Early research suggests theacrine may potentially have nootropic effects akin to caffeine.
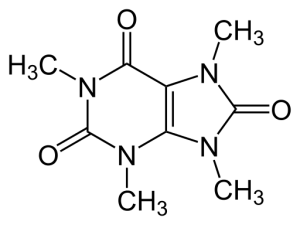
Theacrine is a chemical compound found in the plants Cupuaçu and kudingcha. It may promote such potential nootropic benefits as:
- Anxiolytic activity. Theacrine has demonstrated stress reducing properties.
- Analgesic activity. Theacrine has been shown to reduce pain.
- Boosting excitatory neurotransmitters. Stimulation of such brain chemicals as dopamine may allow theacrine to energize the mind and body.
- Sedation. Low doses of theacrine may have a sedative effect.
Overview
A purine alkaloid found in a variety of plants, including fruits of the Cupuaçu tree and leaves of the Chinese kucha herb, theacrine has recently attracted interest as an ingredient with potential therapeutic and medicinal uses.
Theacrine can be converted from pure caffeine via a 3-step process involving hydration, oxidation, and methylation, and this fundamental link to caffeine has led many to suppose theacrine to function similarly to other nootropics.1
Thus far, research has uncovered theacrine’s potential role in managing the levels of neurotransmitters, namely adenosine and dopamine, as well as decrease oxidative stress and inflammation. These biochemical activities may enable theacrine to impart stimulatory effects on mood, cognition, and energy production.

How Theacrine Might Help the Brain
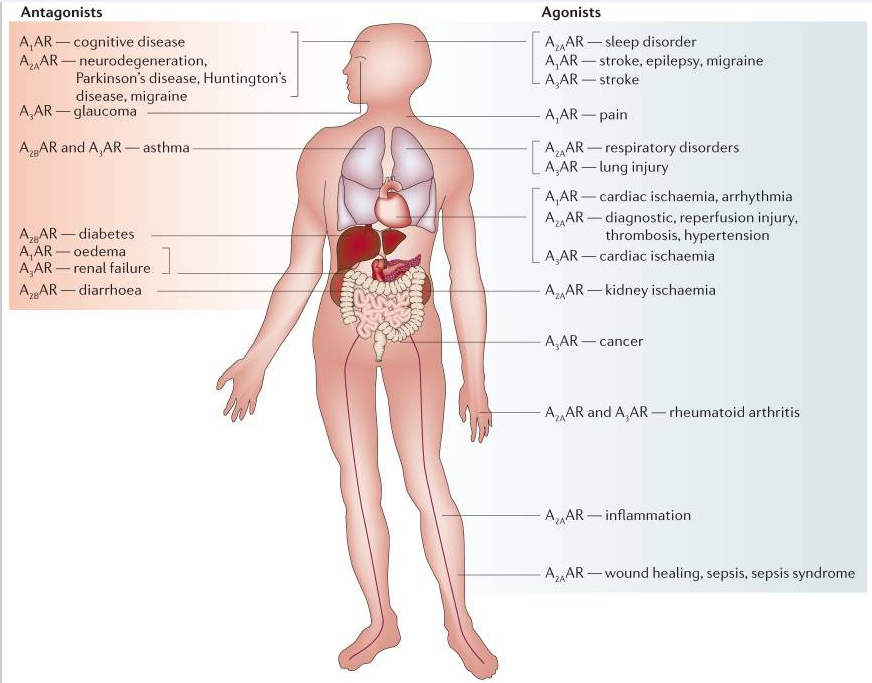
Binding to adenosine receptors
The principal proposed mechanism of action of theacrine centers around its ability to bind to adenosine receptors.2 Whether theacrine activates or deactivates adenosine seems to hinge on dosage.
- Stimulation. At higher doses, theacrine has been shown to mimic caffeine’s arousal and stimulant effects by antagonizing A2A adenosine receptors.
- Sedation. At lower doses, theacrine has been theorized to act on A1 and A2A adenosine receptors, which promote sleep when activated.
Activating dopamine
Theacrine has also been shown to boost stimulatory activity by triggering the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is known not only to activate the adrenergic system, but also serve as a precursor for noradrenaline.
