
The history of cannabis is almost as old as civilization itself. Indeed, cannabis was said to be used medicinally in Assyria – an ancient Mesopotamian kingdom existing from 2000 to 600 BC. Despite its long history, it wasn’t until the advent of modern science and increased marijuana use in the 20th century that we finally began to uncover how it works. THC and CBD – the main active compounds in cannabis – were first isolated and described in the 1960s, and in the late 1980s scientists found that they act on unique receptors in the brain.
What they had discovered was the endocannabinoid system – a network of receptors that responds to compounds known as cannabinoids and plays a role in controlling everything from appetite to anxiety. Since then, it has become apparent this system is a promising target for helping with a wide variety of health conditions characterized by pain, inflammation, neurodegeneration, and other issues.
In this article, we are going to talk about what this system is, how it is affected by CBD, and how it can be harnessed to benefit human health.
The Endocannabinoid System
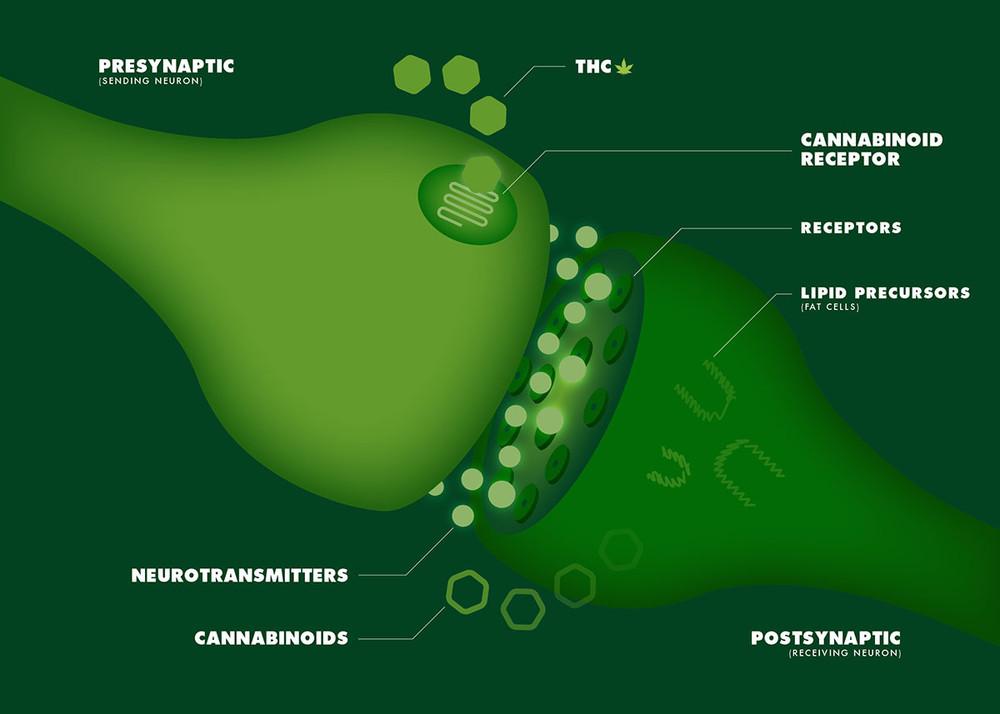
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) includes cannabinoid receptors (protein molecules on the surface of a cell that respond to specific chemicals outside of the cell), the endocannabinoid (endo meaning made inside the body) compounds that interact with these receptors, and the enzymes that help produce and break down endocannabinoids.
A growing volume of research suggests that the ECS is involved in a wide range of critical physiological processes, including: 1
- Appetite, digestion, and metabolism
- Anxiety, mood, fear, stress, and emotions
- Immune system function & inflammation
- Memory and learning
- Pain
Overall, the main role of the ECS seems to be to help maintain homeostasis – a state of balance and equilibrium. For example, our bodies need to feel some anxiety because it can be beneficial to our performance and even survival, but too much anxiety can wreak havoc on our mental health.
