
Welcome to SiR’s in-depth guide on joint supplements! Here, I will walk you through the basic information about how these supplements can benefit your joints, and how to choose the right one and use it to complement your healthy lifestyle.
If you are new to joint supplements, this guide will equip you with practical, evidence-based information needed to make an informed choice.
For those experienced, this is a great one-stop reference guide. It is replete with clear and actionable info on navigating the world of joint supplements.
Each section of this guide contains links to more in-depth individual articles about a particular topic, such as benefits of supplements and comparative analysis of different options on the market. You should be able to find everything you need about joint supplements here—no need to go anywhere else. Let us dive straight in!
The Joint Health Problem
Joints are structures where different bones connect together. Certain disorders, physical trauma, and the natural wear and tear of everyday use can damage joints, leading to a drastic reduction in quality of life.
Most notably, the modern sedentary lifestyle, characterized by desk-bound office jobs and the correlated rise in obesity, has a profound negative effect on joint health. According to recent data, roughly 54.4 million Americans have been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, which, simply put, is joint pain that refuses to go away on its own.1
Given this staggering statistic, it’s not surprising that more and more people are turning to joint supplements combined with physical therapy to improve their joint health. In this guide we’re going to provide a background on joint supplements, including how they work and for what they’re best suited.
Joint Structure
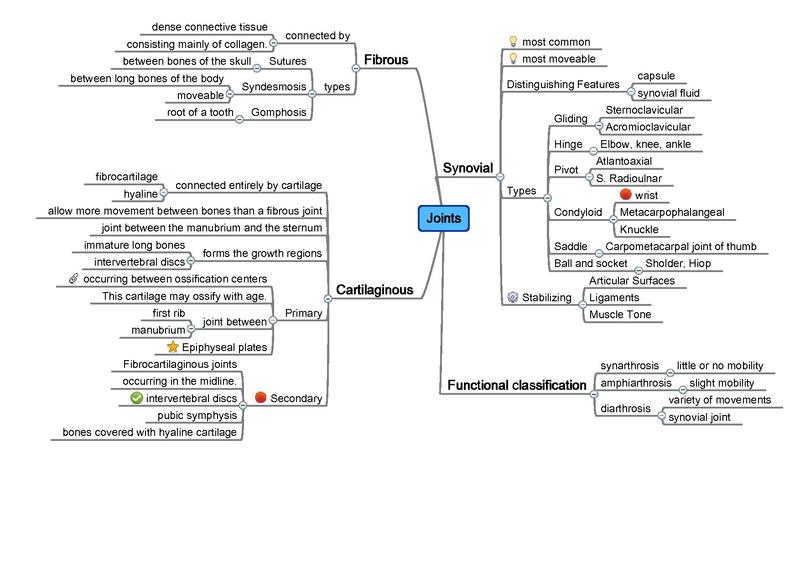
A joint is the connection between bones and all of the pieces that help keep them together. Joint tissue includes ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and bones.
Cartilage, made up of shock-absorbent elastic fibers and protein complexes called proteoglycans, is especially designed to help reduce weight pressure on bones while allowing them to move smoothly. Ligaments and tendons, on the other hand, are made of connective tissue and help connect bone to bone and muscle to bone.
The fluid surrounding joints is also important, as it contains compounds that promote and sustain the development and well-being of bones and cartilage. Certain joints have a tiny cavity between the bones that is filled with this fluid.
Joints are divided into three structural categories:
- Fibrous joints — hold dense tissue rich in collagen (e.g. skull)
- Cartilaginous joints — connected directly by cartilage (e.g spine)
- Synovial joints — have a small fluid-filled cavity between the bones (e.g. knee)
Despite how resilient joints are built to be, they eventually wear down. Excessive use and certain illnesses can increase inflammation around joints and speed up the breakdown process that ultimately leads to joint pain and reduced mobility.
What are Joint Supplements?
Joint supplements are dietary products designed to sustain, improve, and protect joint health and function.
- They come in a pill or powder form and contain ingredients such as omega-3 fatty acids, MSM, vitamins, minerals, and herbs. All of these have been shown to support joint function.1 As a result, joint supplements are popular among athletes, elderly, and people who seek a relief from osteoarthritis.
There are joint supplements with only one ingredient, and there are those that contain more than 10. The more comprehensive formulas are generally more effective because they offer a wider spectrum of benefits.
To understand joint supplements’ role, we must first realize the importance of joint health. Many people only start looking for joint supplements once they notice symptoms like joint pain, stiffness, and arthritis show up. But root causes of these symptoms have already been there for years.2
The good news is that you can benefit from joint supplements, no matter your background. Joint supplements are not only used by people who need a relief from pain and injuries, but also by those who want to reduce the risk of developing a joint problem later in life.
A quality joint care formula offers you several benefits:
- Reduce pain and inflammation
- Protect joints from daily wear and tear
- Enhance cartilage healing and repair
- Support synovial fluid which cushions your joints and provides shock absorption
How Joint Supplements Work
They work through several major mechanisms:
Decreasing inflammation
Inflammation is the leading cause of joint pain, swelling, and other common symptoms. Many natural joint supplements contain bioactive substances that can inhibit pro-inflammatory molecules (including phospholipase, lipooxygenase, cyclooxygenase 2, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and nitric oxide), promote anti-inflammatory ones, and reduce overactive immune system responses that are heavily involved in inflammation.2 3 4
Minimizing cartilage loss
The capacity of joint supplements to protect or even restore cartilage is still hotly debated. There is some evidence that certain supplements can reduce cartilage loss, specifically shown by an elevated expression ratio of osteoprotegerin (OPG) to receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL), which means that these compounds can decrease the presence of cartilage-destroying cells.5 Ultimately however, more research is needed to say anything conclusive.
