Brassaiopsis herb may increase testosterone levels by inhibiting aromatase but lacks research backing.

Brassaiopsis glomerulata is a plant whose leaves contain bioactive compounds with potential health benefits. It may have a notable impact on masculinity by:
- Blocking aromatase. Brassaiopsis has demonstrated an ability to inhibit aromatase from converting testosterone into estrogen, thereby potentially increasing T levels.
Overview
Brassaiopsis glomerulata, or brassaiopsis for short, is a small tree that hails from the lowland rainforests of Vietnam. Its broad leaves have long been rumored to carry ingredients with health boosting properties.
Traditional medical practices have utilized brassaiopsis leaves as a kind of tonic for symptoms associated with old age and joint complications, especially rheumatism and back pain.1 Reports from India have stated that liquid extracts of brassaiopsis may ameliorate minor digestive complaints, such as constipation. Traditional Chinese herbalists have also categorized it as a “tongcao,” a class of herbs that assist urination and lactation. Various other claims suggest the possibility of anti-inflammatory benefits.
Despite such claims, early scientific investigations into brassaiopsis have instead unearthed the presence of multiple aromatase blockers – compounds that prevent testosterone’s conversion into estrogen. There are noteworthy implications of this discovery in the realm of testosterone boosting, primarily estrogen control.
How Brassaiopsis Might Help With Testosterone
Inhibiting aromatase
Although brassaiopsis glomerulata might not directly boost testosterone production or release, it contains several bioactive ingredients that have been noted as aromatase inhibitors in petri dish experiments: 2 3 4
- N-benzoyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester, a weak aromatase inhibiting (AI) peptide
- (−)-dehydrololiolide, a terpenoid with strong AI activity
- Linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid with potent AI activity
Blocking aromatase reduces the conversion of testosterone into estrogen, which has potential to not only boost T levels but also reduce estrogen.5
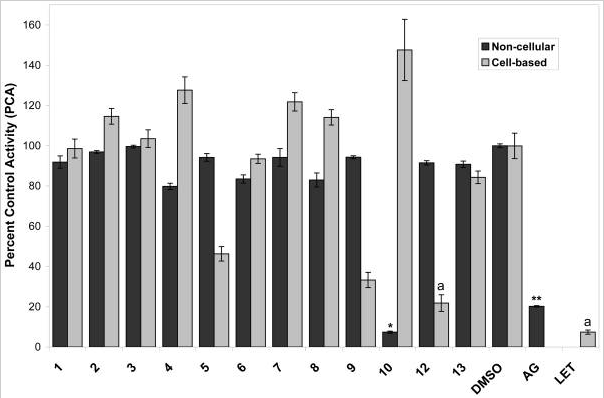
Brassaiopsis Benefits & Uses for Testosterone
By blocking aromatase, brassaiopsis may impart a handful of benefits, including:
- Increasing testosterone levels6
- Minimizing the negative consequences of estrogen increase, such as gynecomastia and male hypogonadism7
- Combating age-related testosterone decline8
Brassaiopsis is thus occasionally used as an ingredient in testosterone boosters. It has also been taken as a type of mild fat burner for its purported ability to promote lean muscle mass, albeit unsupported by evidence.
Research
Animal Research
The effect of brassaiopsis glomerulata on animals has not been investigated to any significant capacity.
Human Research
Clinical research on brassaiopsis glomerulata has yet to be conducted.
Dosage for Testosterone
- There are no presently available clinical studies using brassaiopsis in any capacity
- Typical supplements range from 200 – 500 mg of brassaiopsis, which is often combined with other testosterone-boosting herbs
Available Forms
- Leaf extract for dihydrololiolide
- Ground leaf as a powder or in a capsule
Supplements in Review Says
- Brassaiopsis at 200 mg for testosterone.
We do not recommend brassaiopsis for testosterone. There is currently no existing research or data illustrating the effects of brassaiopsis on living systems—human or animal.
Try brassaiopsis in low doses with other natural aromatase inhibitors. If insistent on using brassaiopsis, take it in conjunction with zinc, diindolylmethane (DIM), or another aromatase inhibitor in order to potentially heighten the testosterone-boosting effect.
Leave a Reply