Widely available vitamin B5 helps the body generate energy and produce essential biological molecules.
- Energy production. Like other B vitamins, B5 helps convert food into energy.
- Biomolecule synthesis. B5 is needed to synthesize a large variety of essential molecules, including fats, hormones, and proteins.
Overview
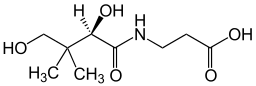
Vitamin B5, frequently referred to as pantothenic acid, is an essential nutrient that is required for the metabolism of dietary carbs, proteins, and fats consumed on a daily basis. Its principal role in the body is serving as a precursor of coenzyme A, an enzyme needed to convert food into energy (ATP) and facilitate the production of fatty acids, hormones, sterols, and many other important biological compounds. More on vitamin B and energy.
Its name originates from the ancient Greek word “pantothen,” which means “from everywhere,” and lo and behold, the vitamin is naturally present in nearly all categories of food, such as fortified whole grain cereals, liver, egg yolk, and mushrooms. As a result, dietary insufficiency of vitamin B5 is extremely rare.
It is, however, still included in multivitamin complexes for its numerous health benefits, including lowering cholesterol, maintaining vibrant skin, and even possibly mitigating the symptoms of arthritis.1 2

Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Vitamin B5
| Age | Males | Females |
| 0 – 12 months | 1.7 – 1.8 mg | 1.7 – 1.8 mg |
| 1 – 8 years | 2 – 4 mg | 2 – 4 mg |
| 9 – 13 years | 4 mg | 4 mg |
| 14 – 18 years | 5 mg | 5 mg (6 mg for pregnancy, 7 mg for breast-feeding) |
| 19+ | 5 mg | 5 mg (6 mg for pregnancy, 7 mg for breast-feeding) |
Foods High in Vitamin B5
| Food | Serving Size | Amount per serving (mg) |
| Chicken liver | 3 ounces | 8.3 |
| Avocado | 1 fruit | 2 |
| Sunflower seeds | 1 ounce | 1.98 |
| Salmon | 3 ounces | 1.9 |
| Yogurt | 1 cup | 1.45 |
| Corn | 1 cup | 1.18 |

How Vitamin B5 Supports General Health
Among vitamin B5’s various functions, one sticks out more than the rest:
Facilitating the synthesis of coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA) is pivotal to a handful of essential biological processes, most notably:
- Energy generation. CoA is not only involved in generating essential fats and cholesterol, but is also required to break down dietary fat, carbs, and proteins, and then convert the food into useable energy via the citric acid cycle.
- Hormone and neurotransmitter production. The multi-purpose coenzyme A plays a part in making the hormone melatonin, the neurotransmitter acetycholine, and the part of red blood cells that carries iron, known as heme.
- Liver function. The liver needs CoA to breakdown substances that enter the body, including harmful drugs and toxins.3
None of these core reactions would be possible without vitamin B5, since it is the precursor to coenzyme A.
Vitamin B5’s Benefits as a Multivitamin
Although most people get plenty of vitamin B5 from their diets, it is still frequently included in multivitamin supplements to provide a form of “nutritional insurance.” The primary health benefit of vitamin B5 is to sustain a number of fundamental reactions in the body—including energy and hormone production—by making coenzyme A. Its other noteworthy health benefits are associated with healing skin wounds on various fronts: 4
- Cell proliferation and migration. Calcium pantothenate, derived from vitamin B5, accelerates red blood cell growth and development, which is central to effective wound healing.5 6
- Structural differentiation. Vitamin B5 is critical for the growth and differentiation of keratin and collagen, which are key components of healthy skin.7
- Skin closure. In ointment form, vitamin B5 has been found to strengthen and speed up the process of skin wound closure.8
Multivitamin Dosage
- Multivitamins typically include 5 – 25 mg of vitamin B5
- Cholesterol multivitamins use 300 mg of vitamin B5, although up to 10,000 mg (10 g) may safely be taken
Supplements in Review Says
- Vitamin B5 5 mg as part of a multivitamin.
Vitamin B5 is essential to good health. Vitamin B5 is needed for proper energy metabolism and the synthesis of a wide variety of essential biological molecules, prompting its frequent inclusion in multivitamins.
Take a multivitamin with 5 mg of B5. Look for a multivitamin that contains at least 5 mg of B5 – the RDA for adults – to make sure your daily needs are met.
Leave a Reply