Maintaining bone growth and development
Protein and mineral supplements, collagen in particular, may not only facilitate the development of bone cells in a process known as osteoblast differentiation, but also enhance bone density, mass, and strength.6
Types of Joint Supplements
Supplements that improve joint health come from an assortment of sources. Check out our list of joint health supplements for more details.
Plants
A variety of plants have thoroughly backed anti-inflammatory properties, and keeping inflammation at bay is pivotal for joint health. The curcumin found in turmeric and CBD (cannabidiol) drawn from cannabis plants are prime examples.

SA-2.0], via Flickr
Fats
Fish oil is a standout fat-based joint supplement because of its knack for reducing inflammation. Its abundant supply of omega-3 fatty acids are believed to have an especially potent anti-inflammatory effect in cases of arthritis.
Proteins
The most popular protein-based supplements are based on collagen, which is the main structural protein of connective tissue. Such supplements serve the dual purpose of promoting joint tissue growth while decreasing inflammatory and autoimmune damage.
Minerals
Certain minerals, most prominently methylsulfonylmethane (MSM), are used as joint supplements. Similar to the benefits of many plant-based supplements, MSM has shown a tendency to reduce inflammation.
Cartilage
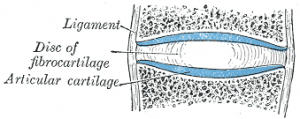
The most popular joint supplements are made from extracts of cartilaginous animal tissue, including that of cows, pigs, sharks, shellfish, and birds.7 They not only offer a strong anti-inflammatory effect, but might also, according to certain groups, diminish the amount of cartilage-deteriorating cells near joints. Glucosamine and chondroitin are the best examples of this category.
Selecting A Joint Supplement
“How to choose the right joint supplement?” This is a reasonable question when you consider how many options are out there on the market. If you are new to joint supplements, it can seem confusing and overwhelming, sometimes to the point of giving up.
This guide was created to make it easy to find the right joint supplement for you. Just make sure to concentrate and read each section one by one.
Here are some factors you should consider when looking for the best joint supplement:
1. Identify Your Needs
First, pinpoint why you need a joint supplement. Is it for general health a.k.a just in case, to ease pain & swelling, or to support recovery from an injury? Answering this question will help us narrow the choice down.
2. Learn About Ingredients
Joint supplements typically contain ingredients like glucosamine, MSM, omega-3s, green tea extract, and turmeric. Each one affects joint health from a different angle.3 Knowing the science-backed benefits of these ingredients that I will lay out in later sections will serve you as a compass.
3. Quality Matters
Many supplements use low-quality fillers and synthetic compounds which might be unhealthy for long-term use.4
When looking for a joint supplement, make sure it is third-party tested. Read ingredient labels—they should be transparent, clearly showing ingredient dosages, which are as important as ingredients themselves.
Some supplement manufacturers put many ingredients in a formula in very small amounts. Even if ingredients are studied, underdosing or obscure doses could mean they are ineffective.
The top joint supplements should contain patented ingredients, which usually indicates a higher-quality and more effective product, although the price might be higher too.
4. Lifestyle & Health Status
You may not be a fan of swallowing pills. In this case, a powdered product that you can mix with water or another beverage is a good alternative, even though high-quality powdered joint supplements are more difficult to find.
- You should also be aware of any allergies, health conditions, or medication interactions. Check with your physician when in doubt.
5. Decide Your Budget
There are some effective and safe joint supplements that are also affordable. However, for the very best products that use top-of-the-line ingredients in large effective doses, you will generally need to fork out a more premium price.
6. Read Reviews
There are people who have been in your shoes and found a joint supplement that works for them. Reading other people’s experiences can help you narrow your choice down, filtering out ineffective and scam products from ones that give concrete, healthy results.
7. Trial
There is no way around it—testing a product for yourself is the best way to truly know if it is worth the money. Once you have done your ingredient research and checked other people’s reviews of a product, it is time to try it for at least 30 days. Start with a smaller package to see its results before ordering a larger supply of a product.

Benefits of Joint Supplements
Joint supplements are in high demand for a good reason—they have a range of benefits that can significantly improve joint health and your quality of life. They present a safe and natural alternative to prescription drugs which, as potent as they can be, come with a slew of potential side effects.
Whether you are dealing with age-related wear and tear, a lifestyle that puts strain on your joints, or discomfort due to conditions like arthritis, here is how joint supplements can help:
Supporting Joint Health
The obvious main benefit of joint supplements is their support for healthy joints. Ingredients like glucosamine and chondroitin help to repair cartilage and lubricate connective tissues for smoother movement and improved long-range joint health.5 Even if you do not have joint problems, taking a joint supplement may act as a protective measure in maintaining longevity.
Related: Boosting Joint Health Improvement Through Supplements
Reducing Pain
One of the biggest joints issues – if not the biggest – is pain, sometimes debilitating. This can severely limit your day to day activities. The good news is that joint supplements work to relieve pain.
These include Boswellia Serrata and others, which have been shown to block inflammatory molecules like NF-kB and COX-2, diminishing joint aches in the process.6 Joint supplements are beneficial for arthritis sufferers, too.
Related: Understanding the Benefits of Supplements for Inflammation
Improving Mobility
Injuries and age can aggravate joint stiffness, limiting movement in things we once enjoyed. Joint supplements support flexibility and mobility by assisting in joint tissue repair and lubrication, as well as lowering inflammation and swelling.
Enhancing Day-to-Day Comfort
Some people may dread simple activities like walking down the stairs or getting up from bed due to sharp joint pain. Regular use of joint supplements can make these scenarios a thing of the past, thanks to their anti-inflammatory and joint-healing properties.
Joint supplements can even support and promote bone health.
