Amino acid L-tyrosine may be a potent anti-stress supplement that improves cognitive performance.
- Supporting stress hormones. L-tyrosine helps increase levels of the hormone norepinephrine, which is critical for a healthy stress response.
- Enhancing performance. L-tyrosine helps improve mental performance during stress.
Overview
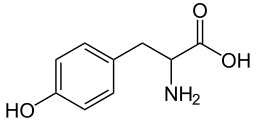
L-tyrosine, or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of twenty standard amino acids that serve as protein building blocks. Its name comes from the Greek word for cheese, tyros, since it was first discovered by Justus von Liebig inside the casein protein found in cheese.
L-tyrosine is naturally made in the body from phenylalanine and can also come from food sources, such as soy, turkey, and sesame seeds.
One of tyrosine’s most critical roles is to act as a precursor to several vital neurotransmitters and hormones; it is capable of entering the brain and adrenal glands and then converting into dopamine, L-dopa, epinephrine, and norepinephrine, all of which are often used up as a consequence of excessive work and stress.

Given these effects on brain chemistry, it’s not surprising that tyrosine is considered a nootropic that may be able to improve mood, relieve stress, and even enhance cognitive performance.
How L-Tyrosine May Help With Stress
Replenishing stress hormones
In addition, one study identified that L-tyrosine not only replenished NE levels, but also suppressed corticosterone, which would otherwise deplete NE.2
L-Tyrosine Benefits & Uses for Stress
As a precursor to fundamental neurotransmitters, L-tyrosine plays a key role in maintaining adequate levels of dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, all of which are necessary for body to handle stress. In that sense, L-tyrosine is an important part of the body’s natural anti-stress system.3
The military has been especially curious about the impact L-tyrosine can have on soldiers as an anti-stress supplement, and have discovered that it may protect against numerous types of stressors, including excess heat or cold, long hours, loud noise, fatigue, depression, lack of sleep, and general work-related stress.4
Studies have even gone so far as to highlight L-tyrosine’s potential to bolster cognitive performance5 and support memory6 in the absence of stress.

Research
Animal Research
Research indicates that L-tyrosine may be capable of:
- Protecting against psychological stress. Rats subjected to psychological stress for 21 days had significantly reduced behavior and performance impairments with tyrosine supplementation.7
- Mitigating the adverse effects of heat stress. Rats subjected to heat stress had improved coping behavior and memory after taking tyrosine due to increased central NE release.8
Human Research
Clinical studies corroborate the belief that L-tyrosine helps the body cope with stress.
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 23 military personnel exposed to 4.5 hours of cold and hypoxia were given placebo or 100 mg/kg of tyrosine. The tyrosine group seemed to withstand the stressful environment significantly better than the control group and showed improvements in cognitive function and mood.
- The study concluded that “tyrosine significantly decreased symptoms, adverse moods, and performance impairments in subjects who exhibited average or greater responses to these environmental conditions. These results suggest that tyrosine should be evaluated in a variety of acutely stressful situations.”9
L-tyrosine drink (2 g) may reduce the effects of stress on mental performance
In this placebo-controlled, double-blind investigation, 21 cadets received a placebo protein drink or one with 2 grams of L-tyrosine daily for 5 days before running through a combat course. The tyrosine group performed better on the memory and tracking tasks than placebo, and had decreased systolic blood pressure.
- The study concluded that “supplementation with tyrosine may, under operational circumstances characterized by psychosocial and physical stress, reduce the effects of stress and fatigue on cognitive task performance.”10
L-tyrosine (100 mg/kg) may improve cognitive performance and blood pressure under stress
In this randomized, placebo-controlled investigation, 16 adults were given placebo or 100 mg/kg of tyrosine on 2 separate days 1 hour before performing stress-sensitive tasks during exposure to loud noise (90 dB). The tyrosine group demonstrated improved performance on 2 cognitive tasks and had decreased diastolic blood pressure.
- The study concluded that “while performing a number of stress sensitive tasks…tyrosine was found to improve the performance on two cognitive tasks.”11
L-tyrosine (150 mg/kg) may sustain performance during sleep loss
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind investigation, workers were asked to complete performance tasks and mood scales for 13 hours in the evening after remaining awake all throughout the day. 6 hours into the task, workers were given placebo or 150 mg/kg of tyrosine. At the end of the study, tyrosine was shown to significantly reduce performance decline from stress on the psychomotor and vigilance tasks.
- The study concluded that “tyrosine may prove useful in counteracting performance decrements during episodes of sustained work coupled with sleep loss.”12
L-tyrosine (100 mg/kg) may enhance cognitive function during cardiovascular stress
In this double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 20 adults were given placebo or tyrosine at 100 mg/kg of body weight and then exposed to 2 sessions of a form of cardiovascular stress known as Lower Body Negative Pressure (LNBP). The tyrosine group was found to have an overall increase in pulse pressure (LBNP typically reduces pulse pressure) and enhanced cognitive activation.
- The study concluded that “the detected effects of tyrosine include an overall increase in pulse pressure…which may indicate enhanced cognitive activation.”13
Dosage for Stress
- Research studies tend to offer L-tyrosine based on weight, ranging from 100 –150 mg per kg of bodyweight (~8.8 grams for the average male and ~7.5 grams for the average female)
- Typicalsupplemental capsules range from 500 – 1500 mg
- L-Tyrosine supplements have optimal effects when taken on an empty stomach and mixed with water
Supplements in Review Says
- L-tyrosine, 500 mg for stress.
We recommend L-tyrosine for coping with stress. L-tyrosine seems to help the body perform well under stress, be it physical or mental.
Take L-tyrosine with vitamins B6 and C. We suggest starting with a low, 500mg L-tyrosine dose and then increasing the dosage if necessary. In addition, combining tyrosine with vitamins B6 and C may further optimize its stress-alleviating effects.
Leave a Reply