Controversial supplement shark cartilage may stifle cartilage deterioration.
- Reducing cartilage breakdown. Shark cartilage has been shown to promote anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and antioxidant effects.
- Improving cartilage growth. Shark cartilage may enhance the quality of cartilage.
Overview
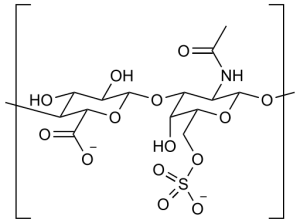
Self-explanatory in its name, shark cartilage is a preparation of cartilage from sharks that consists of 40% protein, 5 – 20% glycosaminoglycans (mostly chondroitin), 25% calcium salts, and various other trace elements, nutrients, and minerals.
The application of animal cartilage to health and medicine was reportedly first suggested by a Canadian scientist in the mid-20th century, although the relatively new supplement did not really make much headway until the 1970s when research uncovered its anti-inflammatory properties and potential to stimulate the immune system.
Since that time, the use of shark cartilage for a plethora of health reasons has seen an enormous surge in public enthusiasm. It has primarily been hailed as a remedy for diseases related to uncontrolled cellular growth, but it has also been used to relieve pain and manage inflammatory conditions, including macular degeneration, psoriasis, and arthritis.1

How Shark Cartilage Might Help With Joint Health
Promoting anti-inflammatory activity
Shark cartilage has been shown to inhibit several inflammatory pathways, specifically that of the cytokine interleukin-1 (IL-1), which would otherwise synthesize inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandin E2.2 This anti-inflammatory activity has further been associated with pain and edema relief in numerous animal studies by blocking nitric oxide.3 4
And yet shark cartilage has also been shown to support inflammatory activity by inducing the production of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ).5 In what instances the contradictory activity takes place has yet to be determined.
Reducing cartilage deterioration
Shark cartilage contains a molecule, TIMP-like protein, that helps keep cartilage intact by stopping proteolytic enzymes known as matrix metalloproteinases from breaking down the extracellular matrix.6 7
Inhibiting angiogenesis
The rapid growth of blood vessels, i.e., angiogenesis, has long been known to play a part in facilitating inflammation. Shark cartilage has been shown to stop vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from binding to endothelial cells and thus inhibiting the formation of blood cells and blood vessels.8 9
Inducing protein folding
A constituent of shark cartilage, trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) has demonstrated, in vitro, to promote the growth of high quality cartilage. It is believed to function by inducing vital protein folding, particularly tied to collagen, which is often hampered in shark tissue due to its naturally high levels of urea.10
Shark Cartilage Benefits & Uses for Joint Health
Though a considerable amount of research has investigated the benefits of shark cartilage, few reputable studies have focused on its immediate impact on healthy joints. Collectively, its bioactivity has been suggested to help reduce the symptoms of joint conditions such as osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, as well as everyday or sports injuries affecting the bone and joints.
A popular use of shark cartilage is to incorporate it into the production of the prominent joint supplement chondroitin sulfate, which also has great potential for joint health.11
Research
Animal Research
Many animal studies have shown the ability of shark cartilage to mitigate various symptoms connected to joint conditions but only in isolation.12 But little research has demonstrated the actual impact of shark cartilage on joint health.
Shark cartilage may improve conditions of rheumatoid arthritis in rats
In this controlled investigation, rats with rheumatoid arthritis were given 1 of 2 types of shark cartilage polysaccharides (SCP), type 1 and type 2, for 24 days. X-ray revealed that the shark cartilage groups had more normal joint alignment and a smoother joint surface compared to the control. Shark cartilage also resulted in reduce paw swelling and lower levels of the inflammatory markers IL-6 and IL-12.
- The researchers concluded that “SCP have excellent anti-RA activities and thus have great potential as a drug for treating RA diseases.”13
Shark cartilage may improve symptoms of allergic arthritis
In this investigation, polar shark cartilage was given to rabbits with allergic arthritis, and it was found to facilitate overall improvements in the affected joints.
- The researchers concluded that there was “improvement of the general state of the affected joints.”14
Human Research
Although many clinical studies on shark cartilage have been conducted, none of them have successfully examined its effect directly on joint health.
Dosage for Joint Health
- Clinical research has yet to identify ideal shark cartilage doses.
- Typical shark cartilage supplements range from daily servings of 750 – 4500 mg.
Available Forms
- Capsules or pills
- Powder
- Topical ointment
Supplements in Review Says
- Shark cartilage 750 – 4500 mg for joint health.
Shark cartilage may benefit joint health but research is early. In theory, shark cartilage seems to be suited to reducing symptoms of detrimental joint conditions, especially arthritis, but limited research and the few adverse side effects call for special care to be taken for its use.
Try a low 750 mg dose of shark cartilage. It may be best to start with a low daily 750 mg dose of shark cartilage until clinical research finds optimum dosage for joint health.
Leave a Reply