Brazilian infusion herb catuaba may improve mood and help protect brain cells from damage.

Catuaba is a bark extract taken from a number of trees and widely used in Brazil to promote health. It may specifically offer such potential benefits for brain health as:
- Protecting the brain. Catuaba has demonstrated a neuroprotective effect in animal brain cells.
- Supporting neurotransmitters. The herb was shown to boost the presence of dopamine.
Overview
Derived from a variety of different tree species, catuaba is a bark extract believed to wield sexual benefits and nootropic effects. Several of its known tree sources include:
- Trichilia catigua (most common)
- Erythroxylum vaccinifolium
- Anemopaegma
- Ilex
- Micropholis
- Phyllanthus
- Secondatia
- Tetragastris
Although somewhat obscure outside of South America, catuaba has long been used in Brazilian herbal medicine as an aphrodisiac to heighten sexual arousal and help improve male sexual performance. Recent research has also identified its potential capacity to stimulate the central nervous system (CNS) and promote brain health, led by its primary bioactive ingredients — catuabine A, B, and C.1

How Catuaba Might Help the Brain
Inhibiting serotonin and dopamine reuptake
By blocking the reuptake of serotonin and dopamine, catuaba may promote the various nootropic effects associated with those neurotransmitters, including positive mood and enhanced mental performance.2
Neuroprotection
Catuaba demonstrated an ability to significantly reduce oxidative stress and apoptosis in brain cells when applied before but not after damage took place.3 4 It was also found to inhibit the activity of an integral piece in the inflammatory pathway known as platelet phospholipase A2 (PLA2).5 Together, antioxidation and anti-inflammation may protect neurons and brain cells and keep them healthy.
Catuaba Nootropic Benefits & Uses

The majority of catuaba’s potential nootropic benefits are based on hearsay and personal anecdotes. It’s been rumored by casual users to be invigorating, help make people smart, and support good mood.
Early animal research has found that a medium-dose catuaba drug is capable of promoting mental alertness and memory as well as imparting anti-depressant effects, mostly because of its strong antioxidating power.6
Interestingly, one study reported that catuaba sharply increased brain cell proliferation, which means it could play a role in neurogenesis.
Research
Animal Research
Animal research has shed light on various potential nootropic effects of catuaba supplementation.
Catuaba fraction may protect against cognitive impairment in mice
In this investigation, male mice with brain ischemia were administered 200, 400, or 800 mg/kg of a Trichilia catigua ethyl-acetate fraction (EAF) every day for 7 days. The extract significantly improved recovery from the cognitive impairments caused by ischemia.
- The researchers concluded that “T. catigua EAF promoted functional recovery, decreased the delayed hippocampal cell loss, and mitigated the ongoing neurodegenerative processes.”7
Catuaba fraction may have anti-depressant effects in mice
In this investigation, mice were given 200 or 400 mg/kg of a Trichilia catigua ethyl-acetate fraction (EAF) every day for 14 days. The higher dosage triggered antidepressant-like effects in mice as well as increased cell proliferation in the hippocampus.
- The researchers concluded that “Trichilia catigua EAF produced antidepressant-like effects.”8
Catuaba fraction may promote cognitive improvement in mice
In this experiment, mice were administered Trichilia catigua drugs either in extract form at 200 – 800 mg/kg or as an ethyl-acetate fraction (EAF) at 100 – 400 mg/kg before participating in stress tests. Though animal behavior was not altered, the 400 mg fraction dose demonstrated an antidepressant effect, and both the 800 mg extract and 200 and 400 mg fraction doses improved memory.
- The researchers concluded that “the present results showed an in vitro antioxidant activity for EAF and suggested that it may be useful for cognitive improvement.”9
Catuaba extract may prevent oxidative damage
In this investigation, rat brain cells were given 40 – 100 μg/mL of a Trichilia catigua extracts before and after being subjected to oxidative stress. The catuaba extract was found to significantly protect brain cells from oxidative stress when given before but not after damage took place.
- The researchers concluded that “T. catigua should be used as preventive and not as a curative agent against brain damage.”10
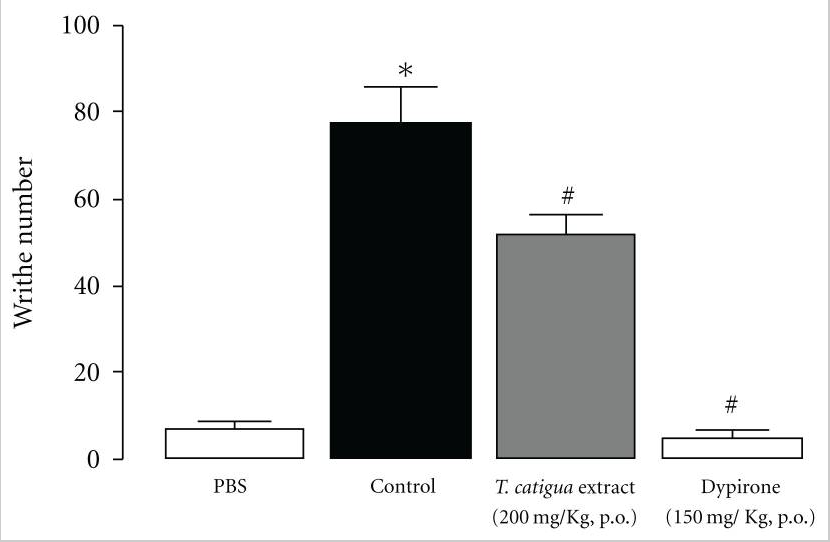
Catuaba extract may reduce pain sensation in mice
In this controlled scientific investigation, male mice were given 200 mg/kg of Trichilia catigua extract and then submitted to hot pain. The extract was found to have a significant antinociceptive effect on the mind of the mice.
- The researchers concluded that “the antinociceptive effects of T. catigua extract seem to be mainly associated with the activation of dopaminergic system.”11
Human Research
There is currently no clinical research discussing any significant nootropic effects of catuaba.
Nootropic Dosage
- No clinical research studies have provided effective dosage for catuaba as a nootropic.
- A typical catuaba supplement provides 465 mg or 1 mL (30 drops) daily servings.
Available Forms
Catuaba is a tree bark extract that is taken in various forms:
- Infusion (as either a juice or hot tea)
- Tincture or droplets
- Tablet or capsule
Supplements in Review Says
- Catuaba 465 mg as a nootropic.
Catuaba may be good for brain health. Animal research has shown that catuaba, like other herbal nootropics, has great potential, particularly in regards to combating cognitive impairment and depression. The lack of clinical support makes it difficult to recommend catuaba for regular use.
Stick with trustworthy catuaba providers. The potential adverse side effects of catuaba supplements have not been well studied. Try natural preparations of catuaba at 465 mg of dry extract or 1 mL of liquid extract.
Leave a Reply