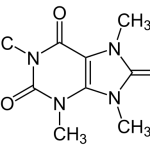
Early research suggests theacrine may potentially have nootropic effects akin to caffeine. Theacrine is a chemical compound found in the plants Cupuaçu and kudingcha. It may promote such potential nootropic benefits as: Anxiolytic activity. Theacrine has demonstrated stress reducing properties. Analgesic activity. Theacrine has been shown to reduce pain. … [Read more...]
Artichoke as a Nootropic
The high luteolin content in artichoke may facilitate memory formation, particularly when combined with other nootropics. Artichoke is an edible plant long believed to impart various health benefits. Its influence in brain health involves such nootropic effects as: Supporting memory. Bioactive ingredients in artichoke may play a critical role in the formation and … [Read more...]
Citicoline for Vision
Naturally-occurring citicoline may help combat the development of neurodegenerative eye disorders. Citicoline is an intermediate in the generation of phosphatidylcholine and is believed to help improve eye health by: Promoting neuroprotection. Citicoline has displayed a capacity to protect retinal cells by enhancing the synthesis of phospholipids. Triggering … [Read more...]
Apoaequorin as a Nootropic
Calcium-binding protein apoaequorin may improve memory, focus, and learning, according to contentious research. Apoaequorin is a calcium-binding protein drawn from jellyfish that has demonstrated some brain boosting activity. Its nootropic effects seem to stem from its penchant to: Promote neuroprotection. Apoaequorin has been shown to protect brain cells from death … [Read more...]
Vitamin E for Vision
Antioxidant vitamin E may reduce risk of cataracts and slow down macular degeneration, but high doses should be avoided. Vitamin E is a popular antioxidant compound. It may support healthy vision by: Delaying AMD. Vitamin E in combination with other antioxidants, carotenoids, and zinc may slow the progression of AMD. Protecting against cataracts. Higher dietary … [Read more...]