced mitochondrial function
The mitochondria serve as the energy-generating centers of cells, and their dysfunction is believed to play a role in some conditions, including neurodegenerative disorders and cognitive impairment. Studies show that ketones may be capable of protecting and enhancing mitochondrial function through mechanisms such as: 2
- Reducing the high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in mitochondria through antioxidant activity and other pathways 3
- Stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis – the creation of new mitochondria 4
MCT Oil’s Nootropic Uses & Benefits
In addition, some healthy (and young) individuals take MCT oil as a performance nootropic believed to improve mental energy, focus, and mood. It’s possible that this effect is the result of the brain’s increased reliance on ketone bodies as an energy source. However, no research has been performed to date on the nootropic benefits of MCT oil in healthy individuals.
Research
Animal Research
There haven’t been many studies of isolated MCTs in animals; however, studies using ketogenic diets (which increase the body’s reliance on ketones for energy, much like MCTs) report that they may:
- “Have antidepressant properties” as demonstrated in a rat model of depression 5
- “Be of use in the treatment of ADHD” as shown by decreased activity in rats 6
- Improve cognitive performance in aged rats and protect against neurodegenerative conditions 7
Human Research
Clinical studies indicate that MCT supplementation can improve cognitive function in people with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s, and could potentially enhance brain energy metabolism in healthy adults.
MCT supplementation (40 ml) may improve cognitive function in elderly patients with memory disorders
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined the efficacy of MCT supplementation for older adults with memory disorders. A total of 20 older adults (average age 75) with Alzheimer’s or mild cognitive impairment (MCI) were given a single dose of a placebo drink or one containing emulsified MCTs (40 ml).
Patients given MCTs who were APOE4 negative (a gene variation that increases risk of AD) saw improved cognitive performance as measured by the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-cog).
- The researchers concluded that “Additional research is warranted to determine the therapeutic benefits of MCTs for patients with AD…“8
Caprylic acid (20 g) may help slow Alzheimer’s decline
This study reported on the use of caprylic triglyceride (CT) – one specific MCT – for Alzheimer’s. Eight people with Alzheimer’s received CT for 6 or more months in addition to standard AD medication. Compared to reports of patients receiving standard drugs alone, the patients also receiving CT had a slower rate of decline of cognitive function as measured by the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE).
- The researchers concluded that “Results from this case review study indicated that addition of CT to pharmacotherapy for AD was associated with stable disease or improvement for some patients.“9
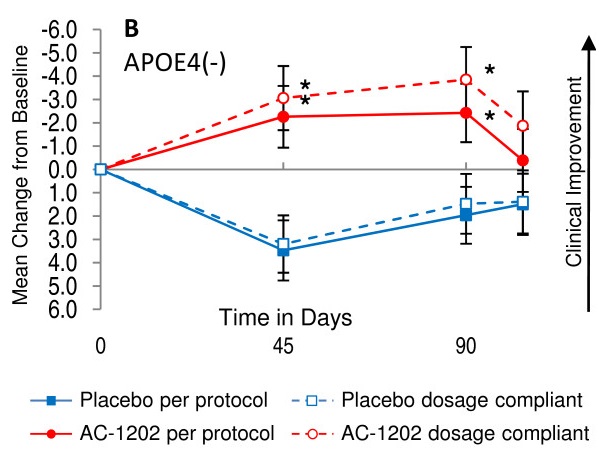
AC-1202 MCT supplementation may improve cognitive function in APOE4-negative Alzheimer’s
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled tested the efficacy of AC-1202, a synthetic MCT, for Alzheimer’s. A total of 152 people with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s were given placebo or AC-1202 daily for 90 days in addition to their standard AD medication. AC-1202 supplementation increased blood ketone levels in all participants, but only improved cognitive function in those without the APOE4 gene, with particularly notable improvements in patients who were dosage compliant (Graph 1).
- The researchers concluded that “AC-1202 resulted in significant improvement in the ADAS-Cog test in E4(-) AD patients relative to Placebo.” 10
MCT supplementation (20 – 30 g) appears to support brain energy metabolism
This study examined whether supplementing with MCTs can increase ketone levels and affect brain energy metabolism. Eight adults (average age 26) were given MCT four times daily (20 g total) for 1 week and 30 g total for another 3 weeks.
Supplementation resulted in a significant increase of blood ketone levels, which the researchers estimated would increase the contribution of ketones to brain energy metabolism from 3% to 8-9%, an effect that could theoretically improve cognitive function in people with dysfunctional brain energy metabolism, such as the elderly and individuals with Alzheimer’s, and possibly even enhance cognition in healthy adults.
- The researchers concluded that “This MCT supplementation protocol was mildly and safely ketogenic…This degree of ketonemia is estimated to contribute up to 8% to 9% of brain energy metabolism.” 11
MCT supplementation (40 g) may improve cognitive function in type 1 diabetes
This randomized, placebo-controlled study tested the usefulness of MCTs for alleviating hypoglycemia-induced cognitive impairment in diabetes. A total of 11 type 1 diabetics were given placebo or MCT drinks (40 g) and performed cognitive tests. MCT ingestion was found to reverse the negative effects of hypoglycemia on memory and other aspects of cognitive function.
- The researchers concluded that “Medium-chain triglyceride ingestion improves cognition…in intensively treated type 1 diabetic subjects.” 12
Nootropic Dosage
- Successful clinical studies most commonly use 20 g MCT doses
- Most MCT oil supplements suggest taking 1 teaspoon 1 – 3 times daily
- MCT oil can cause indigestion, especially when you first start taking it. Be sure to start off with small doses and slowly work your way up to minimize digestive issues.
Available Forms
- MCT oil is typically isolated from coconut or palm kernel oil.
- Most MCT oil supplements contain a combination of caprylic and capric acid with or without lauric acid. Although it’s not yet clear which MCTs are more effective, research studies tend to use a mixture of caprylic and capric acid.
- MCT oil is sometimes added to multi-ingredient nootropic drinks and beverages.
Supplements in Review Says
- MCT oil 1 – 3 teaspoons daily as a nootropic.
MCT oil offers neuroprotection and may enhance healthy brain function. Research suggests that MCT oil helps protect the brain from age-related cognitive decline, whether natural or progressing into Alzheimer’s and other disorders. In addition, it’s possible that it may also enhance cognition in healthy adults, but this claim has yet to be clinically tested.
Start off low and move up to 3 teaspoons. MCT oil is known to cause digestive discomfort, so start with small doses (half – 1 teaspoon) and slowly work your way up. In addition, medical researchers suggest that daily intake of 20 – 70 g MCT oil is ideal for protecting against Alzheimer’s, but such a large amount may not be realistic for everyone.
Leave a Reply