Everyone experiences a lack of energy at some point in their life, whether it be because you slept poorly, had a stressful day, or seemingly without reason. Energy supplements – also known as energy boosters or stimulants – are dietary supplements that can help with this common problem by reducing mental and physical fatigue. They can also promote alertness, focus, motivation, improve mood, and other related cognitive and physical parameters.
In this guide, we’re going to look at how energy boosters work and discuss other important information so you can figure out whether energy supplements are right for you.
The Science of Energy
The term “energy booster” sounds simple enough – a supplement that increases your energy levels. Having said that, there is currently no standardized, scientific way for defining or measuring exactly what is meant by energy, let alone changes in energy levels. The definition becomes even muddier when you consider that we often distinguish between physical and mental energy.
This is important to note because companies that sell energy supplements make strong claims about how their products enhance energy – which people consider a highly desirable effect – but these claims are difficult to test and back up with scientific proof. As such, it’s important to look to widely accepted scientific measures – such as improved physical performance or enhanced mood – when attempting to figure out whether a given supplement will actually enhance your energy.
How Do Energy Boosters Work?
Energy supplements can enhance your energy via multiple methods. The four most prominent mechanisms of action are:
CNS stimulation
The reason caffeine and similar compounds are called stimulants is because they increase the body’s activity. More specifically, caffeine stimulates the central nervous system (CNS) – comprising of the brain and spinal cord. This effect can be achieved by:
- Influencing the levels of brain chemicals (neurotransmitters) that control mood, wakefulness, and other functions, such as dopamine, adenosine, and serotonin
- Promoting adrenaline release – a fight-or-flight hormone that increases heart rate and blood sugar levels, and other effects
A specific compound found in ginseng – called Rg1 – is another example of a CNS stimulant that works by influencing neurotransmitters.
Energy production
Some energy supplements are naturally present in the body and are involved in producing ATP – the main energy molecule of all life. For example, acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) is needed to transport fatty acids into a cell’s mitochndria so they can be burned to supply energy to the cell.
However, supplementing such compounds tends to only help those individuals whose levels of these important chemicals are suboptimal, and have little to no effect for healthy individuals. Prominent examples include include alpha lipoic acid, acetyl-L-carnitine, CoQ10, and the B vitamins.
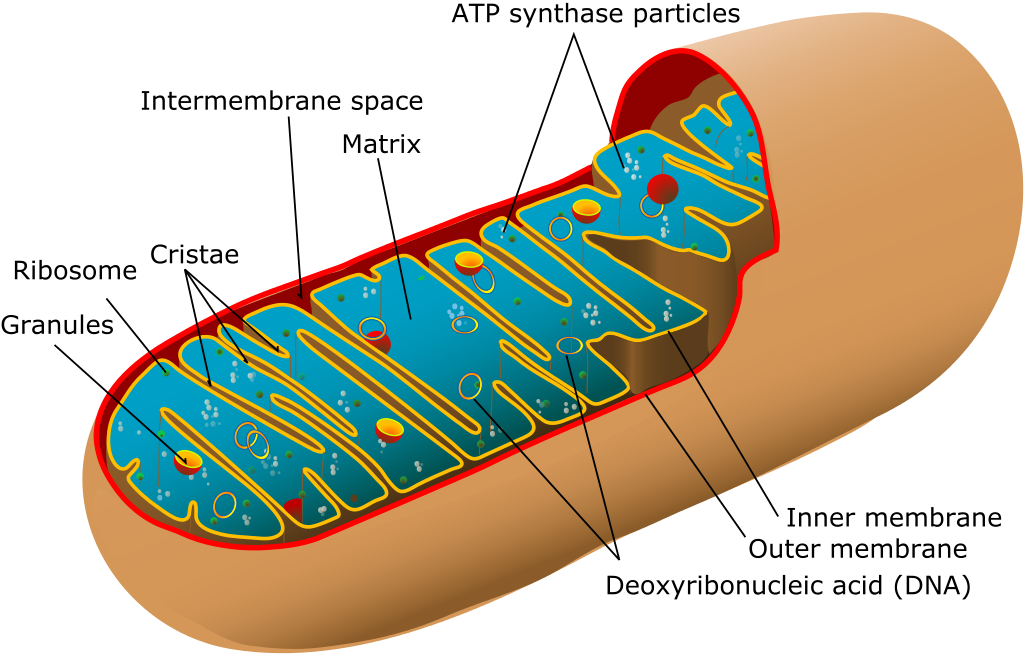
Antioxidant activity
Oxidative stress generated by reactive oxygen species has been implicated in a wide range of health disorders, including chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Of most relevance to energy is the fact that oxidative stress can damage mitochondria – the energy (ATP) generating centers of cells. Because of this, certain antioxidant supplements can increase cellular energy production by protecting mitochondria from oxidative stress.
Much like compounds that are involved in energy production, however, such antioxidants tend to only help those people whose antioxidant defenses are not up to par, and tend to have no effect in healthy individuals. PQQ and bee pollen are just a few examples of antioxidants used to boost energy levels.
Adaptogenic activity

These herbs can be useful for improving energy during periods of stress, whether it be caused by sleep deprivation, physical exertion, temperature changes, or any other form of physical or mental stress.
Energy Booster Benefits
As discussed above, there is no strict, scientific definition for what is meant by energy. But thankfully, there are a number of measurable effects associated with enhanced energy. Because of this, researchers are able to test whether some of claimed benefits associated with energy boosters – such as the ever-popular caffeine – are actually true.
Energy boosters can be expected to improve at least one of the following cognitive and physical parameters:
- Fatigue
- Sleepiness
- Focus & concentration
- Reaction time
- Mood & well-being
- Creativity & self-confidence
- Overall cognitive performance
- Perceived exertion (a measure of how physically intense an activity is)
- Libido
- Physical performance – e.g. faster running times, more weight lifted, extended time to exhaustion, and many other examples
Do Energy Boosters Have Side Effects?
Generally speaking, most energy-boosting supplements do not have any serious side effects. However, stimulants such as caffeine or ginseng can produce some unwanted side effects, such as:
- Nervousness
- Restlessness
- Insomnia
- Sweating
- Heart palpitations
- Digestive issues such as diarrhea
- Elevated heart rate
- Headache
Who Takes Energy Boosters?
If counting tea and coffee, then we can make the argument that the large majority of people across the globe take energy boosters every day. But even if we don’t, they are still incredibly popular among different age groups and lifestyles.
Among the younger crowd, energy boosters are a popular way to help with studying, especially when cramming the night before a test. Similarly, working professionals use energy boosters to keep up with the demands of a busy work life. Finally, energy supplements are also popular with athletes seeking to improve their physical performance.

What is the Best Energy Booster?
It’s difficult to say which energy supplement is the best because everyone is different. Generally speaking, however, we suggest that:
- Individuals with stressful lives (e.g. shift work, long hours, physically-demanding tasks) should start with adaptogenic energy boosters such as rhodiola
- Older adults should look into energy-related compounds and antioxidants, as there is an increased chance that their natural levels of these compounds are low
- Healthy individuals would likely benefit most from stimulants such as caffeine or ginseng
Conclusion
Energy supplements can provide a wide range of invigorating effects, and make it easier to cope with the natural decrease of energy levels that occurs with aging. Furthermore, with some products you may even be able to get away with continuous supplementation with no side effects and little decrease in effectiveness. However, as must be repeated with all dietary supplements, they are no replacement for a healthy lifestyle. Good sleep, a healthy diet, and plenty of exercise are still the best way to keep your energy levels at their natural peak.
