Natural carbohydrate energy source dextrose seems to aid post-workout recovery.
Dextrose is the form of glucose most readily available in nature. Its high energy content may make it viable for post workout supplementation through:
- Improving recovery. Dextrose helps to quickly replenish the body’s energy levels that get used up during strenuous exercise.
- Potential support of muscle protein synthesis. There is a popular theory that carbohydrate ingestion post-workout further increases muscle growth, but more evidence is needed to support this.
Overview
The only naturally occurring form of glucose, dextrose (also known as D-glucose) serves as the main energy source for nearly all of the body’s needs, packing about 3.75 kilocalories of energy per gram. It is generated through photosynthesis in plants and then converted into energy in animals and humans through cellular respiration.
People consume dextrose daily in a typical carbohydrate foods such as honey, oats, oranges, and starchy foods. The body uses dextrose in the citric acid cycle to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body’s main energy molecule. Meanwhile, when excess amounts of dextrose are ingested, it is stored in the liver and muscle as glycogen.
In health and medicine, dextrose is most commonly used to help manage diabetes and other disorders associated with sugar imbalances. In fitness circles, bodybuilders and athletes have long been known to utilize dextrose-containing foods or supplements in pre or post-workout supplements in order to optimize energy status.

How Dextrose Might Help Post Workout Formulas
Fueling muscle
The essential role of carbohydrates for endurance exercise has been documented as far back as a century ago, and the prime carb source in muscles is dextrose stored as glycogen. Larger stores of glycogen mean more energy for muscles, which has been directly correlated with an increased capacity to exercise and possibly even to rebuild muscles.2 3 The longer the duration of a workout and the more physically demanding it is, the more glycogen supplies get drained.4
Dextrose’s Proposed Post Workout Benefits & Uses

Meanwhile, there is still some debate on just how involved glycogen is in strength (anaerobic) training. Some believe that consuming dextrose after resistance training can enhance muscle protein synthesis, but there isn’t enough research data to back up this claim.
Finally, it’s important to consider that carbohydrate-rich foods such as pasta can be used as an easy source of glucose/dextrose after a workout, putting the need for supplementation in question.
Research
Animal Research
Research indicates that restoring dextrose stores after working out may:
- Sustain endurance during exhaustive exercise and training in rats.6
Human Research
Clinical research agrees that dextrose is a fundamental energy source for muscles, but the extent of its ability to increase muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is still being investigated.
Dextrose plus protein post-exercise may aid muscle growth
In this investigation, 13 adults took 20 g of essential amino acids (EAA) with either 30 or 90 g of carbohydrates, mainly dextrose, 1 hour after completing leg resistance exercises. Both groups saw significantly increased muscle protein synthesis (MPS) and a slight reduction in muscle protein breakdown (MPB).
- The study concluded that “enhanced muscle protein anabolic response detected when EAA+carbohydrate are ingested postresistance exercise is primarily due to an increase in MPS with minor changes in MPB.”7
Dextrose may be needed for post workout muscle protein and glycogen synthesis
This review examined the impact of nutrition after exhaustive exercise. The researchers found that carbohydrate consumption is the most important factor to replenish glycogen stores after exercise. Certain macronutrients, dextrose included, were identified as playing a significant role in muscle and glycogen synthesis after exercise.
- The study concluded that “post-exercise nutrient intake is essential for promoting protein synthesis and glycogen synthesis.”8
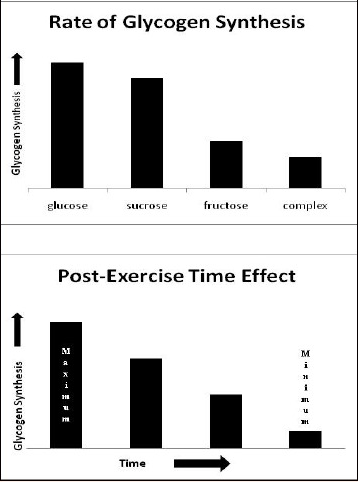
Dextrose (0.88 g/kg) may mitigate muscle damage caused by exercise
In this investigation, adults exercising on a treadmill for 3.75 hours were given glucose at a rate of 0.88 g per kg of body weight after every hour of exercise. Glucose supplementation was found to reduce the amount of exercise-induced muscle damage and deterioration.
- The study concluded that “glucose given at the rate of 0.88 g . kg-1 . h-1 depressed the rate of whole-body protein degradation and appeared to suppress the exercise-induced increase in nitrogen excretion.”9
Dosage for Post Workout
- Research studies have successfully used from 50 – 200 g of dextrose as a carbohydrate
- Dextrose supplements typically come in the form of powder with doses of 4 – 75 g daily
- The most common supplemental stacks combine roughly 30 grams of whey protein with 45 – 60 grams of dextrose powder
Supplements in Review Says
- Dextrose powder 45 – 60 g post-workout.
Dextrose seems to aid in muscle recovery. There is some evidence that dextrose can improve workout recovery, particularly for exercise that significantly depletes glycogen stores. Having said that, it’s far simpler and easier to just get all your dextrose from dietary carbohydrates such as pasta.
Stack dextrose with protein if you undergo resistance training. If you do decide to give dextrose supplements a try, you can either go for a standalone dextrose product, or a multi-ingredient pre-workout formula that contains it. And if your main goal is muscle growth, then dextrose is best stacked with protein at a 1.5:1 ratio.
Leave a Reply