Aiding the Repair of Connective Tissues
Daily wear and tear can limit your joint function as you age. Joint supplements work to not only protect your joints from the relentless side-effect of time, but to actually undo and repair damage to your cartilage and connective tissues. This is especially important for athletes who want to improve their sports performance.
Improving Well-Being
Everyone who has experienced major joint pain and stiffness knows that it does not just affect you physically, but also emotionally, having a negative impact on multiple aspects of life, including relationships.7 By improving joint function and enhancing daily comfort, these supplements can really make a difference in how you move, think, and feel.
Uses of Joint Supplements
Joint supplements are versatile. You can use them to address various needs from providing osteoarthritis relief to supporting an active lifestyle. Here is what they are commonly used for:
Osteoarthritis Relief
Osteoarthritis is a common joint disorder that leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility due cartilage breakdown. Joint supplements, particularly those that contain ingredients like glucosamine, chondroitin and MSM8, have been shown to provide osteoarthritis relief by:
- Reducing inflammation. Leading to less pain and improved mobility.
- Slowing cartilage deterioration. Research indicates that some joint supplements protect from connective tissue breakdown.
- Enhancing lubrication. Improving joint fluid (also known as synovial fluid) for smoother movement and better shock absorption.
These benefits make joint supplements especially helpful for senior osteoarthritis sufferers, including those who are active and want to stay active.
Related: Exploring Natural Joint Supplements for Osteoarthritis Relief
Training Recovery Aid
Are you an athlete or just someone who exercises hard and often? Joint supplements are a valuable tool for training recovery, helping to:
- Reduce muscle & joint soreness. Ingredients like omega-3s and MSM diminish inflammation9, promoting post-workout recovery in the process.
- Nurture cartilage. Constant impact of physical activity makes it crucial to take care of your cartilage. Supplements enhance your body’s ability to protect and mend this vital tissue.
- Optimize flexibility. By supporting your overall joint health, these supplements can improve your range of movement & strength, reducing injury risk.
Daily Comfort & Movement Support
Even for those who do not suffer from a certain condition or engage in intense exercise, joint supplements can still offer you benefits, including:
- Improve daily comfort. By enhancing your overall joint function, these nutraceuticals can make your daily tasks more manageable and enjoyable.
- Increase mobility. Less stiffness and improved range of motion enable a more active and independent lifestyle.
- Preventive joint care. Regular use of these products supports long-range joint health, potentially reducing the risk of problems later in life.

How to Use?
Using joint supplements the right way ensures maximum effectiveness and safety. Here is an easy-to-digest guide on making them a part of your routine.
- Dosage
Always stick to what the product label tells you, unless told otherwise by your physician or dietitian/nutritionist.
If not sure, start with the lowest dosage. For example, if a product’s recommended dosage is 2 capsules per serving, but you want to start low, you may want to take only 1 capsule. Note, however, that this may result in weaker effects, or no effects at all.
- Timing
Taking a supplement every day at the same time may lead to stable levels in the body, contributing to its efficacy. Most joint supplements should be taken with meals for optimal absorption and utilization.
- Duration of Use
Joint problems do not tend to appear overnight, and the same is with experiencing joint supplement benefits. Just as inflammation was causing damage behind the scenes for months or years before symptoms started to show up, it may take 4-8 weeks for a joint supplement to undo some of the damage and diminish deeply rooted symptoms.
Joint Supplement Ingredients
Knowing which ingredients work and which to avoid helps you to find a supplement that is effective, safe, and best suited for your goals.
Joint supplements can be single ingredients – think omega-3, glucosamine, Boswellia – or they can be a combination of those ingredients.
The most effective joint supplements offer multiple evidenced ingredients for synergistic and comprehensive joint support, often time outmatching the effectiveness of a standalone formula (e.g. one that only contains glucosamine and nothing else).
Here I will break down some of the most research-backed ingredients to look for in a joint supplement, as well as those to consider avoiding.
Joint Supplement Ingredients to Look For
- Algae Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Glucosamine
- Chondroitin
- MSM
- Boswellia Serrata
- Curcumin
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Type-II Collagen
Let us break each one down in more detail.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are anti-inflammatory fats found naturally in fish as well as plant sources like flaxseeds. They can help to reduce symptoms of arthritis and muscle aches, along with promoting a healthy immune system. 10 11
The best omega-3s I recommend are sourced from algae which is where fish get their omega-3s from. A quality algae-based omega-3 supplement is generally cleaner and more eco-sustainable. While there are some excellent fish oil supplements on the market, many of them contain at least trace amounts of heavy metals and other toxins, which is why I opt for a algae-based omega-3 supplement instead.
Glucosamine
Glucosamine is a natural compound found in our cartilage, a tissue which cushions your bones and joints, reducing friction between them and providing shock absorption throughout your body.
Glucosamine levels in our body go down as we age.
While studies are still inconclusive, supplementation is shown to benefit some people in the context of osteaoarthritis relief, inflammation & pain reduction, and stronger cartilage and connective tissues.12
Chondroitin
Chondroitin is another compound found in our cartilage. Since chondroitin is known to help retain water in joints, reduce pain and inflammation, and slow down the breakdown of cartilage, supplement manufacturers commonly pair it with glucosamine for synergistic benefits on your joints.
MSM
MSM, or Methylsulfonylmethane, is an organic sulfur compound that is naturally occurring in humans, plants, and animals, as well as synthesized in a lab.
MSM benefits your joints in the following ways13 14:
- Reduces pain by inhibiting inflammatory molecules in the body such as Nf-kB.
- Increases collagen production for more flexible joints.
- Enhances glutathione production, which is a master antioxidant that protects long-term joint health.
