
Joint health supplements include a diverse collection of herbs, minerals, and other natural compounds that promote the well-being of bones, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and other tissues that make up joints. Although injured joints can never be completely restored, supplements have been shown to reduce inflammation, pain, and other symptoms of joint disorders and injuries. For more information on joint supplements, check out our guide.
On this page, we’re going to discuss the most popular joint supplements on the market today and attempt to determine their usefulness. Supplements highlighted as Editor’s Choice represent our top picks for supporting joint health.
Boswellia Serrata

The native Indian tree Boswellia serrata bears a gum resin ripe with bio-active ingredients that have a wide array of health benefits. It is most popularly used to mitigate joint complications, such as pain, swelling, and stiffness. B. serrata is believed to work by reducing inflammation through blocking the nF-κβ pro-inflammatory pathway.
Numerous research studies back up B. serrata’s ability to diminish joint problems and improve function, especially in people facing osteoarthritis. More on Boswellia serrata.
Cannabidiol (CBD)
Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, is one of the main bioactive components of cannabis (marijuana) plants. Its widespread use in managing arthritis stems from its potent capacity to reduce inflammation and pain by:
- Activating TRPV1, a receptor that controls pain and inflammation
- Elevating levels of the neurotransmitter anandamide, which may reduce inflammation and pain
- Blocking the receptor GPR55, reducing pain sensation
Although human research is just beginning, CBD has been shown to improve arthritis in animal studies. An additional plus is that, unlike other cannabinoids, CBD does not impart any unwanted psychoactive effects. More on CBD and joint health.
Chondroitin – Editor’s Choice
As the main structural component of cartilage, chondroitin is regarded as a core component of healthy joints. It mainly seems to protect cartilage by cutting back on the production of inflammatory molecules, such as p38MAPK.
On top of that, chondroitin has been shown to increase joint mobility by absorbing excess fluid and blocking cartilage-deteriorating enzymes. Current research is supportive of chondroitin’s pain and joint mobility benefits for osteoarthritis patients. More on chondroitin.
Cissus Quadrangularis

One of the lesser known members of the grape family, Cissus quadrangularis is a tropical plant traditionally used to help heal broken bones. This Indian herb is now rising in popularity as a joint supplement for athletes and bodybuilders, largely due to the positive results of early clinical research.
C. quadrangularis is believed to work by reducing inflammation and promoting the growth of bone, effects which may work together to reduce joint pain and improve function. More on C. quadrangularis.
Collagen – Editor’s Choice
Collagen is not only the principal structural protein in connective tissue but also the most abundant form of protein in humans. Among the 16 types, collagen type II seems to be the most relevant for joint growth and development. It promotes joint health in a number of different ways:
- Facilitating cell growth and regeneration in joints by differentiating bone cells, or osteoblasts
- Enhancing bone density
- Reducing inflammation and pain by limiting inflammatory markers, managing the production of antibodies, specifically IgG2A and IgG1, and decreasing autoimmune responses
The capacity of collagen to reduce joint pain and swelling and improve joint mobility is well backed by research. More on collagen.
Eggshell Membrane
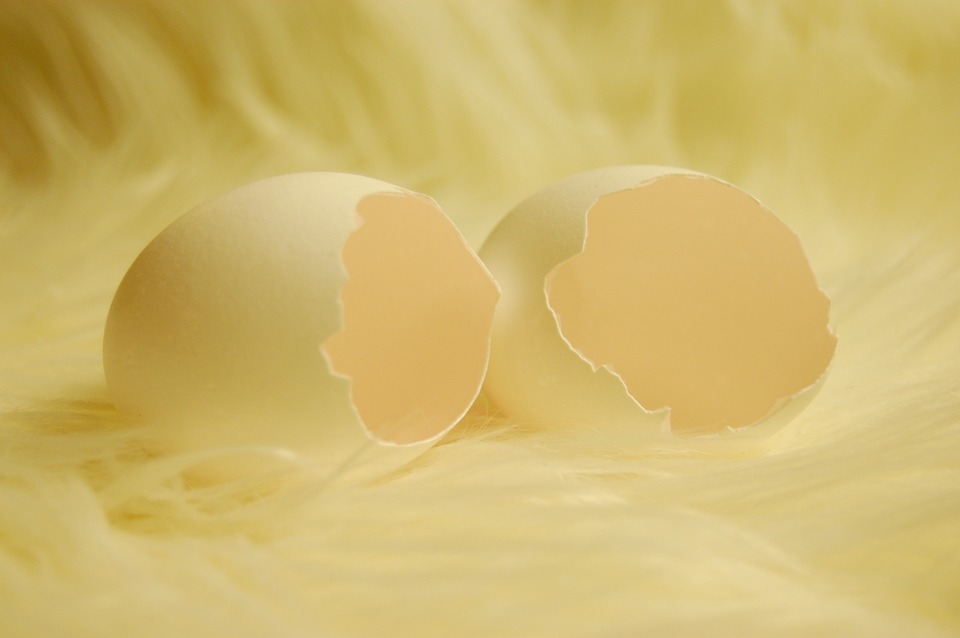

Eggshell membrane is the thin film found between a chicken egg shell and the actual egg. It is increasingly being used as a joint health supplement by both individuals with joint conditions and workout enthusiasts. Eggshell membrane provides its beneficial effects through supplying a number of nutrients that support joint health, including:
- Collagen
- Glucosamine
- Chondroitin
- Hyaluronic acid
Early human studies indicate that eggshell membrane can reduce joint pain, but research has only just begin. More on eggshell membrane.
Fish Oil

Fish oil is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, such as alpha-linoleic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexanoic acid (DHA), which are not only essential to proper body function, but also appear to have multiple health benefits.
In terms of joint health, omega-3’s appear to decrease inflammation by cutting back the production of the pro-inflammatory compounds such leukotriene B4 and platelet activating factor. Current research indicates that fish oil is effective at improving the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. More on fish oil.
Ginger

Ginger is one of the most popular medicinal herbs in the world. Its most promising joint-related use appears to be helping alleviate the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Current research suggests the most likely way ginger works is through a combination of inhibiting pro-inflammatory molecules and increasing anti-inflammatory ones. More on ginger.
Glucosamine – Editor’s Choice
Naturally present in joint fluid, glucosamine is a compound that supports cartilage health. Glucosamine may decrease as we age; as such, supplementation can help increased its levels and benefit the joints. Research suggests that glucosamine supplements can improve the symptoms of osteoarthritis and slow its progression, and also improve joint mobility following injury. More on glucosamine.
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM)
MSM is an organic compound that is first produced by oceanic plankton and then activated after reacting with ozone and sunlight. It is believed to promote joint health through:
- Antioxidant activity
- Inhibiting the inflammatory markers interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα)
- Providing sulfur, which is a critical part of healthy joints.
Research suggests that MSM can help relieve the symptoms of osteoarthritis in particular. More on MSM.
Turmeric

Turmeric has long been used in ancient Indian Ayurvedic practices to manage all kinds of ailments. Modern research has identified a compound known as curcumin as the main bioactive ingredient in turmeric.
Curcumin is believed to improve joint health through two mechanisms:
- Inhibiting the formation of osteoclasts, which are cells responsible for breaking down bone
- Reducing inflammation by blocking inflammatory molecules, including phospholipase, lipooxygenase, cyclooxygenase 2, and leukotrienes
Extensive research has been conducted on the health benefits of turmeric, including studies showcasing its ability to improve arthritis. More on turmeric.