Neurotransmitter GABA helps lower anxiety and promote relaxation, but supplementation remains controversial.
- Relieving anxiety. GABA is a natural relaxant known to reduce anxiety.
- Potentially improving mood. GABA dysfunction may be linked to depression and other mood disorders.
Overview
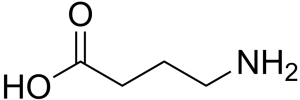
First confirmed as an essential element of the central nervous system in 1950, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) is now considered the key inhibitory neurotransmitter in the human body.1 GABA’s main function is to reduce neuron activity, resulting in relaxation and lowering anxiety. As such, GABA is critical for proper communication between nerve cells, especially when it comes to staving off stress and anxiety-related impulses.
In most cases, sufficient amounts of GABA are produced directly in the brain, which makes it a natural nootropic. But when GABA levels are low, the body may react by instinctively triggering anxiety or irritation.
The potential physiological impact of GABA is multifold and includes promoting sleep, alleviating pain, increasing growth hormone, and managing all kinds of stress-related conditions. Having said that, supplementing GABA remains controversial because it has difficulty crossing the blood-brain barrier.
How GABA May Help With Stress
Reducing neuron activity
As the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system, GABA is known to slow down neuron activity. As a result, it promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety, acting as an effective stress reliever.2
GABA Benefits & Uses for Stress
Gaba is popularly used as an all-around anxiety reducer as well as a sleep aid. Given that anxiety plays a huge role in stress, GABA can be an effective way to calm the mind and promote relaxation.
Nonetheless, it’s important to reiterate that GABA supplements have difficulty crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Some people argue that supplementation can still work by affecting other regions of the body or parts of the brain not protected by the BBB, but more research is needed to say anything conclusive.
Research
Human Research
Although limited in number, clinical studies concerning GABA seem to lean toward its capacity to relieve stress.
GABA (100 mg) may provide relief and reduce anxiety during stressful situations
In the first part of this placebo-controlled investigation, 13 adults took a series of 3 exams and took either water, L-theanine, or GABA. 1 hour after supplementation, EEG findings showed that GABA induced relaxation and reduced anxiety. In the second part of the investigation, 8 adults with acrophobia were given either placebo or GABA and asked to cross a suspended bridge. The GABA group had higher levels of IgA and thus elevated relaxation.
- The study concluded that “GABA could work effectively as a natural relaxant and its effects could be seen within 1 hour of its administration to induce relaxation and diminish anxiety. Moreover, GABA administration could enhance immunity under stress conditions.”4
GABA (100 mg) may alleviate stress from mental tasks
In this randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation, 63 adults were given either placebo or 100 mg tablets of GABA 30 minutes after completing a challenging mental task. The results of a subsequent electroencephalogram (EEG) showed that GABA led to decreases in alpha and beta band brain waves, which indicate reduced stress signaling.
- The study concluded that “GABA might have alleviated the stress induced by the mental tasks.”5
GABA (1000 mg) seems to minimize stress during resistance training in cyclists
In this placebo-controlled investigation, 8 endurance-trained men cycled at 65% peak oxygen usage for 30 minutes and were then asked to immediately drink either a placebo or a 1000 mg sports drink infused with GABA. The sympathetic nervous system was inhibited in the GABA group, which led to lower esophageal temperature, lower sweat rate, and the inhibition of catecholamines.
- The study concluded that “the inhibition of plasma catecholamine concentrations [was] caused by the GABA-induced attenuation of the sympathetic nervous system during exercise.”6
Dosage for Stress
- Research suggests that GABA doses of 100 – 1000 mg are effective for dealing with stress
- GABA supplements provide doses of 200 – 1000 mg daily
Supplements in Review Says
- GABA 700 – 800 mg daily for stress.
GABA is a viable stress reliever. GABA’s ability to relieve stress and promote relaxation is well documented. However, we can’t recommend GABA supplementation outright because the debate around its efficacy is still ongoing.
700 – 800 mg should be sufficient. If you do take GABA, a total dose of 700 – 800 mg per day may be effective.
Leave a Reply