Key component to RNA may help build new neural connections and enhance overall cognition.
![By Jynto [CC0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Uridine_3D_ball-300x205.png)
- Better Memory. Increased ACh levels are associated with improved memory, especially in age-related memory decline and degenerative cognitive dysfunctions like Alzheimer’s.
- Increased Learning Ability. Uridine helps with brain plasticity by indirectly promoting cell membrane health and enhancing synapses in new parts of the brain (i.e. synaptogenesis).
- Improved Mood. Uridine boosts dopamine, which helps improve focus and attention while also relieving stress and anxiety.
Overview
Uridine is one of four repeating units that make up ribonucleic acid (RNA), DNA’s molecular sibling. Aside from sci-fi movies and pseudo-scientific Jeff Goldblum monologues, we imagine the last time most of you heard these terms were in high-school lab–so here’s a quick recap:
- DNA is the primary molecular component responsible for storing information in all living organisms. RNA is simply DNA’s replicating messenger–it relays DNA’s info to the ribosomes, the molecular factories of protein-synthesis, where DNA’s info is used as a reference point on which proteins to build.
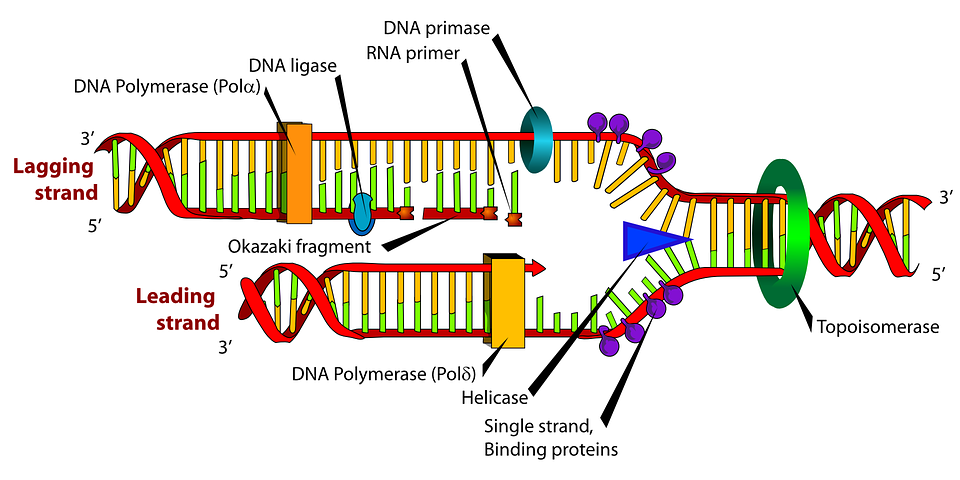
In other words, without Uridine to help make up RNA, DNA’s info would be trapped, protein wouldn’t be accurately synthesized, and organic life as we know it would cease to exist.1
What happens when Uridine is low?
Life still goes on, but much less smoothly–symptoms of low Uridine levels include:
- Poor memory
- Impaired learning
- Mood disorder
- Inattention
- Anxiety
Plus many more bodily issues.
Dietary sources of Uridine include broccoli, beer, parsley, oats, yeasts, sugar cane, tomatoes, fish, and mushrooms, but if you’re looking to achieve Uridine’s full nootropic benefits, supplementing the compound may help.
How Uridine Might Help Brain Health
Formation of new neural synapses
One of Uridine’s most valuable properties from a cognitive viewpoint is its promotion of new synaptic centers in the brain. Synapses send and receive messages from neurotransmitters and release those messages throughout the rest of the brain, the central nervous system, and the body. Synaptogenesis enhances cognitive function and can alleviate the mental “hiccups” of aging.2 On that point, the scientific community is increasingly interested in Uridine’s synaptogenesis for its possible use in age-related neurodegeneration.3
Increased learning ability
Synapses facilitate learning, and new synapses develop when we learn something. By increasing the neural plasticity that accompanies synaptogenesis and delivering an indirect supply of acetylcholine (neurotransmitter associated with learning), Uridine helps bolster this relationship between learning & synaptogenesis–in effect, promoting the cognitive functions required of learning, as well as the formation and storage of memories.4
In particular, Uridine’s boost on ACh production helps facilitate neuronal communication, allowing the brain to process information with greater ease for “in the moment” thinking. More on nootropics that help with learning
Decreased stress hormones
In addition to increasing ACh levels, Uridine stimulates the release of the “feel-good” neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain, a chemical that stimulates feelings of pleasure, happiness & motivation, while diminishing excess levels of stress hormones cortisol & adrenaline. Due to these hormones negative effects on the brain’s ability to form new synapses, Uridine’s stimulation of dopamine offers a neuroprotective effect on neural communication.5
Combined with the previous benefits, Uridine’s indirect inhibition of stress creates a neural environment that’s conducive to higher-level cognitive function. More on anti-stress nootropics
Research
Animal Research
Uridine & choline combination improves cognitive deficits in hypertensive rats.
