“Golden spice” turmeric fights brain aging and inflammation, helping maintain sharp mental function.

Turmeric is an important medicinal herb in India’s Ayurvedic health system. Its potent anti-inflammatory qualities support brain health through:
- Neuroprotection. Turmeric has shown antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity that defends brain cells from damage, such as that seen in Alzheimer’s.
Overview
Turmeric (Curcuma longa, related to ginger) is a popular spice that is perhaps best known for imparting flavor to curry. In addition to its widespread use in global cuisine, turmeric is also widely used in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurvedic health practices. It’s main active ingredient is curcumin, which also gives turmeric its distinct yellow color.
Turmeric is most strongly associated with India, where about 78% of the world’s supply is grown. As a major spice in the region’s cuisine, turmeric is consumed in large amounts: about 2.5 g per day from foods alone.
Today, turmeric is highly regarded as a nootropic used to fight neurodegeneration. Its potent anti-inflammatory properties can also help with other issues, including autoimmunity and arthritis.
How Turmeric Might Help the Brain
Curcumin has 3 main activities that support brain health:
Reducing oxidative stress
As the body’s most energetic organ, the brain is exposed to high levels of oxidative stress that can play a role in a wide range of neurological disorders. As a potent antioxidant, curcumin can help fight oxidative stress.3
Reducing inflammation
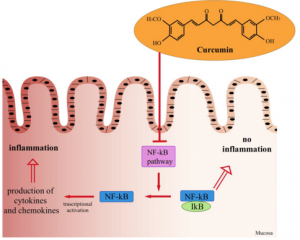
Curcumin is also known as a potent anti-inflammatory compound.4 Brain inflammation is a contributing cause to various degenerative brain problems.
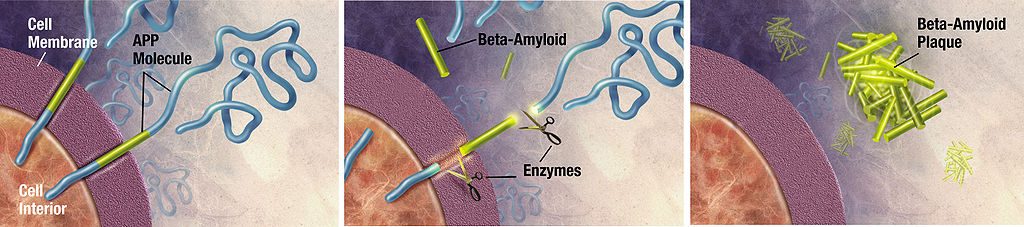
Combating brain plaques
Amyloid plaques are irregular clusters of proteins that interfere with normal brain activities and are a major contributing factor to Alzheimer’s. Curcumin helps diminish amyloid plaques from developing in the brain by crossing the blood-brain barrier and binding to them.5
While these are the 3 main bio-activities of turmeric, it is worth noting that early animal studies suggest curcumin may also:
- Boost the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine6
- Activate the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) that acts as a “brain fertilizer” for new neurons7
- Help block enzymes that degrade the memory neurotransmitter acetylcholine8
Turmeric Potential Nootropic Benefits & Uses
All in all, turmeric’s main, research-backed benefit is neuroprotection. As such, turmeric is more of an anti-aging nutrient than a cognitive performance booster. Its curcuminoids help protect brain cells from inflammation and oxidative stress, most notably resulting in improved defense against Alzheimer’s and other degenerative brain conditions.9
Clinical and animal research alike suggest that turmeric may help defend the brain against the ravages of aging. Its brain-protective qualities can be readily seen in India, which incorporates turmeric into its cuisine and enjoys some of the best cognitive health in the world. Indeed, one study reported that Indian citizens between the ages of 70-79 have a lower rate of Alzheimer’s than American citizens in the same age group by more than 4 times.10

Always read the label. Some manufacturers will advertise a turmeric product as “organic turmeric standardized to 95% curcuminoids.” But then when you look at the supplement facts, you might find something like this:
- Organic turmeric root, 400 mg
- Turmeric standardized to 95% curcuminoids, 50 mg
This means most of the supplement is simple root powder, and a much smaller amount of the potent, standardized turmeric.
Research
Animal Research
There’s a good deal of animal research on curcumin’s brain health potential, most of which are models focusing on the onset and progression of various brain-degenerative conditions:
- Curcumin was found to protect against amyloid plaques in rat brains, thus helping fight Alzheimer’s. Researchers concluded that “curcumin may find clinical applications for AD prevention.”11
- Low- and high-dose curcumin were found to reduce brain oxidation and inflammation in mice. Low-dose also reduced beta-amyloid and brain plaque burden by 43-50%. Researchers concluded curcumin “shows promise for the prevention of Alzheimer’s.”12
- Researchers reported “curcuminoids can restore susceptibility for plastic changes” in rat brain cells with amyloid-induced injury. This “plasticity” is critical for learning, memory and brain health.13
- Pretreatment with curcumin to rat brain cells with neurotoxic beta-amyloid appeared to have neuroprotective effects. Researchers reported that curcumin “significantly reversed the effect of [amyloid] by decreasing oxidative stress and DNA damage.”14
- Curcumin treatment prior to and during homocysteine-induced brain toxicity in rats was found to reduce markers of oxidative stress, leading researchers to suggest it “improved learning and memory deficits by protecting the nervous system” against toxicity.15
These investigations represent only a sampling of animal research on turmeric’s curcuminoids and their potential for supporting brain health.