Theacrine Benefits & Uses for Brain Health
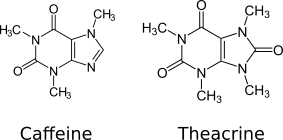
Curiously, research has also identified that, when taken at lower doses, theacrine may behave more like a sedative than energy enhancers or stimulants.
Research
Animal Research
Animal research has demonstrated a wide range of nootropic effects stemming from theacrine ingestion:
- Promoting sedation in mice4
- Decreasing pain sensation and inflammation5
- Fortifying the antioxidant system and reducing stress in mice6
Human Research
Clinical studies, although few in number, have reported theacrine’s capacity to improve overall mood, motivation, and energy levels.
Theacrine as TeaCrine® (200, 400 mg) may increase energy, motivation, and concentration
This two-part study observed the effect of theacrine supplementation on various cognitive and psychometric parameters. Part 1 was a randomized investigation in which 3 adults were given 400 mg and 6 adults were given 200 mg of TeaCrine theacrine every day for 7 days. Participants noted subjective increases in willingness to exercise and motivation to change, as well as improvements in anxiety and libido in the 200 mg but not the 400 mg dose.
Part 2 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation in which 15 adults took either a placebo or 200 mg of TeaCrine theacrine every day for 7 days. Significant improvements were noted in energy, fatigue, and concentration after taking theacrine compared to the placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “after consuming a single 200 mg dose, significant group × time interaction effects were seen for energy, fatigue, and concentration.”7
Theacrine as TeaCrine® (200, 300 mg) may improve mood profile
In this placebo-controlled investigation, 60 adults were given a placebo, a low 200 mg dose of TeaCrine theacrine (LD), or a high 300 mg dose of TeaCrine theacrine (HD) every day for 8 weeks. Mood profile was found to improve overall but not to a statistically significant degree. Vigor was shown to drop in the early stages of the low dose group. Theacrine has been found to be safe and have no adverse side effects or drug tolerance typical to stimulants.
- The researchers concluded that “these findings support the clinical safety and non-habituating neuro-energetic effects of TeaCrine® supplementation.”8
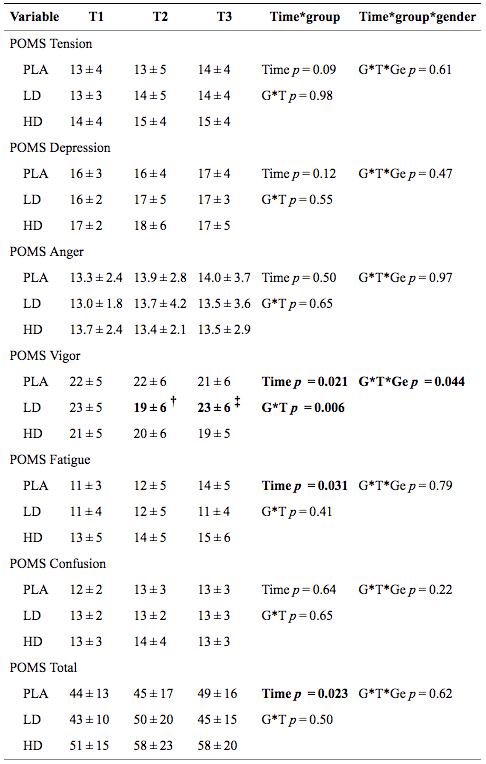
Abbreviations: PLA Placebo, LD Theacrine Low Dose, HD Theacrine High Dose, G Group, T Time, Ge Gender, T1 base, T2 4 weeks, T3 8 weeks.
Nootropic Dosage
- Successful clinical research studies have used from 200 – 400 mg of theacrine per day.
- Typical theacrine supplements come in daily servings of 50 – 100 mg.
Available Forms
- Capsules or tablets
- Powder
- Tea or other drink
Supplements in Review Says
- TeaCrine® Theacrine 50 – 200 mg as a nootropic.
Theacrine may have both relaxing and stimulating properties. Theacrine may improve various aspects of mood and cognition, but only a very limited amount of clinical research has been conducted thus far.
Take 50 – 200 mg of TeaCrine supplements. If intent on trying out theacrine as a nootropic, take the theacrine supplement with some clinical backing — TeaCrine®. Try ≤ 100 mg of theacrine for its sedating effects, and higher, 200 mg doses for stimulation.
Leave a Reply