Similarly, inflammation can be a beneficial process that promotes healing, but too much inflammation can lead to health disorders. This where the ECS can step in and help nudge things in the right direction, to keep these and other processes at just the right level.
Structure of the Endocannabinoid System
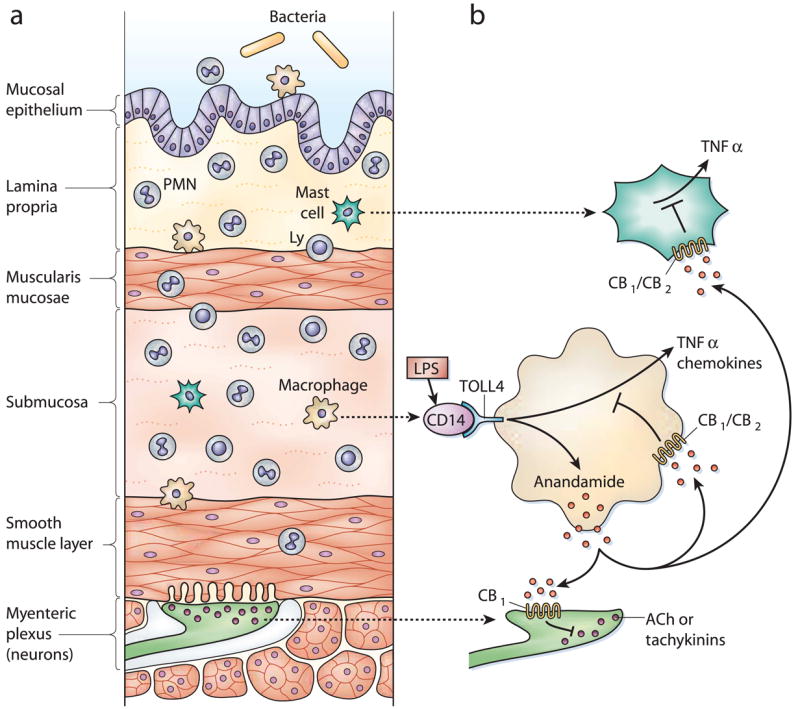
So far, researchers have identified two cannabinoid receptors – CB1 and CB2. CB1 is abundant in the brain, whereas CB2 is present more in periphery parts of the body. However, scientists believe there are many more novel cannabinoids receptors, such as GPR55 and TRPV1, which may eventually be reclassified as CB3 and CB4. Different cannabinoids can activate (or block) different receptors to a varying extent, which explains the differences in their effects.
The CB1 and CB2 receptors are activated by the two main endogenous cannabinoids – anandamide and 2-AG, which also function as neurotransmitters in the brain. These two endocannabinoids are mimicked by plant-derived phytocannabinoids – THC (an analogue of anandamide), CBD (an analogue of 2-AG), and dozens of other cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. This means that ingesting cannabis products or isolated THC or CBD can activate the endocannabinoid system in a similar – albeit not identical – way that our own natural endocannabinoids do.
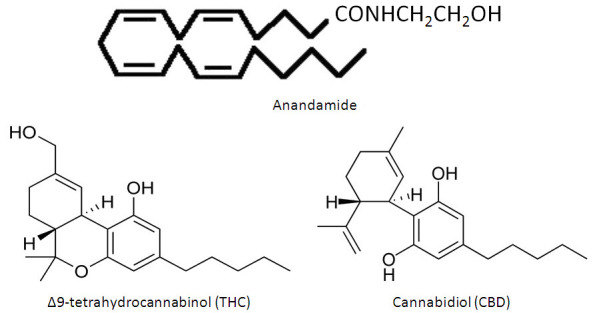
CBD

The past few years have seen a surge in interest surrounding cannabidiol (CBD) – the second-most abundant cannabinoid in cannabis plants after THC. This is largely due to the fact that unlike THC, CBD does not have any psychoactive effects, but maintains the many health benefits of cannabis. Because of this, CBD hemp oil is increasingly used as an over-the-counter dietary supplement for a wide range of conditions. Let’s take a look at how CBD interacts with the ECS to produce its benefits.
