Aside from a few special cases, there are essentially only two reasons to supplement T-boosters:
- You’re a mature older man with naturally diminished T levels.
- You’re a bodybuilder.
Most men aged 18 through 35 are in their testosterone prime and thus aren’t in any immediate need for boosted testosterone levels. But bodybuilders aren’t “most men.” Building a muscular body requires an inordinate amount of mental & physical maintenance–maintenance of time, diet, exercise, sleep, rest, relationships, and, yes, testosterone.
While they aren’t the only key to a successful bodybuilding regime, T-boosters can help keep the bodybuilding system in working order.
About Bodybuilding
![Arnold Schwarzenegger, 1974. By Madison Square Garden Center (RMY Auctions) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Arnold_Schwarzenegger_1974-206x300.jpg)
Women secrete testosterone from their ovaries.
Both sexes also produce small amounts in the adrenal glands of the kidneys, but, for the most part, testosterone originates from the sex organs unique to man & woman. Regarding the body itself, both man & woman share identical skeletal muscle tissue—yet, men are more biologically inclined to increase muscle mass than women.
The reason: Male testes produce about 40 – 60% more T than the female ovaries do.
Thus, illustrating the importance of T with regards to increasing muscle mass—or building body. And for the bodybuilder, male & female, maintaining T is half the battle in maintaining muscle & strength gains.
The other half involves maintaining other various hormones & proteins (growth hormone (HGH, cortisol, estrogen, amino acids, etc. etc.) as well as showing up to the gym, eating right, sleeping adequately—all of the lifestyle behaviors associated with healthy muscle metabolism.
Depending on how well these factors are all maintained, the body can fall under two metabolic states:
- Anabolism. The process of building complex molecules (e.g. muscle tissue) out of simpler ones (e.g. protein).
- Catabolism. The process of breaking down complex molecules to simpler ones.

For the bodybuilder, “Anabolism” is the name of the game. In essence, anabolism is just a fancier term for bodybuilding, and it’s accomplished primarily by securing a healthy balance of anabolic influences (T, growth factor, exercise, etc.) and catabolic influences (cortisol, aromatase, alcohol, etc.).1
Yet, even when this balance is met, over time bodybuilders find it harder & harder to maintain due to a phenomenon known as The Bodybuilder’s Paradox.
The Bodybuilder’s Paradox
Have you ever heard the phrase “law of diminishing returns”?
Economically, it’s defined as:
The decrease in incremental output of production as the amount of a single factor of production is increased.
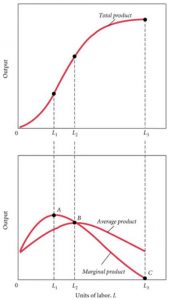
Translating to the world of bodybuilding: You maintain a pristine diet. Sleep early every night. Drink adequate amounts of water. All the while increasing your workout load every day, week, month, only to yield less & less gains with each increase. Your returns (muscle & strength gains) diminish as the factor of production (lifting weights) increases.
This frustrating trend is The Bodybuilder’s Paradox.
On one hand, it’s necessary: If we push our muscles & strength beyond their limits, our bodies would literally buckle under the increased physical demands (i.e. stress) of maintaining that muscle & strength. Think about it: Your deadlift may increase by 250 pounds, but your body gains only a small fraction of that weight. Thus, there’s an overall higher demand placed on the body.
Metabolically, this can be problematic:
- When overworked, the body can fall into a significant state of catabolism that, if left unchecked, may induce a series of health problems, such as chronic fatigue, adrenal insufficiency, & mental/physical burnout.2
Luckily, there are measures that can be taken to ensure that a healthy anabolic state is maintained while more & more body is being built.
One such measure is the Testosterone Booster.
How T-Boosters Might Help Bodybuilders
Technically, if a supplement can boost T, then it’s apt to benefit bodybuilding to a certain degree—considering the strong relationship between T and muscle gains. With that in mind, we narrowed down the T-booster bio-actions that seem specifically geared towards aiding bodybuilders.
Here they are:
Increase Muscle Mass
While testosterone isn’t the primary active androgen in the male body (that title belongs to dihydrotestosterone, or DHT), it is the primary active androgen in skeletal muscle tissue. Thus, when T levels diminish, so does muscle mass—highlighting the importance of testosterone to bodybuilders, who are essentially skeletal muscle tissue builders.
Testosterone seems to support muscle mass by:
- Signaling protein synthesis
- Promoting tissue regeneration
- Increasing growth factor3
Combined, these bio-actions enhance an overall anabolic muscle-building environment inside the T-boosting bodybuilder.
Decrease Stress Hormone Cortisol
One of the worst criminals of muscle loss: Cortisol.
When stress elevates, cortisol elevates—and vice versa. If stressed too often, cortisol levels can run amok on muscle metabolism, not to mention other various bodily functions.4 And considering that intense physical activity (i.e. exercise) is processed by the body as a stressor, bodybuilders are at an ironic risk of diminishing their muscle gains by working too hard to achieve them.