Hypertension is thought to be a risk factor for the development of cognitive disorders due, and this animal study used hypertensive rats as a model for human subjects with cognitive deficits. The trial specifically studied deficits in learning, attention and memory. Researchers tested a group of 5-7 month old hypertensive rats (SHR) against normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats for short-term memory function, attention, reaction time, and spatial learning capabilities. The hypertensive rats exhibited significantly inferior performance on spatial learning and attention tests. After a solution of Uridine and choline was administered, the SHR group’s performance improved to normal in spatial learning, attention and reaction time.
- This study’s findings suggested, “A combination of uridine and choline administration improved selective attention and spatial learning in SHR.”6
Uridine & DHA combined effects help regulate synaptogenesis.
Researchers gave normal rats uridine & docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) orally and measured dendritic spine formation and cognitive functions. The study showed increased dendritic spine levels and enhanced cognitive function, along with an increase in biochemical markers for neurites.
- Researchers found, “It is possible that giving uridine plus DHA triggers a neuronal program that, by accelerating phosphatide and synaptic protein synthesis, controls synaptogenesis. If administering this mix of phosphatide precursors also increases synaptic elements in brains of patients with Alzheimer ’s disease, as it does in normal rodents, then this treatment may ameliorate some of the manifestations of the disease.”7
Human Research
Maximum tolerated dose for Uridine calculated at 10-12 g/m2.
Researchers administered oral doses of uridine to human volunteers in single doses ranging from 0.3 to 12 g/m2, and in multiple doses of 5-10 g/m2 every 6 hours for three days. 10 to 12 g/m2 was the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) for a single dose, and 5 g/m2 in multiple doses. Diarrhea was the dose-limiting indicator. Single-dose uridine raised plasma uridine by 60 to 80 microM after 8 to 12/g/m2 dosage with bioavailability between 5.8% and 9.9%. In the multiple-dose schedule with 5 g/m2 doses, plasma uridine levels stayed a steady 50 microM.
- This study’s conclusion stated simply, “Further studies should explore the role of oral uridine in the modulation of the toxicity of fluorouracil.”8
Dosage
Recommended dosage varies greatly between:
- 500 mg to 2 g per day
However, many users hover around 1 g daily for Uridine’s brain health benefits–typically as part of a well-rounded nootropic stack.
Side Effects
Most reports of this nootropic contain little to no complaints. However, Uridine can have some unpleasant side effects at higher doses, including:
- Diarrhea
- Upset Stomach
- Headache
- B Vitamin depletion
Luckily, this last side effect can be easily remedied by Vitamin B supplementation (which isn’t a bad idea anyways).
Available Forms
Beer contains high levels of Uridine, as do breast milk, infant formula, broccoli, fish, mushrooms, Chinese cabbage, parsley, oats, tomato, liver, sugarcane, and brewer’s yeast. Yet, food sources have low oral bioavailability of Uridine, making supplementary Uridine the preferred option.
Uridine supplements come in the basic forms of tablets, capsules, & powder.
Supplements in Review Recommendation
- Uridine powder, 1 gram daily.
Uridine is a core nootropic nutrient. You’re not hearing that from us so much, nor are you hearing it from definitive human research studies. However, we’re hearing it from so many nootropic enthusiasts on the Interwebs. Uridine is such an integral component of human biology that has some promising research to back its supplementary intake as well.
Or better yet, try Citicoline, 250-500 mg. Rarely do Uridine users take the nootropic as a standalone ingredient–and most users who stack it do so with a Choline source. Because that’s essentially what Citicoline is: Uridine + Choline.
References
Leave a Reply