Read more: Guide to CBD
Effects of CBD on the Endocannabinoid System
Research on the ECS and its interaction with various cannabinoids is still ongoing. So far, studies have shown that CBD interacts with the ECS in three major ways:
- Acting as an antagonist (a compound that binds to a receptor and blocks its effects) of GPR55, considered by many to be the 3rd cannabinoid receptor. This receptor is known to control nociception – the response of the nervous system to potentially harmful stimuli that can result in pain. 4
- Acting as an agonist (a compound that binds to a receptor and activates a cellular response) of the TRPV1 receptor, which also seems to act as a cannabinoid receptor. TRPV1 regulates the sensation of heat, as well as inflammation and sensitivity to pain. CBD appears to desensitize this receptor, resulting in analgesia (pain relief). 5
- Reducing the uptake and breakdown of anandamide, which ultimately increases its levels. Anandamide’s proposed effects include regulation of appetite, anxiety, pain, pleasure, and reward. 6
Other Effects of CBD on the Central Nervous System
Besides the endocannabinoid system, CBD is also known to affect other brain-related receptors and compounds:
- Activation of the 5-HT1A receptor that typically binds to serotonin, and is involved in regulating stress, mood, and anxiety 7
- Modulating the effects of agonists on opioid receptors, which help regulate pain 8
- Increasing levels of the neurotransmitter adenosine
- Increasing levels of tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin and melatonin
- Acting as an antioxidant
The Benefits of CBD
We know that CBD interacts with the ECS and other parts of the central nervous system, but what are the tangible benefits of this interaction? The fact that CBD interacts with so many different parts of the brain means that it can help with a wide range of health problems.
CBD and Anxiety
Reduction of anxiety is arguably the most research-backed benefit of CBD. Thus far, multiple animal studies have shown the anxiolytic effect of CBD, with several human trials reporting reduced anxiety in individuals with social anxiety disorder. In addition, there is also early evidence that CBD can help with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). 9
CBD and Sleep
CBD is also increasingly being used as a sleep aid. Rather than directly making you sleepy, CBD helps reduce anxious thoughts that are often responsible for difficulty falling and staying asleep. In addition, there is also some evidence that high CBD doses can act as a sedative. 10
CBD and Neuroprotection
The gradual deterioration of brain cells is the central feature of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Animal research indicates that CBD may help protect neurons primarily through its antioxidant activity. 11
CBD and Epilepsy & Psychosis
CBD has shown remarkable promise for epilepsy disorders. For example, a report on the use of CBD-rich cannabis for children with treatment-resistant epilepsy noted significant reductions in seizures, as well as improved mood, sleep, and alertness. In some cases, the seizures went away completely.12
In addition, research also indicates that CBD has antipsychotic properties that can help with schizophrenia and other disorders characterized by psychosis. 13
CBD and Depression
CBD’s interaction with both the endocannabinoid system and the serotonin receptor in particular may result in improved mood and help fight depression. So far however, evidence is restricted to animal studies. 14
CBD and Inflammation
Inflammation is an essential part of the body’s immune response, needed to deal with infections and injuries. However, when the immune system does not function properly it can cause too much inflammation, which can then lead to inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. CBD’s interaction with the ECS has the potential to reduce inflammation and help with conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and diabetes. 15 16
CBD and Pain
The fact that CBD affects so many receptors associated with pain and inflammation means that it can act as an analgesic to help alleviate chronic pain, a common symptom of many health disorders. In fact, there is already a research-backed pharmaceutical drug called Sativex that combines equal doses of THC and CBD to provide pain relief to people with difficult-to-treat conditions such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. 17
Read more: CBD for pain
Conclusion

By using non-intoxicating cannabinoids such as CBD we can harness this natural system for the benefit of human health, potentially helping with conditions that include depression, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, anxiety disorders, stress, arthritis, diabetes, epilepsy, psychosis, insomnia, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, and possibly even obesity. 18
The future is bright as increasing research efforts provide more evidence for CBD’s beneficial effects and continue to elucidate the inner workings of the endocannabinoid system.
Leave a Reply