Boswellia Serrata
Boswellia Serrata, also known as Indian Frankincense, is known to reduce inflammatory markers in the body15, leading to:
- Reduced joint pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis sufferers
- Improved flexibility and mobility
- Slower degradation of cartilage

Curcumin
Curcumin is a component of the Indian spice turmeric, making up 3% of turmeric but being responsible for its most powerful health benefits. Curcumin is known for promoting long-range joint function.16 Its potent anti-inflammatory properties are shown to rival those of some anti-inflammatory drugs.17
Curcumin also works through your body’s antioxidant pathways to reduce joint pain and swelling, improve mobility and comfort, and slow down the degradation of connective tissues to preserve joint health over time.
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic Acid is a molecule naturally found in high amounts in our eyes, skin, and joint tissues. It promotes cartilage health and nourishes the synovial fluid in joints18, which contributes to:
- Joint tissue water retention for improved shock absorption
- Improved joint lubrication
- Osteoarthritis relief
- Reduced breakdown of connective tissues
Type-II Collagen
Type-II collagen is a protein found in our joint cartilage. Supplementation of type-II collagen has been shown to reduce symptoms of autoimmunity, resulting in less joint inflammation in the context of osteoarthritis and rheumatism.19
Joint Supplement Ingredients to Avoid
The following ingredients are best avoided for two reasons: either because they are not proven to work or have the potential to do more harm than good.
Generic Fish Oil
Finding a high-quality fish oil brand can be difficult due to sheer number of options on the market. Even high-quality fish oils contain at least trace amounts of toxins like mercury.20 There is also the issue of overfishing and potential environmental harm due to fish oil supplements.
However, another problem with fish oil is the risk of oxidation due to temperature, air, and light exposure, turning fish oil rancid. Fish oil is especially susceptible to oxidation which leads to not only bad smell and taste, but also reduced nutritional value and higher levels of damaging free radicals in the fish oil, which could make it harmful.21
Processing and storing fish oil can be tricky with generic brands, especially the ones that cut corners during manufacturing. This is why I opt for a premium algae-sourced omega-3 supplement instead. It is cleaner, more eco-friendly, and with a low risk of oxidation since it is produced in a controlled environment.
High-Dose Vitamin E
Although rare, some omega-3 supplements might also come with a hefty dose of vitamin E which is fat soluble and builds up in the body. Amounts higher than 150mg per day can lead to side effects when taken long-term.22
Epimedium (Icariin)
This is a type of weed that is known to have some benefits on male sexual health. However, its effects on joint health are not well-studied in humans.
The idea behind some joint supplements that contain Epimedium is that Icariin (its active compound) is anti-inflammatory and can promote cartilage health. However, the evidence is not strong at this point, which makes this ingredient a potential waste of capsule space that could be used for more researched compounds.
Low-budget turmeric powder
There are a few reasons why cheap turmeric powder is not a good idea when it comes to joint health.
First up, turmeric only contains 2-5% of the key anti-inflammatory compound curcumin, which might make it far less effective than concentrated curcumin supplements.
Secondly, the absorption efficacy of curcumin in turmeric powder is low by itself, until you add black pepper extract, which significantly increases curcumin’s bioavailability. Curcumin supplements tend to have black pepper extract or a specific source of fat (which also increases absorption) attached to it, which is not the case with plain turmeric powders.
Lastly, and most importantly, is that low-budget turmeric powder can be contaminated with toxins such as led due to poor manufacturing practices and the turmeric plant being grown on a contaminated soil. Purity and quality are extremely important when it comes to turmeric, which is why I always recommend choosing a premium curcumin supplement.

Natural Joint Supplements vs Synthetic Compounds
Two options for supporting joint health include natural joint supplements and pharmaceutical drugs. Each has its role, but they are ultimately very different from each other. Choosing the right one for you depends on your current health status, wellness goals, and lifestyle, among other factors.
Natural Joint Supplements
Of course, these are extracted from natural sources, such as plants, minerals, or animals. Sometimes, natural joint supplements can also include those that have been synthesized in a controlled lab environment to mimic nature’s conditions and development.
Natural joint supplements include glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, Boswellia Serrata, and other compounds we mentioned earlier in this guide, all of which support your joint health and function through natural means.
Pros of natural joint supplements include:
- Long-term joint support and mild benefits in combating joint pain, inflammation, and cartilage breakdown.
- Low risk of side effects.
- Preventive potential at reducing the risk of joint-related conditions and their progression.
Cons of natural joint supplements include:
- Varied effectiveness and efficacy.
- It might take longer to notice benefits.
- Quality and purity concerns due to less strict regulations when compared to pharmaceutical drugs.
The bottom line on natural joint supplements: they offer a gentler, more holistic, long-term approach to improving joint health and function. There are many ineffective joint supplements on the market, however. Choosing a reputable brand with high-quality, science-backed ingredients is paramount if you want to see concrete results.
Synthetic Compounds
Synthetic medications, as the name suggests, are pharmaceutical drugs that are either prescribed by your physician or obtained over-the-counter (OTC). They are designed to relieve joint pain, manage inflammation, or slow disease progression. These medications include NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) and corticosteroids.23
Pros of pharmaceutical drugs include:
- Rapid-acting, more potent effects.
- Strict testing & regulations for safety, effectiveness, and consistency in quality & dosage.
- Evidence-backed for effectiveness.
Cons of pharmaceutical drugs include:
- A higher risk of major side effects.24
- Typically deals with symptoms and not underlying causes of joint health problems.
- Potential interactions with other medications.
The bottom line on pharmaceutical drugs for joint health: they are a more potent option for people with serious and chronic joint health conditions. However, they may not be a healthy long-term solution. Advisement with your MD is the best way to see which route to take.
Do Joint Supplements Have Side Effects?