Human Research
Clinical studies confirm the findings of animal research, suggesting that curcumin is a potent anti-inflammatory that helps fight age-related cognitive decline.
Curcumin in curry may boost cognitive performance in older adults
In this controlled survey, 1,010 Asians between the ages of 60 and 93 reported on their curry consumption and were given Mini-Mental State Examinations, which measure cognitive performance across functions, including attention span, language, memory, calculation, and awareness. Researchers found that study subjects who ate curry more often had better scores on the tests than those who ate rarely or never ate it.
- The researchers reported “tentative evidence of better cognitive performance from curry consumption.“16
Curcumin as Longvida® (400 mg) may help attention, memory, & mood in older adults
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 60 adults aged 60-85 years were given either 400 mg of Longvida®, an enhanced-bioavailability form of curcumin, or a placebo daily for 4 weeks. Study subjects were evaluated for cognition 1 hour and 3 hours after acute doses, and then again at the end of the entire 4-week study. Curcumin significantly improved cognitive performance on several tasks measuring sustained attention and working memory when compared with placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “curcumin significantly improved performance on sustained attention and working memory tasks.“17
Curcumin C3 Complex® (2, 4 g) may not significantly help with Alzheimer’s
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 36 patients over the age of 49 years believed to have mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s were administered placebo or Curcumin C3 Complex® at dosages of 2 or 4 g daily for a span of 24 weeks. The mental exams did not demonstrate significant evidence of curcumin’s effect on cognitive performance in people with Alzheimer’s. Failure may have been due to poor bioavailability or differences in outlets for curcumin metabolism in humans compared to animals.
- The researchers concluded that they were “unable to demonstrate any clinical or biochemical evidence of [curcumin’s] efficacy against Alzheimer’s.” 18
Curcumin may help alleviate neurodegeneration
This literature review examined hundreds of research studies regarding the health effects of curcumin. In general, curcumin was found to be safe with no major side effects, have antioxidant activity, and block inflammatory mediators, such as as NFkappaB, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), lipooxygenase (LOX), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Significant preventive and/or curative effects were noted for various health complications, including neurodegeneration.
- The researchers concluded that “Turmeric… has shown surprisingly beneficial effects in experimental studies of acute and chronic diseases characterized by an exaggerated inflammatory reaction.”19
Nootropic Dosage
Turmeric dosage depends on the form.
- Plain turmeric, whether as a whole root or a dried-and-powdered supplement, is typically dosed at 1.5 g – 3 g daily for cognitive benefits.
- Turmeric standardized to contain 95% curcuminoids has higher amounts of the active ingredients and a smaller serving size: 400 – 600 mg, taken 2 or 3 times daily.
- Liquid extract of turmeric is typically dosed at 50 – 100 drops daily, mixed with a little water.
Available Form
- Whole turmeric root. Turmeric is widely available as a raw spice, but it is impossible to know exactly much curcumin is present.
- Plain turmeric root, dried and powdered. This form can be presented in capsules, tablets, and complexes, but like whole root, does not supply a specific level of curcuminoids. It is cheap and difficult to absorb.
- Standardized turmeric root powder. This form will supply a guaranteed level of curcuminoids, the main active ingredient in turmeric. Supplements are typically standardized to contain anywhere from 5% – 95% curcuminoids.
- Meriva™. This branded form uses patented technology to combine curcumin extract with phosphatidylcholine, which is advertised to increase absorption by 29 times.
- Longvida®: This patented form protects curcumin in the digestive tract so more can reach the bloodstream. It is said to achieve 65 times the bioavailability of regular curcumin.
- Curcumin C3 Complex®: This form supplies 95% curcuminoids in the following ratios: 70% – 80% curcumin; 15% – 25% demethoxycurcumin; 2.5% – 6.5% bisdemethoxycurcumin.
Supplements in Review Says
- Curcumin as Longvida® 1000 mg as a nootropic.
Curcumin is a solid option for fighting age-related cognitive decline. Clinical research indicates that curcumin is an excellent supplement for fighting age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s in particular.
Go with curcumin as Longvida® at 1000 mg. Absorption-enhanced formulas do a better job of ensuring that curcuminoids reach the brain. Longvida® is our choice because of its purported 65X increase in bioavailability.
Further Reading: MSM and Turmeric: Can You Combine Them?
Under “Curcumin is difficult to absorb by it’s self,” bio-availability is rated at 60%. I read elsewhere that it is more like 6%.
Just bring this up as the improvement might not seem significant enough to entice purchasing product with pepperine.
Curcumin performs like magic..