*Fact-checked and upated by: Valentino Muza
Siliphos® may boast the highest bioavailability among liver supplements extracted from milk thistle.
 Siliphos is derived from the milk thistle plant for use as a liver and skin supplement. This review details its potential advantages over similar, generic supplements:
Siliphos is derived from the milk thistle plant for use as a liver and skin supplement. This review details its potential advantages over similar, generic supplements:
- Patented. A U.S. patent covers the production of Siliphos.
- Improve bioavailability. Siliphos is made using a proprietary technique that notably increases its absorption, and thus, efficacy in the body.
- Researched. Numerous clinical trials have suggested the liver health advantages of consuming Siliphos compared with similar supplements.
Overview
Siliphos is a patented and branded extract of the fruit or seed of the milk thistle plant (Silybum marianum), commonly referred to as silymarin. All rights to the production of the supplement belong to the Italian company Indena.
The primary bioactive constituent in Siliphos is a silybin, which is a flavonoid that has demonstrated a myriad of potential health benefits for the liver. Like the flavonoid curcumin, silybin is notorious for its poor absorption in humans, unless the ingredient is accompanied by some form of fat. Indena has developed a method for attaching silybin to phosphatidylcholine — effectively improving its absorption approximately fivefold. What’s more, silybin and phosphatidylcholine are believed to work synergistically in supporting liver health.
Siliphos has also demonstrated similar properties to retinoic acid, one of the essential components of vitamin A. As such, it may be able to reduce the expression of keratinocytes, and ultimately, promote healthy skin and limit skin aging.
How Siliphos Works
By combining silybin with phosphatidylcholine, Siliphos is highly absorbed by the human gastrointestinal system. Its high bioavailability enables it to impart two primary effects: 1
- Maintaining healthy liver function. Siliphos protects liver cells from oxidative stress by increasing levels of the antioxidants glutathione and superoxide dismutase (SOD), which neutralize free radicals. It also minimizes inflammation by interfering with the NF-κB inflammatory pathway.
- Mitigating insulin resistance. Through an unspecified mechanism, Siliphos can help insulin perform its job of reducing elevated glucose levels.

Siliphos Patents
Siliphos preparation
U.S. Patent 4764508 covers the preparation of Siliphos by combining the flavonoids of silymarin — silybin, silidianin, and silicristin — with phospholipids. This process enhances the absorption of the compound and allows it to facilitate the treatment of various acute and chronic liver diseases.
Siliphos Nutritional Supplement Uses
Liver Supplements
As a potent antioxidant, Siliphos is capable of fortifying the liver against multiple forms of oxidative stress, including toxins, infections, and cellular degeneration. Among its specific uses include managing cirrhosis, hepatitis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and drug-induced liver damage.
Skin Supplements
A secondary health benefit of Siliphos is shielding skin cells against damage caused by radiation, chemotherapy, ultraviolet (UV) rays, and free radicals. This protective effect may help improve skin and mitigate aging.
Siliphos Advantages
In comparison to other milk thistle extracts, Siliphos has several advantages, including the following:
- Clinical research: There are dozens of peer-reviewed clinical studies verifying the benefits of Siliphos as a liver supplement. No animal or human trials have reported ineffectiveness or serious adverse side effects after using the supplement.
- Patent: Siliphos has held a patent for its manufacturing process for more than 30 years.
- Bioavailability: No other milk thistle extract can match the high absorption of Siliphos, which may exceed other generic supplements by as much as 10 times.
Siliphos Research
Human Research
To follow, are two systematic reviews that include more than a hundred animal and human studies that have confirmed Siliphos’ ability to support liver health.
Siliphos (120, 240, 360 mg) may protect the liver
In this review of more than a dozen double-blinded, placebo-controlled studies, hundreds of patients with liver disorders took either a placebo or Siliphos (phytosome silybin) at doses of 120, 240, or 360 mg per day. The Siliphos groups consistently had reduced levels of liver enzymes ALT and AST, high concentrations of which indicate liver disease, compared with the placebo groups. The Siliphos groups also had lower levels of oxidative stress. There were no adverse side effects reported.
- The researchers concluded that “silybin-phosphatidylcholine complexed as a phytosome provides significant liver protection and enhanced bioavailability over conventional silymarin.”2
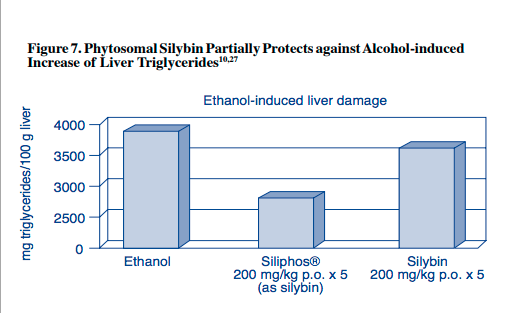
Siliphos (560, 600 mg) may help treat chronic liver disease
In this review, dozens of randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trials examined the effects of Siliphos containing silybin on patients with liver disease. The results indicated not only that the bioavailability of Siliphos was considerably higher than that of generic silymarin, but also that Siliphos taken at doses of 560 or 600 mg demonstrated markedly improved health benefits for the liver.
- The researchers concluded that “experimental studies have clearly demonstrated the antifibrotic, antioxidant, and metabolic effects of silybin … On the basis of literature data, silybin seems a promising drug for chronic liver disease.”3
Siliphos Dosage
- Clinical trials have used 120 – 600 mg daily serving sizes.
- Siliphos supplements typically come in 200 mg capsules containing 30% silybin, or 60 mg.
Siliphos vs Milk Thistle
Siliphos and classic milk thistle extracts both get their benefits from silymarin.
But there are some key differences between them, primarily:
- Bioavailability: Siliphos boasts up to 5 times, sometimes even more, higher absorption than generic milk thistle supplements. It specifically enhances the silybin molecule from the milk thistle plant for improved absorption, whereas standard milk thistle extracts contain silymarin complex, which includes silybin and other compounds, but without the phosphatidylcholine, which results in less efficient absorption.
- Cost and Availability:
- Siliphos is generally more expensive than your local vitamin store’s milk thistle extract due to its patented formulation and enhanced bioavailability.
- Clinical Evidence:
- Okay, when it comes to effectiveness, Siliphos seems to have the edge because of its superior absorption. However, if talking about the sheer breadth of clinical evidence, standard milk thistle extract reigns supreme, simply because it has been studied and used for a longer time.
Which one do we recommend? If you’re able to afford it, go with Siliphos. If you’re on a budget, give a standard milk thistle extract a try, as it should still benefit you to a degree. Ideally, you’ll want to give a test to both variations, as this would give you a complete picture as to what your body reacts better to.
Supplements in Review Recommendation
- Siliphos®, 600 mg.
Siliphos may support liver health. Overall, the consensus among health practitioners is that Siliphos is a reliable addendum for managing liver complications because of the supplement’s high content of flavonoids. The liver health benefits of taking Siliphos compared with generic milk thistle extracts have been corroborated in over 100 animal and clinical trials.
Take 600 mg of Siliphos standardized to 30% silybin per day. Siliphos has proved highly safe and effective for use as a liver supplement when taken at doses carrying at least 160 mg of its main bioactive ingredient silybin.
Leave a Reply