Joint supplements are commonly used by millions of people worldwide to safely enhance their joint health and function.
However, like any dietary supplement (and even food for that matter), they have a potential to cause side effects. How high the risk and severity are depends on the joint supplement in question, its dosage, brand transparency, research, and your lifestyle, diet, and any medications you may be taking.
Most joint supplements on the market today have a relatively low risk of side effects. With that said, some might have mild to moderate negative reactions, such as:
- Nausea and other gastrointestinal side effects. Glucosamine and chondroitin are generally seen as safe, but they may lead to these side effects in rare cases.
- Allergic reactions. If you have shellfish allergy, check that the supplement does not have glucosamine sourced from shellfish.
- Blood sugar impact. There are some suggestions that glucosamine may affect blood sugar, more so in people with diabetes, but there is little research to confirm this, and many people find it safe to use.
- Blood thinning. This effect can happen with omega-3s and turmeric.25 26 If you take a blood thinning medication, avoid these supplements before checking with your physician.
How to Minimize The Risk of Joint Supplement Side Effects
The good news is that by following common safety guidelines you can slash down the already low risk of side effects from joint supplements to a minimum:
- Start with the lowest dosage. For example, if a supplement recommends 2 capsules per day on a label, start with just 1 to asses your tolerance.
- Opt for high-quality brands. Cheap supplements often come with a hidden cost due to a lack of third-party testing, and can be ineffective, or contain unproven ingredients that may lead to side effects.
- Inform yourself. If you are new to joint supplements, it is best to speak with your doctor before buying one, just to make sure you are fine to take it.
Recommended Dosages
Taking a correct dosage of a joint supplement maximizes its effectiveness while minimizing the risk of side effects. Here are the recommended dosages for common joint supplements based on the available evidence:
- Glucosamine: 1500 mg, taken at once or split into three doses per day
- Chondroitin: 800-1200 mg per day
- MSM: 3000 mg per day
- Omega-3s: 1000 mg of combined EPA+DHA per day
- Curcumin: 500mg per day, in combination with piperine (black pepper extract) for optimal absorption
- Boswellia Serrata: 100-250 mg of AprèsFLEXTM per day, or 2400 mg per day for generic Boswellia supplements
- Hyaluronic Acid: 120mg per day

User Reviews
Reading user reviews can help you pick the right joint supplement. They give you real-world experiences that can complement scientific research and professional opinions.
Here are some guidelines for reading joint supplement user reviews online:
- Look for verified customers. People who actually used the product.
- Look for patterns. Consistent positive feedback on a joint supplement is a good sign. On the other hand, if you see many comments about side effects or lack of results, it is a red flag.
- Seek out relevant reviews. Find reviews from individuals who have similar joint issues as you.
User reviews should complement the scientific research of supplement’s ingredients, not replace it. In other words, testimonials should not be your sole deciding factor. The placebo effect, user bias, and subjective experience can all significantly influence a review.
As impartial as we aim to be, this even applies to our own reviews at SiR. Doing your own research of the supplement’s ingredients and ultimately testing the product for yourself is the only true way to know its effects on you.
A Joint Supplement Buying Guide With Practical Examples
Navigating the sea of joint supplements can be daunting. This section’s main goal is to simplify this process, giving you practical advice and examples to help you find the right joint supplement for you.
To make this as easy as possible, I have broken this supplement buying guide down into three steps:
- Define your needs and goals
- Research joint supplement ingredients
- Build your joint supplement stack or buy a pre-made joint supplement
Related: Tailoring Joint Supplement Regimens for Advanced Osteoarthritis Management
Let us explain each step in more detail.
Define Your Needs and Goals
To narrow down your choice, first determine your goals and struggles when it comes to joint health.
Are you an athlete looking to recover faster and improve longevity? You might want to consider an omega-3 and MSM supplement to relieve inflammation and speed up healing time.
- Are you a person who started experiencing joint pain and stiffness as you got older and are looking for osteaorthritis relief? Then perhaps a combination of glucosamine, Boswellia Serrata, and chondroitin is a good starting point for you.
Are you a healthy person who has no joint problems and only wants to maintain joint health and reduce the risk of joint problems developing later in life? You may want to combine omega-3s with collagen and hyaluronic acid to improve joint lubrication, block inflammation, and support long-range joint function.
Research Joint Supplement Ingredients
I have only mentioned a few compounds, but the truth is, the most comprehensive joint supplements will contain at least 6 ingredients, because their benefits are often synergistic. The very best joint supplements should contain most of the following, if not all these ingredients:
- Glucosamine
- Chondroitin
- MSM
- Boswellia Serrata
- Curcumin
Other evidenced joint health compounds include hyaluronic acid, collagen, and omega-3s. Although, you will generally need to buy an omega-3 supplement separately from a joint supplement. This is because of capsule space limits—omega-3s are taken in high dosages, which leaves no space for other compounds to be included.
Build Your Supplement Stack or Buy a Pre-Made Joint Supplement
When choosing a joint supplement, there are two routes you can take:
- Combine some of the aforementioned ingredients together to make your own joint supplement stack. For example, you can buy a glucosamine supplement and an omega-3 supplement, and you start taking them together.
- Buy a pre-made professional joint supplement which already contains multiple science-backed ingredients. This is easier, saves you time and money, and is what I recommend for most people.
The majority of high-quality joint supplements on the market contain more than only one ingredient, simply because multi-ingredient formulas target joint health from different angles, which results in more significant benefits, both in terms of pain reduction and long-term joint support.
Comparative Analysis of Different Joint Supplements
The joint supplement market is as varied as the needs it serves. Here is a comparative joint supplement analysis and the brands I recommend. Note: I am not affiliated with, nor sponsored by any of the brands mentioned in this guide.
