The inflammation-modulating properties of fish oil omega-3 fatty acids may improve post workout recovery.

- Reducing exercise-induced joint and muscle damage. The omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil are widely known to modulate inflammation, accelerating recovery and helping athletes return to training faster.
- Improving body composition. Fish oils have been suggested to assist with body fat reduction when combined with exercise.
Overview
A staple of healthy diets, fish oil is a natural component of fatty fish and contains a high amount of polyunsaturated fats known as omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are a mainstay of healthy nutrition and are widely recognized for promoting cardiovascular prosperity.1
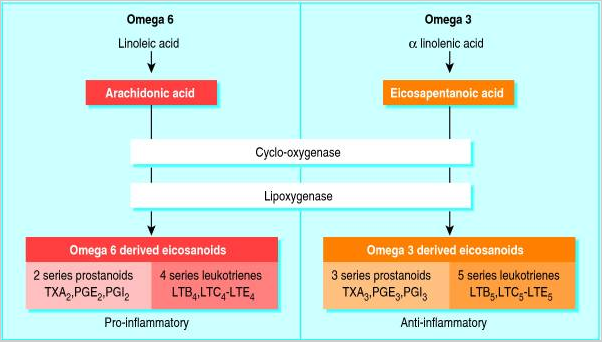
The principal omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil are alpha-linoleic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexanoic acid (DHA), none of which are produced in the human body and therefore must be consumed from outside sources. There is an impressively long list of proposed health benefits associated with fish oil:
- Promoting cardiovascular health2 3
- Alleviating mood disorders4
- Ameliorating joint conditions
- Supporting clear vision
- Stimulating the growth of neurons
- Managing blood sugar balance
- Promoting early childhood development5
- Supporting healthy respiration6
The powerful inflammation-modulating activity of fish oil is an underlying factor for many of these benefits, as well as contributing to its popular use among athletes in pre and post workout supplementation.

How Fish Oil Might Help Post-Workout Formulas
Reducing the production of inflammatory markers
Post workout inflammation plays a major role in joint swelling, stiffness, and pain, as well as contributes to muscle soreness. Fish oil is suggested to work by decreasing the production of inflammatory markers, predominantly leukotriene B4 and platelet activating factor.7 8 On a more fundamental level, fish oil has further been shown to decrease the expression of genes responsible for inflammatory pathways.9
Enhancing fat oxidation
When combined with exercise, fish oil supplementation has been shown to improve body composition by increasing the rate of triglyceride (fat) metabolism without lowering cholesterol levels.10 11 12
Fish Oil Post-Workout Benefits & Uses
Research concerning the properties of fish oil’s essential omega-3 fatty acids have discovered a long list of health benefits that may enhance workouts and improve post workout recovery, although the true extent of their effects is still being investigated.13 Among its chief post workout advantages are:
- Decreasing inflammation and discomfort associated with intense training and body building
- Reducing muscle soreness
- Minimize fatigue14
- Attenuating post workout strength loss and decreased range of motion
- Burning fat in conjunction with exercise15 16
- Maintaining healthy vision
- Augmenting bone density17
- Boosting post workout immunity18
Albeit only indirectly, fish oil may also be useful for athletic competition, fitness, bodybuilding, and gaming by promoting cardiovascular health19, preserving kidney function (which is crucial for stabilizing blood pressure), slowing the rate of bone loss, improving thinking skill20, enhancing night vision21, and reducing eye dryness.
Research
Human Research
Numerous clinical studies have corroborated the health benefits of fish oil in the context of specific conditions, but the results are somewhat conflicting when applied post workout. Some research has found that fish oil may reduce soreness and pain, boost immunity, and improve body composition after working out, whereas others have suggested fish oil at low doses might not reduce inflammation and likely increases oxidative stress.
Fish oil (3 g) may boost post workout immunity
In this double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled investigation, 16 males participated in a maximal exercise test and a 1-hour bout of endurance exercise and then given either a placebo or 3 g of fish per day for 6 weeks. Two markers of immune function (IL-2 and NK cell activity) significantly increased after fish oil supplementation compared to the placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “fish oil supplementation increases PBMC IL-2 production and NK cell cytotoxic activity in the recovery period after exercise.”22
Fish oil (1.8 g) may ameliorate delayed onset muscle soreness caused by exercise
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 27 men were administered either a placebo or 1.8 g of omega 3 per day for 60 days while regularly performing eccentric exercises. No significant differences in pain or range of motion were noted until 48 hours post workout.
- The researchers concluded that “omega-3 can be effective in ameliorating delayed onset muscle soreness induced by eccentric exercise.”23
Fish oil (600 mg EPA, 260 mg DHA) may protect muscle nerves and reduce muscle damage after exercise
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 21 men were given a control or 8 fish oil softgel capsules containing 600 mg EPA and 260 mg DHA per day for an 8-week period. The fish oil group demonstrated significantly greater muscle torque, range of motion, and less delayed onset muscle soreness after exercise compared to the placebo group.