This within itself can be stress-inducing for the competitive bodybuilders who are constantly tempted by their competitive streak to hit the gym one more time, do one more set, add two more plates, etc. etc.
With that in mind, certain T-boosters that can diminish cortisol while also increasing T are of the utmost value to bodybuilders looking to increase that T:cortisol ratio to anabolic standards.
Regulate Estrogen Levels
Typically through inhibiting aromatase, the enzyme responsible for converting T to estrogen (yikes), certain T-boosters may help regulate estrogen levels—essentially delivering a two-for-one benefit to male health:
- Preventing T’s conversion to estrogen sustains overall T levels.
- Decreasing overall estrogen levels subsequently diminishes estrogen’s antagonist bio-effects on T-synthesis & T-expression.5
Ideally, aromatase aids male health by countering excessively high T levels. This is why pro-hormone users are at-risk of developing gynecomastia over their giant pecs, because their excess T levels are matched by excess estrogen levels.
However, even men who supplement natural, legal T-boosters may be at-risk of overactive aromatase and thus resort to estrogen blockers late in their T-boosting cycles to keep the “girly” side effects at bay.
List of Bodybuilding T-Boosters
D-Aspartic Acid (DAA)
![The oyster is a rich source of DAA. By User:Anthere (personal picture of an oyster harvested in france) [GFDL or CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/1200px-OysterL-300x225.jpg)
Many ingredients claim to boost T. Others conditionally boost T. But DAA just does it—effectively & unconditionally. The bio-mechanisms by which DAA may enhance T levels act directly & indirectly on the following glands:
- Hypothalamus. Releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
- Pituitary. Secretes luteinizing hormone (LH) and growth hormone (GH).
- Testes. Promotes cAMP activity in the Leydig cells, increasing T-synthesis.6
By acting across the HPG Axis in such a way, DAA rounds out many edges on the T-production process—stimulating & sustaining male sex hormone levels, in addition to growth hormone for additional muscle building support. More on D-Aspartic Acid.
Vitamin D
![Muscle Beach, CA. By Db9023 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Muscle_Beach_California-300x225.jpg)
In dietary terms, Vitamin D is labelled as a vitamin, but in the body this important T-booster acts as a hormone. As such, Vitamin D engages the male endocrine system, particularly along the pituitary gland—promoting the release of LH & GH (similar to DAA).8 For men at risk of Vitamin D-deficiency, supplementing Vitamin D may provide significant advantages in normalizing hormone levels back to an anabolic state. More on Vitamin D.
Fenugreek
![By കാക്കര (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Fenugreek_-_ഉലുവ-300x225.jpg)
Instead, the seed primarily hails from India and has a long history of use in Traditional Chinese & Ayurveda health systems—particularly sexual & athletic health. This is why you’ll find Fenugreek in both sex-enhancing & sports nutritional supplements:
- Specifically, Fenugreek’s benefits on libido, testosterone, & muscle recovery make it a unique multi-purpose herb for in-the-moment & after-the-moment male activity. Bodybuilders in particular may benefit from the recovery aspect, one study showing 63% quicker muscle recovery following strenuous physical activity.9
However, bear in mind that one of Fenugreek’s multiple purposes includes deactivating 5-alpha reductase—the enzyme responsible for converting T to DHT. While this bio-action helps sustain “free” T levels, it diminishes DHT, which is the body’s primary male androgen.10 For this reason, it may be unwise to solely rely on Fenugreek for bodybuilding gains. More on Fenugreek.
ZMA
![By User Supplements on en.wikipedia [Copyrighted free use], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Bottle_of_ZMA_02171.jpg)
Originally formulated by Victor Conte, founder of the infamous BALCO Labs that allegedly distributed steroids to athletes Bill Romanowski, Marion Jones, & Barry Bonds, ZMA has become a staple of sports nutritional for its well-studied effects on T levels & muscle metabolism. The results of those studies:
- The most referenced study, conducted by Dr. Lorrie Brilla & Victor Conte on Western Washington University football players, found increases of muscle gains by 11.6% & increases of T levels by 30% with ZMA supplementation.11
- Another study performed at Baylor University’s Exercise and Sports Nutrition Lab found that “ZMA supplementation during training does not appear to enhance training adaptations [i.e. muscle & strength gains] in resistance trained populations.”12
The take-home: ZMA seems to work conditionally, most likely dependent on initial ZMA levels in the body. In other words, if you’re already consuming adequate amounts of Zinc + Magnesium + B6 through your diet, then ZMA won’t do much for you.
The exact ingredients forms used in the original ZMA formula include Zinc Monomethionine Aspartate, Magnesium Aspartate, and Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxine HCl)—although there are better, more absorbable forms of these T-boosters. More on Zinc.
