Lutein protects the eyes from age-related disorders and may enhance visual performance in healthy eyes.
- Warding off eye disorders. Lutein may reduce the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts, and improve vision in people with these conditions.
- Enhancing vision. Lutein supplementation may improve several aspects of vision performance such as contrast sensitivity, particularly in low-light conditions.
Overview
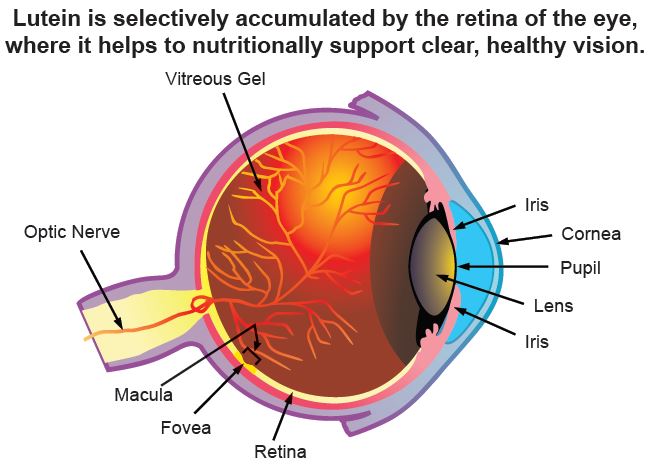
“Lutein”, derived from the word Latin luteum for “yellow”, is a yellow-colored carotenoid compound. Like other carotenoids, lutein has potent antioxidant qualities, but is especially important for vision because it naturally settles in the eye.
Indeed, together with zeaxanthin – another yellow carotenoid – lutein is heavily concentrated in the eye’s retina and particularly the macula – a yellow spot at the center of the retina that enables sharp, central vision. Here, they constitute the macular pigment (MP) which plays a key role in protecting the eye from damage caused by sunlight and oxidative stress.
Because of this, lutein is often considered the “eye vitamin”, even though it is not technically a vitamin at all. However, some clinical experts believe that it should at least be considered a conditionally-essential nutrient because it plays a key role in eye health and cannot be synthesized by the human body, having to come from dietary sources instead.
Lutein is one of the most promising vision supplements available. Current research evidence indicates that “Supplementation with L [lutein], Z [zeaxanthin] and MZ [meso-zeaxanthin] augments MP and enhances visual performance in diseased and non-diseased eyes, and may reduce risk of AMD development and/or progression.” 1
Where do we get lutein?
Lutein is present in colorful fruits and vegetables, especially dark, leafy greens. The problem is, these days many of us are not getting enough fruits and vegetables, let alone those most rich with lutein. Check out this list, and see how many of these lutein-rich vegetables are in your daily diet:
Best Dietary Sources of Lutein | |
| Dietary Source | Lutein Content |
| Kale | 23.7 mg |
| Spinach | 20.4 mg |
| Collard Greens | 14.6 mg |
| Turnip Greens | 12.2 mg |
| Mustard Greens | 8.3 mg |
| Summer Squash | 4.0 mg |
| Green Peas | 3.8 mg |
| Pumpkin | 2.5 mg |
| Corn | 2.2 mg |
| Carrots | 1.1 mg |
How Lutein Might Help With Vision
As the major constituent of macular pigment alongside zeaxanthin, lutein is believed to have two key biological functions in the eyes:
Protecting the eyes from blue light
Lutein’s major function is to act as “internal sunglasses” by filtering out blue light, which is known for its short-wavelength and high-energy that can cause damage to the eye’s tissues. Blue light is estimated to be as much as 30 times more damaging as long wavelength light. 2 3
Antioxidant activity
Lutein’s second major role in the eye is to act as an antioxidant, helping fight against free radicals in the retina, especially in the “high-definition” macula – where lutein is naturally highly concentrated – and in the lens. This is critically important for eye health because oxidative and photo-oxidative processes are implicated in eye disorders. 4 5
Lutein’s Vision Enhancement Benefits
The large majority of people take lutein to help ward off and alleviate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts – the two most common eye disorders in older adults. Indeed, there is much research evidence to suggest that lutein reduces the risk of developing these conditions7, and might also slow their progression and enhance vision in people with these conditions. Furthermore, lutein might also help with retinitis pigmentosa – a less common, hereditary eye condition.
In addition, there is a growing volume of research suggesting that lutein can also enhance vision in healthy eyes. 8 In particular, it seems that lutein supplementation can improve vision in low light conditions such as those experienced during night driving. Just some of its researched benefits include improvements in:
- Contrast sensitivity – the ability to tell apart fine increments of light and dark
- Discomfort and reduced visual function caused by glare
- Photostress recovery – the amount of time needed for vision to return to normal after exposure to bright light
- Dark adaptation – the ability to get used to seeing in low light conditions

Research
Human Research
Clinical and observational studies indicate that lutein supplementation and increased macular pigment levels can:
- Enhance vision performance in healthy eyes, particularly in low light conditions such as driving at night
- Reduce the risk of developing macular degeneration, cataracts, and retinitis pigmentosa, and alleviate vision problems in people with these conditions
Lutein (10 mg) may improve vision in individuals with macular degeneration
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study known as LAST (Lutein Antioxidant Supplementation Trial), researchers examined the role of lutein in eye health. A total of 90 patients at a veterans’ hospital with chronic age-related eye problems received one of three treatments for 12 months: placebo, 10 mg of lutein daily, and 10 mg of lutein along with other antioxidants and nutrients. Both lutein groups experienced an increase in macular pigment optical density, which was accompanied by improvement of vision, contrast sensitivity, and glare recovery.