In other, more specific guides, some of the topics we will be looking at when comparing and analyzing different joint supplements include:
- Comparative Analysis of Glucosamine and Chondroitin Supplements
- Comparing Natural and Synthetic Joint Supplements
- Fish Oil Versus Plant-Based Joint Supplements
- Comparing Effectiveness of Various Joint Supplements
- Side Effects Comparison of Popular Joint Supplements
- Joint Supplements Comparison for Arthritis Relief
- Analyzing Cost-Benefit of Different Joint Supplements
- Benefits Comparison of Joint Supplements for Athletes
- Comparing Joint Supplements for Seniors
- Analysis of Joint Supplements for Dogs vs Humans
For now, however, let us compare commonly used joint supplements and brands today.
Glucosamine
The three reputable glucosamine brands I recommend include:
- NOW Foods Glucosamine: 2000 mg of glucosamine HCl per serving (contains shellfish), recommended value for money option, available on iHerb and Amazon.
- Doctor’s Best Vegan Glucosamine with GreenGrown® Glucosamine: 1500 mg of glucosamine HCl per serving, recommended vegan option and for those with shellfish allergies, available on iHerb, Amazon, and The Vitamin Shoppe.
- Thorne Glucosamine & Chondroitin: 500 mg of glucosamine sulfate with added 250 mg of chondroitin sulfate (bovine) per serving, the most premium option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
Chondroitin
The three reputable chondroitin brands I recommend include:
- BulkSupplements Chondroitin Sulfate: 750 mg of chondroitin sulfate per serving, the best value for money option, pure chondroitin powder with no additives or other ingredients, available on Amazon and Bulk Supplements’ website.
- NOW Foods Chondroitin Sulfate (bovine cartilage): 1200 mg of chondroitin sulfate per serving, the best high-dosed option, available on iHerb and Amazon.
- Thorne Glucosamine & Chondroitin: 250 mg of chondroitin sulfate with added 500 mg of glucosamine sulfate per serving, the most premium option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
MSM
With MSM there are many good brands to choose from, including LifeExtension, BulkSupplements, Lake Avenue Nutrition, and Jarrow Formulas, but the two that I recommend are:
- Doctor’s Best MSM with OptiMSM: 3000 mg per serving, recommended high-quality MSM powder and the best value for money overall, available on iHerb and Amazon.
- NOW Foods MSM: 1000 mg per serving, recommended capsule-version MSM, available on iHerb and Amazon.
Curcumin
Curcumin quality can vary more drastically between brands than other joint supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin. Here is a comparative snapshot of curcumin supplements I recommend:
- Doctor’s Best High Absorption Curcumin: 1000 mg per serving, the best value for money option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
- Thorne’s Meriva Curcumin Phytosome: 1000 mg per serving, recommended premium option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
- NatureWise Organic Turmeric Curcumin: 500 mg of curcuminoids per serving, recommended budget option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
Boswellia Serrata
- BulkSupplements Boswellia Serrata: 1000 mg per serving (20:1 extract), the best value for money and overall option, available on Amazon and the official website.
- NOW Foods Boswellia: 500 mg per serving standardized to contain a minimum of 65% boswellic acids, recommended budget capsule option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
- Thorne Research Boswellia Casperome® Phytosome: 350 mg per serving, recommended premium option, available on Amazon and iHerb.
This comparative analysis is only an overview of the most commonly used joint supplements and recommended brands. There are other supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and hyaluronic acid, which I will be comparing and analyzing in other, more detailed guides—stay tuned.

Enhancing Joint Health Naturally
It is easy to forget that joint supplements are only that—a supplement to a lifestyle with healthy foundations.
- Eating ultra-processed foods every day, exercising only once every two months, sleeping 6 hours per day, and expecting to have a healthy body and joints from joint supplements is unrealistic.
With that said, following are three ways you can enhance your joint health naturally and improve the effectiveness of your joint supplement along the way.
- Diet and Nutrition: Adding foods that support joint health and removing ones that cause inflammation.
- Physical Activity: Specific exercises beneficial for joints.
- Lifestyle Changes: Sleep, weight management, sun exposure, stress management, and more.
Diet and Nutrition
Some foods increase inflammation in the body, while others lower it. Best foods to lower swelling, inflammation, and joint pain include:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids foods. highly anti-inflammatory. obtain them from sardines and other small fish, or flaxseeds if you are vegetarian.
- Vitamin D and calcium rich foods. these are often found in dairy and fortified foods. Vitamin D can also be obtained through sunlight exposure.
- Berries and other antioxidant-rich foods. These further contribute to a reduction in inflammation while assisting in protecting joint tissues from oxidative stress.27
- Spices like turmeric and ginger. These are anti-inflammatory in nature.
At the same time, consider reducing your intake of omega-6 fatty acids which can aggravate inflammatory conditions when they are much higher than omega-3s in the body. Some foods that contain omega-6s include:
- Chips and fried foods
- Margarine
- Vegetable oils like sunflower, corn, peanut, and soybean oil
- Fast foods
- Packaged white bread (opt for high-quality rye bread instead)
I also recommend avoiding alcohol which can be highly inflammatory on joints.
Physical Activity
If you suffer from joint pain or osteoarthritis, avoid doing hard exercises such as squats, weightlifting, or running on concrete or asphalt. Instead, weave the following exercises at least 3 times per week into your schedule:
- Swimming, cycling and brisk walking. These are all low-impact exercises that are light on your joints.
- Resistance band training. This is effective for strengthening muscles and stabilizators around your joints, which can reduce pain, without putting much strain on joints themselves.
- Stretching. In addition to helping with flexibility and range of motion, it relieves pain.