- The researchers concluded that “EPA and DHA supplementation may play a protective role against motor nerve function and may attenuate muscle damage after eccentric contractions.”24
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 24 men were given either a placebo or a fish oil supplement containing 600 mg EPA and 260 mg DHA every day for 8 weeks during which period they participated in elbow flexion exercises. The fish oil group was found to have significantly higher maximal voluntary contraction torque, increased range of motion, and reduced muscle soreness after exercise compared to the placebo group.
- The researchers concluded that “EPA + DHA supplementation attenuates strength loss and limited ROM after exercise.”25
In this randomized investigation, overweight volunteers were given 6 g of fish oil (tuna), fish oil after exercise, sunflower oil, or sunflower oil after exercise every day for 12 weeks. Both fish oil and regular exercise were found to burn body fat and improve cardiovascular and metabolic health.
- The researchers concluded that “intake of n-3 FAs could be a useful adjunct to exercise programs aimed at improving body composition and decreasing cardiovascular disease risk.”26
Fish oil (3 g DHA) may reduce exercise-induced muscle soreness, swelling, and stiffness
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 27 women were given 3 g of DHA or a placebo every day for 7 days while participating in bicep flexion exercises. Short-term DHA supplementation was found to reduce exercise-induced muscle soreness and stiffness as well as protect against the loss of joint range of motion significantly more than the placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “DHA would be expected to facilitate recovery and allow for better performance during training and competition.”27
Fish oil (1.8 g) might not significantly reduce delayed onset muscle soreness at low doses
In this randomized, placebo-controlled investigation, 22 participants were assigned a placebo, 120 mg of a soy isolate (ISO), or 1.8 g of fish oil omega 3 fatty acids (FO) every day for 30 days. There were no significant differences among the groups in terms of treating post workout delayed onset muscle soreness.
- The researchers concluded that “FO or ISO, at the doses supplemented, were not effective in ameliorating DOMS with the above-cited protocol.”28
Fish oil (3 g) may minimize post workout soreness
In this controlled investigation, adults performing bicep curls were given either a control or 3 g of omega 3 supplements. Compared to the control, the omega 3 supplements resulted in a 15% lower increase in muscle soreness.
- The researchers concluded that “omega-3 supplementation could provide benefits by minimizing post-exercise soreness and thereby facilitate exercise training in individuals.”29
Fish oil (2.7 g) may improve athletic performance and lower the risk of muscle damage
In this placebo-controlled investigation, participants received either a placebo or 2.7 g of omega 3 supplements (N3) while performing heavy eccentric exercise during a 30-day period. N3 supplementation was found to reduce pain, improve emotional stability, and lower the risk of physical damage to muscle tissue up to 96 hours post workout. No serious adverse side effects were reported.
- The researchers concluded that “subjects with higher N3 index demonstrated reduced DOMS after heavy exerciseSubjects with higher N3 index reported better quality of life.”30
Fish oil (1.2 g) may decrease inflammation and improve vascular function in obese persons
In this randomized, double-blind investigation, 25 obese participants took either a placebo or 1.2 g of fish oil for 6 weeks. Fish oil was found to decrease the amount of inflammatory markers, including TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β, as well as improve vascular function compared to the placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “supplementation with n-3 capsules increases the serum n-3 PUFA concentration, improves vascular function, and lowers the degree of inflammation in obese adolescents.”31
Fish oil (600 mg EPA, 400 mg DHA) might not attenuate exercise-induced oxidative stress
In this randomized investigation, participants took supplements containing either 600 mg EPA and 400 mg DHA or a collection of antioxidants every day for 6 weeks at rest, before exercise, and after exercise. The omega 3 fatty acids did not reduce markers of oxidative stress after working out.
- The researchers concluded that “n-3 LC PUFA supplement increased oxidative stress at rest and did not attenuate the exercise-induced oxidative stress.”32
Fish oil (2.4 g) might not improve exercise performance or counter inflammation
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 23 trained cyclists were given either a placebo or 2.4 g of fish oil before and after a period of intense exercise for 6 weeks. Fish oil did not demonstrate any significant improvements in performance or in countering inflammation.
- The researchers concluded that fish oil “had no effect on exercise performance or in countering measures of inflammation.”33
Dosage for Post-Workout
- Successful clinical research studies use from 1 – 6 g of fish oil omega-3s per day.
- Typical capsule or softgel supplements range from 1 – 3 g of omega-3s taken 2 – 3 times daily.
- Standard serving of fish carrying approximately 900 mg (tuna) – 3890 mg (salmon) of omega-3s.
- Fish oil supplements should be refrigerated and taken with a meal to minimize side effects.
Available Forms
- Softgels, the most common supplement form of fish oil
- Liquid drops; some effectively mask fishy flavor
- Fatty fish, which nourish athletes and bodybuilders with Omega-3s plus ample protein
Supplements in Review Says
- Fish oil, 1 – 3 g of total omega-3s, as a post workout.
Fish oil may help accelerate recovery after intense training. Fish oil imparts a wide-range of research-backed, whole-body health benefits, including inflammation-soothing properties that may enhance post workout recovery while promoting comfort in achy joints and muscles.
Try 1-3 g of fish oil softgels as a postworkout starting point. The American Heart Association recommends people to eat 1 g of fish oil omega-3s per day for cardiovascular health, and clinical studies suggest up to 2 g of EPA and DHA for optimum muscle recovery.34
Leave a Reply