- The researchers concluded that “visual function is improved with lutein alone or lutein together with other nutrients.”9
Lutein supplementation (15 mg) may improve vision in people with cataracts
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 17 people with age-related cataracts were supplemented with lutein (15 mg), α-tocopherol (vitamin E), or placebo 3 times a week for 2 years. Only the lutein group experienced an improvement of visual performance (acuity and glare sensitivity).
- The researchers concluded that “Visual function in patients with age-related cataracts who received the lutein supplements improved…“10
Lutein or zeaxanthin supplementation (10 mg) may improve vision in low light conditions
This double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined the effects of lutein and zeaxanthin supplementation on vision performance in 34 healthy adults. They were given lutein (10 mg), zeaxanthin (10 mg), a combination of the two, or placebo daily for 6 months, and their vision was tested afterwards. The study found that the 3 supplemented groups showed a trend towards decreased amount of light scatter in the eye and contrast sensitivity, which is particularly useful for vision in low light conditions.
- The researchers concluded that “supplementation with L or Z increases MPOD…supplementation can improve CATs at high mesopic levels and hence visual performance at low illumination.”11
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined whether lutein can improve visual function in healthy adults. A total of 120 Chinese drivers were given placebo or lutein (20 mg) daily for 1 year. Supplementation resulted in increased macular pigment density levels, which was accompanied by improvements in contrast and glare sensitivity, especially in low-lighting conditions.
- The researchers concluded that “Lutein may benefit driving at night and other spatial discrimination tasks carried out under low illumination.” 12
Lutein and zeaxanthin may decrease risk of cataracts severe enough to need extraction
This cohort study examined the link between carotenoid intake and cataract extraction. A total of 36644 men aged 45-75 were studied over 8 years of follow-up, revealing that only those who had higher intakes of lutein and zeaxanthin had a lower risk of having cataracts that were bad enough to require extraction. More specifically, men who had the highest intakes of these carotenoids had a 19% lower risk relative to men with the lowest intake.
- The researchers concluded that “Lutein and zeaxanthin may decrease the risk of cataracts severe enough to require extraction, although this relation appears modest in magnitude.”13
Lutein (10, 30 mg) may help alleviate retinitis pigmentosa
This randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study examined the use of lutein for helping with retinitis pigmentosa (RP) – a hereditary eye condition characterized by vision loss due to rod cell degeneration in the retina. A total of 34 RP patients were given lutein (10 mg for first 12 weeks, then 30 mg for 12 more) daily and then placebo for 24 more weeks, while the other group took the placebo for 24 weeks and then the lutein. Lutein supplementation was found to enhance visual field (total area of peripherial vision where objects can be seen) slightly improve visual acuity (sharpness of vision).
- The researchers concluded that “lutein supplementation [in RP patients] improves visual field and also might improve visual acuity slightly…”14
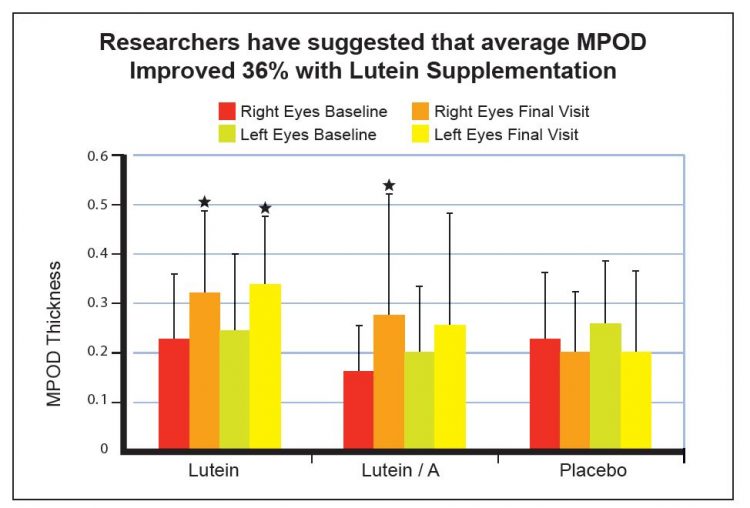
Lutein supplementation (10 mg) appears to increase macular pigment in people with AMD
This follow-up double-masked, placebo-controlled, randomized study examined whether and how lutein supplementation might affect macular pigment optical density (MPOD). Ninety people with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) received one of three treatments for 12 months: placebo, 10 mg of lutein daily, and 10 mg of lutein along with other antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. MPOD was found to increase in both lutein groups – especially in people whose baseline MPOD was lower – and slightly decreased in the placebo group.
- The researchers concluded that “Noteworthy is the observation that those individuals with lowest MPOD, and in greatest need of supplementation, were also most likely to benefit from either the lutein or the lutein plus antioxidant supplementation.”15
Dosage for Vision
- Successful research studies most commonly use 10 mg doses of lutein
- Most lutein supplements come in 10 – 20 mg capsule doses
- Lutein supplements often include zeaxanthin at doses of 1 – 10 mg because it is the second major component of macular pigment
- Lutein supplementation is a long-term commitment, considering that most studies required 6-12 months of supplementation for notable results
- Like other carotenoids lutein is fat-soluble, meaning that its absorption may be improved when taken with fat-containing foods
Available Forms
- Marigold petal extract softgels (most common form)
- Marigold petal extract tablets
Supplements in Review Says
- Lutein 10 – 20 mg daily for vision.
We highly recommend lutein as a vision supplement. Clinical research suggests that lutein not only helps protect the eyes from macular degeneration and cataracts, but might also enhance visual performance in multiple ways, particularly in low-light conditions such as night driving.
Research suggests that 10 mg daily should be sufficient. 10 mg is the most common dose used by successful clinical studies. However, given the lack of official dosage recommendations, doses up to 20 mg can be taken as well.
Leave a Reply