Rhodiola Rosea
![By Alpsdake (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Rhodiola_rosea_s2-300x211.jpg)
Grown in the high-altitudes of the Siberian mountains, Rhodiola is a perennial plant of extreme adaptogenic value. As such, Rhodiola can be found on many of our supplement lists for its long list of anti-stress benefits. The type of people that benefit from this herb include:
- Bodybuilders. Russian research shows remarkable improvements in muscle development & function among Rhodiola-consuming athletes.13
- Brainiacs. Rhodiola’s nootropic bio-effects offer brain-protective support for enhanced cognition in the gym, office, & everywhere in between.
- Workaholics. One study observing Rhodiola’s effect on “Life-Stress” (catch-all term for perceived stress, fatigue, etc.) found two daily doses of 200 mg helps improve Life-Stress symptoms.14
Bodybuilding might be the primary topic of this article, but bodybuilders are humans, too—equipped with all of the daily stresses of typical human life. Rhodiola is a T-booster that not only maintains anabolic T levels, but diminishes the stress & damage induced by the stressful daily grind of bodybuilding & life. More on Rhodiola Rosea.
Tongkat Ali
![By Mokkie (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Tongkat_Ali_Eurycoma_longifolia_2-169x300.jpg)
Due to this, many bodybuilders may overlook this herb, afraid that they’ll spontaneously sport wood in the middle of an intense (public) workout. But that would be a mistake. Aside from aiding sexual function, Tongkat Ali seems to help bodybuilders by regulating the following hormonal pathways:
- Dihydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), the precursor to T.
- Aromatase, the enzyme responsible for converting T to estrogen.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH), to signal T-synthesis.
- Cortisol, the catabolic enemy to manly muscle gains.15
Through optimizing these bio-pathways, Tongkat Ali may support all-around male vitality to get the most out of your workouts. More on Tongkat Ali.
Ginseng
![By Richardfabi (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Red_ginseng-225x300.jpg)
- Ginseng’s vaguely human-like shape looks vaguely manly.
- Ginseng’s vitalizing benefits make men feel
And while, admittedly, these benefits don’t include any major upticks in T counts, Ginseng’s T-booster bio-effects do significantly alter sex hormone levels in an effort to help the body adapt to stress—which includes exercise.16
Due to this, Ginseng is a great T-booster herb to stack with other T-boosters—particularly for its N.O. boosting bio-mechanism that not only helps circulation, but helps other ingredients & nutrients travel throughout the body. More on Ginseng.
Diindolylmethane (DIM)
![By Karelj (Own work (own photo)) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Brokolice_1-300x200.jpg)
Due to the unfortunate estrogen-increasing side effect of elevated T levels, E-blockers such as Diindolylmethane are important additions to any serious T-booster stack. This is why Post-Cycle Therapy (PCT) stacks utilize DIM & other E-blockers: To limit the subsequent surge in estrogen following an intense T-boosting regimen.
However, take note that not all reports of DIM supplementation are positive:
- Under low doses, DIM seems to benefit T levels while inhibiting their conversion to estrogen (via aromatase).17 However, upping the dosage seems to destabilize DIM’s bio-effects, potentially leading to decreases in T levels.18
With that in mind, we recommend sticking to lower doses of DIM—ideally, no more than 100 mg per day—to stay on the “good side” of this E-blocking T-booster. More on Diindolylmethane.
What about Tribulus Terrestris?
![Stan Shebs [GFDL, CC BY-SA 3.0 or CC BY-SA 2.5], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Tribulus_terrestris_5-300x266.jpg)
- Tribulus is the most popular herb in bodybuilding stacks.
- Tribulus doesn’t boost T.
In the world of sports nutrition, Tribulus is heavily marketed as a performance-enhancing, muscle-boosting, testosterone-spiking herb, but in reality… There’s nothing in the scientific literature to suggest that any of this is true. In fact, in a recent review, Tribulus Terrestris was actually not recommended for athletic purposes:
- In the reviews conclusion, the researchers stated, “So far, the published data concerning TT do not provide strong evidence for either usefulness or safe usage in sport.”19
Our take: Tribulus doesn’t do a whole lot for male hormones, but seems great for male health. We can’t imagine it having any negative effect on performance. If anything, the placebo effect of its “energizing” sex enhancements might actually work as a motivational tool to get your muscles moving. This may partially explain why it’s so popular in T-booster stacks: It feels good.
On that point, take Tribulus with other bodybuilding T-boosters, but don’t depend on it to boost T. More on Tribulus Terrestris.
Conclusion
There are plenty of mystery pills and synthetics that can fuel anabolic growth. And while some of these are safe and effective, other anabolic supplements may carry potential side effects, health risks and even legality issues.
Natural supplements are a more conservative strategy for increasing muscle growth, and they do work when used intelligently. T-Boosters are among the best of these supplements for bodybuilding, thanks to their ability to power workouts, modulate androgen levels and more. But really, in a well-rounded bodybuilding stack, testosterone boosters are only one of many good supplements for anabolic muscle gains.
For hormonal support in the context of weightlifting, take note of the ingredients listed above, but don’t forget to also check out our pre-workout supplements for additional bodybuilding strength support and our nootropics for maximum levels of motivation & energy in the gym.
Research

Leave a Reply