Lifestyle Changes
Three key lifestyle interventions you can make for enhancing the effectiveness of your joints supplements are:
- Maintain a healthy body weight to reduce pressure on your joints.
- Practice posture awareness to lighten the load on your bones and joints.
- Try cold-hot therapy or cold shower exposure 3x per week for swelling, pain, and inflammation reduction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best joint supplement?
There is no universal “best” joint supplement. MSM could be the best joint supplement for a person suffering from age-related joint pain and cartilage breakdown. However, for a young and healthy person looking to maintain and protect joint function in the long run, MSM might not be the best choice—in this case, a quality omega-3 supplement paired with glucosamine and chondroitin may offer more benefits. To find the best joint supplement for you, you should research its ingredients, dosages, evidence behind ingredients, and brand reputation, to name just a few.
Do joint supplements work?
Based on extensive research data and user experiences, it is clear joint supplements do work. It is important, however, to do proper research on joint supplements because there are many brands out there that skimp on ingredient choices, quality, and manufacturing processes, which results in a joint supplement that does not work—or worse, causes negative side effects.
Can joint supplements cause joint pain?
While these supplements can sometimes cause mild to moderate side effects in sensitive individuals, the chance of a joint supplement ironically causing joint pain is extremely slim and rarely heard of, especially if we are talking about high-quality, reputable companies.
What joint supplements actually work?
Joint supplements that are the most research-backed and consistently supported by users worldwide include glucosamine, chondroitin, MSM, Boswellia Serrata, omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, hyaluronic acid, and type-II collagen.
How to take joint supplements?
Simply follow the instructions on the label of the product you take. If you have a sensitive stomach, taking a supplement with food is advisable.
Are joint supplements safe for kidneys?
Commonly used joint supplements such as glucosamine, omega-3s, and MSM are generally considered to be very safe for kidneys, assuming a person is healthy and does not take medications. If you have a kidney condition or are taking medications, make sure to speak with your doctor before taking a supplement.
Are joint vitamins worth it?
Joint vitamins can include vitamins D3, K2, B-complex vitamins, and vitamin E. These are worth it if you are not getting enough through foods (and sunshine exposure in the case of vitamin D3). However, vitamins alone are not the best option for resolving joint pain and stiffness. Other science-backed ingredients such as MSM, Boswellia Serrata, and curcumin are helpful for improving joint health and function.
Do joint supplements help with tendonitis?
Anti-inflammatory supplements such as omega-3s, turmeric, and MSM, are shown to help relieve tendonitis and its related symptoms.
Wrapping Up
Improving your joint health is more than just taking a pill (or powder!). The approach should be multi-faceted and include your diet, physical activity, sleep routine, and lifestyle. This is when adding a quality joint supplement will make the most difference in you how move and feel.
To recap, here are what I consider the most important factors to go over when selecting a joint supplement:
- Define your needs and goals. An elderly person looking to mitigate age-accumulated joint damage and pain might not need the same supplement as an athlete looking to improve their recovery and healing from hard exercise, or a healthy young individual who only wants to protect their joint function long-term.
- Do not skimp on quality. There are indeed some effective and inexpensive joint supplements out there, but generally speaking, the most effective premium options from reputable brands will require you to fork out more.
- Give it time. Just because there are no benefits after 3 days of taking a joint supplement, does not mean it is ineffective. Joint supplements take weeks, sometimes months, to show their full potential, because deep joint inflammation and damage take time to heal.
If you struggle with a serious joint condition and are on medications, consult with your physician before taking supplements. While I wrote this guide to share evidenced information about joint supplements with you, it is by no means medical advice.
With that said, thank you for reading. If any questions were not answered in this article, do not hesitate to contact me. May your joint health shine bright, now and in the years to come!
Resources and Further Reading
Here are some useful materials to have a look at if you are interested in learning more about joint supplements and joint health.
Books
- Healing Arthritis by Susan Blum, M.D.
- Healthy Joints for Life by Richard Diana, M.D.
Scientific Journals and Studies
- PubMed Central: Here you can browse a vast database of scientific studies on the safety and efficacy of joint supplements.
- Arthritis Foundation: Follow latest findings in the field of arthritis research and treatment.
