Long-revered herb ginseng seems to help the body cope with different types of physiological stress.

Panax ginseng is one of the most decorated herbal medicines known to man. Its multitude of health benefits includes a potential to relieve stress by:
- Combating physical and mental fatigue. Ginseng seems to impart an energizing effect during periods of stress.
- Improving mood. Subjective ratings of mood have been reported to improve with ginseng.
Overview
Commonly referred to as Asian, Chinese, or Korean ginseng, Panax ginseng has a rich, millenia-old history of use in traditional folk medicine as an all-around health tonic, and is now used all around the world today.1
Among its alleged benefits are:
- Increased energy and stamina
- Improved physical performance and muscle recovery
- Enhanced cognitive function
- Enhanced immunity
Gingseng’s benefits are believed to stem from its adaptogenic nature;2similar to other adaptogens, ginseng helps the body adapt to all forms of physical, mental, and environmental stress.

How Ginseng Might Help With Stress
The potential stress-alleviating activity of ginseng is believe to be related to compounds known as ginsenosides; ginseng carries 30+ types of ginsenosides.
Increasing mood neurotransmitters
Although the exact mechanism behind the process is still being investigated, ginseng does seem to exert an influence on the central nervous system (CNS), and its consumption has been associated with elevated levels of neurotransmitters linked to positive mood, including dopamine, noradrenaline, serotonin.4
Blocking ACTH action
Ginseng has been shown to inhibit the increase of stress hormone levels, specifically corticosterone, by stopping adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from acting on the adrenal gland.5
Antioxidant activity
The anti-oxidizing effects of ginsenosides were found to decrease oxidative stress, and in turn, reduce fatigue factors often caused by stress.6
Ginseng Benefits & Uses for Stress

Although ginseng has not yet been proven to directly provide relief for stress, it has shown promise as a means to:
- Improve subjective quality of life, especially mood7
- Reduce anxiety and promote calmness
- Reduce physical and mental fatigue caused by stress
- Enhance tolerance to environmental, physical, and mental stressors, such as cold exposure and sickness
There is a good deal of research backing ginseng’s wide range of health benefits.
Research
Animal Research
Animal studies suggest that even the isolated compound ginsenoside RB1 can potentially reduce anxiety and distress.8 In addition, ginseng has demonstrated significant anti-stress properties in rats, particularly when managing chronic stress.9
Human Research
Clinical studies suggest that ginseng helps the body cope with various stress factors as well enhances mood and fights fatigue.
In this randomized, double-blind investigation, 625 adults under physical and mental stress took either a multivitamin capsule or a Pharmaton Capsule consisting of vitamins, minerals, trace elements, and ginseng extract G115 every day for 12 weeks. Compared to the 6.4 average increase in subjective quality of life ratings for the multivitamin group, the ginseng group had a significantly superior average increase at 11.9 points.
- The researchers concluded that “Pharmaton Capsules were more effective than the multivitamin capsules alone in improving the quality-of-life in a population subjected to the stress of high physical and mental activity.”10
Panax ginseng (400 mg, 4% ginsenosides) may reduce mental fatigue
In this placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover investigation, 27 adults took placebo or either 200 mg or 400 mg of Panax ginseng with 4% ginsenoside 1 hour before performing 6 cognitive demand tests. Compared to the control, P. ginseng enhanced participants’ performance and subjectively reduced mental fatigue during a stress-inducing cognitive demand task.
- The researchers concluded that “Panax ginseng and glucose enhanced performance of a mental arithmetic task and ameliorated the increase in subjective feelings of mental fatigue.”11
Panax ginseng (1 g) may reduce chronic fatigue
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 90 patients with idiopathic chronic fatigue (ICF) were given either a placebo or 1 gram of P. ginseng daily for 4 weeks. According to a self-rated numeric scale (NRS) and a visual analogue scale (VAS), patients given P. ginseng were found to have reduced mental and physical fatigue compared to those taking the placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “results provide the first evidence of the antifatigue effects of P. ginseng in patients with ICF, and we submit that these changes in antioxidant properties contribute in part to its mechanism.”12Anti-stress effects of Ginkgo biloba and Panax ginseng: a comparative study.
Panax ginseng seems to minimize stress caused by cold and industry work
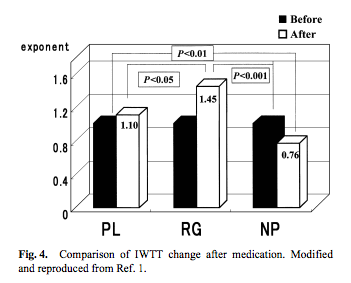
This review reported the results of several studies examining the effects of ginseng on stress caused by various factors, namely cold exposure, work stress (industrial fatigue), and stress caused by illness (cold/flu). In the randomized, placebo-controlled cold exposure trial, 90 adults took a placebo, powdered red ginseng root (RG), or nifedipine (NP) and then underwent a cold stress test. The cold stress test had little effect on the blood pressure of the placebo and RG groups. Compared to the other groups, the RG group had a lower heart rate and significantly better ice water tolerance time (IWTT), which suggests a calmer reaction to stress.
In the work stress study, 23 taxi drivers were given RG or placebo, and RG was found to improve mental fatigue and related symptoms. Finally, in the cold study, RG was found to alleviate cold and flu symptoms and reduce the number of infections.
- The researchers concluded that “We have performed several clinical studies on the human stress model and have reportedt hat red ginseng (RG) has clear anti-stress action.”13
Dosage for Stress
- Successful clinical research studies most frequently use from 200 – 400 mg of Panax ginseng.
- Typical supplemental capsules come in daily servings of 100 – 500 mg, and some are standardized to contain 4 – 8 % ginsenosides.
Available Forms
- A raw herb or organic dried root, 1 – 2 g
- Chewable tablet or softgel, in 50 – 100 mg serving sizes
- Powder, often encapsulated
- Ginsana®, a patented ginseng supplement that uses G115®, a ginseng extract commonly used in clinical studies
Supplements in Review Says
- Panax ginseng root extract standardized to 4-8% ginsenosides at 200 – 400 mg for stress.
Panax ginseng seems to help the body cope with stress. Although research pertaining specifically to stress is somewhat lacking, ginseng seems to help the body cope with different kinds of physiological stressors such as fatigue from physical exertion, mental fatigue, and cold temperatures.
Take 200 – 400 mg of standardized Panax ginseng. Start with a 200 mg dose of P. ginseng root extract containing 4 – 8% ginsenosides, and then increase the amount for up to 400 mg per day based on need.
Leave a Reply