Universal antioxidant compound alpha lipoic acid appears to slow age-related cognitive decline.
- Slow age-related cognitive decline. Alpha Lipoic Acid has been shown to slow the progression of cognitive decline in those with dementia and brain trauma.1
Overview
Lipoic acid, better known as alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is an antioxidant fatty acid molecule found in every cell of the human body. ALA helps the function of enzymes present in the mitochondria—the structures which generate much of a cell’s energy. Moreover, ALA is known for being a powerful, “universal” antioxidant because it is both fat and water-soluble.
Research suggests that ALA plays an important role in reducing oxidative stress caused by free radical damage, protecting brain cells from degradation, and helps preserve the ability of brain cells to function and communicate properly. 2
Furthermore, ALA has been tested in a significant number of studies for its efficacy in stabilizing cognitive function in those with neurological damage as a result of neurodegeneration, stroke, multiple sclerosis, or traumatic brain injury.
How Alpha Lipoic Acid Might Help the Brain
Antioxidant Support
As an antioxidant, ALA helps neutralize and remove free radicals from the body, and also has the advantage of easily crossing the blood-brain barrier and helping recycle Vitamin C and glutathione after the body has used them up. Furthermore, in addition to its own antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, ALA also amplifies the effects of other naturally occurring antioxidants like glutathione and CoQ10, important compounds that protect against aging and illness.
Increase acetylcholine levels and promote glucose metabolism
ALA is known to increase the production of acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter for cell communication. Furthermore, ALA promotes glucose metabolism, increasing the production of available energy for use by neurons.4
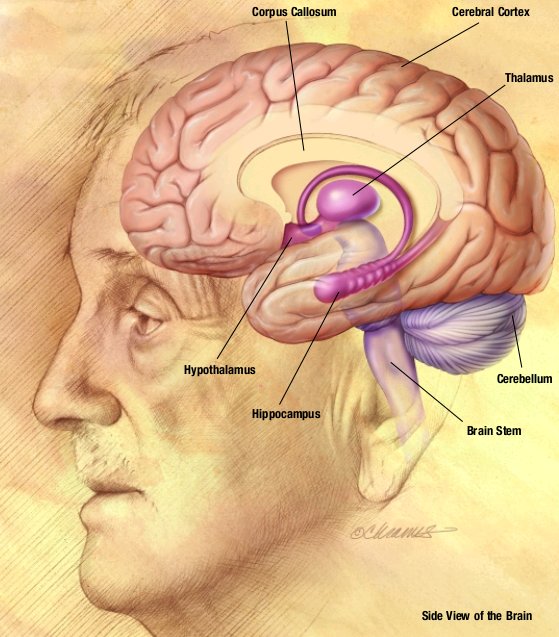
Alpha Lipoic Acid‘s Proposed Brain Benefits
Alpha lipoic acid is considered to be a potent antioxidant. The main way ALA may improve cognition is by neutralizing damaging free radicals — the chemical byproducts of the oxidation process. ALA’s protective effects on brain and nerve tissue may help slow cognitive decline associated with aging and related neurodegenerative conditions.
In addition, some people also claim to experience increased energy levels from ALA supplementation; although this effect has not been tested in clinical research, there is a biological basis for this effect, since ALA is known to promote energy metabolism.
Research
Animal Research
Studies done in animals report that alpha lipoic acid is capable of:
- Reducing brain damage by 35% to 40% and improving function and recovery in mice subject to a stroke5
- Helping the brains of rats recover more effectively from traumatic brain injury by reducing scar tissue formation and cell death and increasing blood flow to the damaged area6
- Protecting the mitochondria of older rats from aging by decreasing free radical damage and oxidative stress7
Human Research
Alpha lipoic acid (600 mg) plus omega-3 fatty acids appears to slow down Alzheimer’s progression
In this randomized clinical trial, patients with Alzheimer’s were given a combination of 600 mg alpha lipoic acid and omega-3 fatty acids or placebo. The patients receiving the ALA/fatty acid combination showed less cognitive and functional decline over a one-year span than the group that received placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “further evaluation of the combination of omega-3 fatty acids plus alpha-lipoic acid as a potential treatment in AD is warranted” 8
Lipoic acid (600 mg) may be an effective neuroprotective treatment for Alzheimer’s
This clinical review suggests that lipoic acid may be an effective neuroprotective treatment for Alzheimer’s, particularly in its early stages. In addition, the authors discuss a study in which 43 patients with AD were given 600 mg lipoic acid daily for 48 months. While the group with moderate dementia showed little response to LA, the disease progressed extremely slowly in those with mild dementia.
- The authors of the review concluded that ” LA could be combined with nutraceuticals such as curcumin, (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (from green tea) and docosahexaenoic acid (from fish oil) to synergistically decrease oxidative stress, inflammation, Aβ levels and Aβ plaque load and thus provide a combined benefit in the treatment of AD“9
Nootropic Dosage
- Standard dosage is 300-600 mg ALA daily, although clinical research has only been performed with the 600 mg dose thus far
Supplements in Review Says
- Alpha lipoic acid 300-600 mg daily.
Alpha lipoic acid seems like a good option for staving off age-related cognitive impairment. Although clinical research is a little lacking, ALA has been found to slow down Alzheimer’s progression, which suggests that it may help with the general decline in cognition seen in elderly individuals.
300 mg is an effective dose to start out with. This dose is high enough to see an effect, although moving up to 600 mg is ideal since that is the dose used by most successful clinical trials.
References
Leave a Reply