References & Literature
- Mathieu S, Soubrier M, Peirs C, Monfoulet LE, Boirie Y, Tournadre A. A Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Nutritional Supplementation on Osteoarthritis Symptoms. Nutrients. 2022 Apr 12;14(8):1607. doi: 10.3390/nu14081607. PMID: 35458170; PMCID: PMC9025331. ↩︎
- Demoruelle MK, Deane KD, Holers VM. When and where does inflammation begin in rheumatoid arthritis? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014 Jan;26(1):64-71. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000017. PMID: 24247116; PMCID: PMC4033623. ↩︎
- Henrotin Y, Mobasheri A. Natural Products for Promoting Joint Health and Managing Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 Sep 19;20(11):72. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0782-9. PMID: 30232562. ↩︎
- Blaznik U, Krušič S, Hribar M, Kušar A, Žmitek K, Pravst I. Use of Food Additive Titanium Dioxide (E171) before the Introduction of Regulatory Restrictions Due to Concern for Genotoxicity. Foods. 2021 Aug 17;10(8):1910. doi: 10.3390/foods10081910. PMID: 34441686; PMCID: PMC8391306. ↩︎
- Zhu X, Sang L, Wu D, Rong J, Jiang L. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 Jul 6;13(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0871-5. PMID: 29980200; PMCID: PMC6035477. ↩︎
- Cuaz-Pérolin C, Billiet L, Baugé E, Copin C, Scott-Algara D, Genze F, Büchele B, Syrovets T, Simmet T, Rouis M. Antiinflammatory and antiatherogenic effects of the NF-kappaB inhibitor acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid in LPS-challenged ApoE-/- mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008 Feb;28(2):272-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.155606. Epub 2007 Nov 21. PMID: 18032778. ↩︎
- Kang W. Global and Dimensions of Mental Health in Arthritis Patients. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;11(2):195. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11020195. PMID: 36673563; PMCID: PMC9859167. ↩︎
- Butawan M, Benjamin RL, Bloomer RJ. Methylsulfonylmethane: Applications and Safety of a Novel Dietary Supplement. Nutrients. 2017 Mar 16;9(3):290. doi: 10.3390/nu9030290. PMID: 28300758; PMCID: PMC5372953. ↩︎
- Kostoglou-Athanassiou I, Athanassiou L, Athanassiou P. The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2020 Jun 30;31(2):190-194. doi: 10.31138/mjr.31.2.190. PMID: 32676556; PMCID: PMC7362115. ↩︎
- Schwalfenberg G. Omega-3 fatty acids: their beneficial role in cardiovascular health. Can Fam Physician. 2006 Jun;52(6):734-40. Erratum in: Can Fam Physician. 2006 Aug;52:952. PMID: 16812965; PMCID: PMC1780156. ↩︎
- Deng W, Yi Z, Yin E, Lu R, You H, Yuan X. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation for patients with osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 May 24;18(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03855-w. PMID: 37226250; PMCID: PMC10210278. ↩︎
- Vo NX, Le NNH, Chu TDP, Pham HL, Dinh KXA, Che UTT, Ngo TTT, Bui TT. Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Pharmacy (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;11(4):117. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy11040117. PMID: 37489348; PMCID: PMC10366893. ↩︎
- Kim LS, Axelrod LJ, Howard P, Buratovich N, Waters RF. Efficacy of methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) in osteoarthritis pain of the knee: a pilot clinical trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006 Mar;14(3):286-94. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2005.10.003. Epub 2005 Nov 23. PMID: 16309928. ↩︎
- Nakhostin-Roohi B, Barmaki S, Khoshkhahesh F, Bohlooli S. Effect of chronic supplementation with methylsulfonylmethane on oxidative stress following acute exercise in untrained healthy men. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;63(10):1290-4. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01314.x. Epub 2011 Aug 1. PMID: 21899544. ↩︎
- Siddiqui MZ. Boswellia serrata, a potential antiinflammatory agent: an overview. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2011 May;73(3):255-61. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.93507. PMID: 22457547; PMCID: PMC3309643. ↩︎
- Shep D, Khanwelkar C, Gade P, Karad S. Safety and efficacy of curcumin versus diclofenac in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized open-label parallel-arm study. Trials. 2019 Apr 11;20(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3327-2. PMID: 30975196; PMCID: PMC6460672. ↩︎
- Hewlings SJ, Kalman DS. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods. 2017 Oct 22;6(10):92. doi: 10.3390/foods6100092. PMID: 29065496; PMCID: PMC5664031. ↩︎
- Oe M, Tashiro T, Yoshida H, Nishiyama H, Masuda Y, Maruyama K, Koikeda T, Maruya R, Fukui N. Oral hyaluronan relieves knee pain: a review. Nutr J. 2016 Jan 27;15:11. doi: 10.1186/s12937-016-0128-2. PMID: 26818459; PMCID: PMC4729158. ↩︎
- Bakilan F, Armagan O, Ozgen M, Tascioglu F, Bolluk O, Alatas O. Effects of Native Type II Collagen Treatment on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eurasian J Med. 2016 Jun;48(2):95-101. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2015.15030. PMID: 27551171; PMCID: PMC4970562. ↩︎
- Gribble MO, Karimi R, Feingold BJ, Nyland JF, O’Hara TM, Gladyshev MI, Chen CY. Mercury, selenium and fish oils in marine food webs and implications for human health. J Mar Biol Assoc U K. 2016 Feb;96(1):43-59. doi: 10.1017/S0025315415001356. Epub 2015 Sep 8. PMID: 26834292; PMCID: PMC4720108. ↩︎
- Cameron-Smith D, Albert BB, Cutfield WS. Fishing for answers: is oxidation of fish oil supplements a problem? J Nutr Sci. 2015 Nov 23;4:e36. doi: 10.1017/jns.2015.26. PMID: 26688722; PMCID: PMC4681158. ↩︎
- Owen KN, Dewald O. Vitamin E Toxicity. [Updated 2023 Feb 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan. ↩︎
- Crofford LJ. Use of NSAIDs in treating patients with arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S2. doi: 10.1186/ar4174. Epub 2013 Jul 24. PMID: 24267197; PMCID: PMC3891482. ↩︎
- Vonkeman HE, van de Laar MA. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: adverse effects and their prevention. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Feb;39(4):294-312. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Sep 27. PMID: 18823646. ↩︎
- Wang CZ, Moss J, Yuan CS. Commonly Used Dietary Supplements on Coagulation Function during Surgery. Medicines (Basel). 2015 Sep;2(3):157-185. doi: 10.3390/medicines2030157. Epub 2015 Jul 27. PMID: 26949700; PMCID: PMC4777343. ↩︎
- Kim DC, Ku SK, Bae JS. Anticoagulant activities of curcumin and its derivative. BMB Rep. 2012 Apr;45(4):221-6. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2012.45.4.221. PMID: 22531131. ↩︎
- Currie TL, Engler MM, Olsen CH, Krauthamer V, Scott JM, Deuster PA, Flagg TP. The Effects of Berry Extracts on Oxidative Stress in Cultured Cardiomyocytes and Microglial Cells: A Potential Cardioprotective and Neuroprotective Mechanis. Molecules. 2022 Apr 27;27(9):2789. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092789. PMID: 35566133; PMCID: PMC9100120. ↩︎
Leave a Reply