Amino acid DAA seems to stimulate the production of luteinizing hormone and increase testosterone levels.
![By SubDural12 (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://supplementsinreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/N-Methyl-D-Aspartic-Acid-300x197.png)
- Triggering activity of luteinizing hormone (LH), which in turn signals the testes to produce and release testosterone.1
- Increasing sperm count. DAA is highly concentrated in the testes and boosts sperm count.
- Triggering human growth hormone (HGH) synthesis in the pituitary gland.
Overview
The amino acid D-aspartic acid (DAA) is a relatively recent nutritional discovery for human health. For decades, scientists thought DAA only existed within the brains of octopus, squid and cuttlefish. Its presence in mammals—and humans—was only discovered in 1996.2 This short history means research is still early. But so far, evidence suggests DAA might universally support hormonal health.
DAA is present in endocrine systems of both vertebrates and invertebrates. In mammals, DAA exerts a strong influence on sex hormones, especially testosterone, which is what the spotlight is focused on now, as researchers, formulators, and consumers explore DAA’s potential for men’s health.
Despite being naturally generated in the human body, additional DAA is frequently supplemented and consumed in everyday foods, such as soy, oysters, oats, and egg white.

How DAA Might Help Testosterone Levels
Triggering hormone release for testosterone production
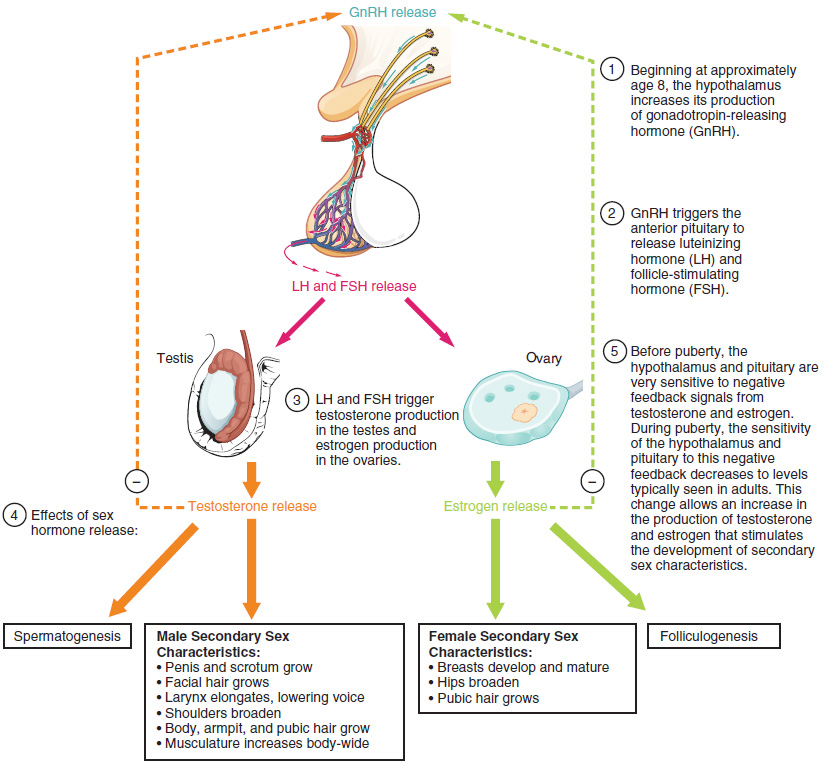
DAA has been theorized to trigger the production and release of hormones throughout the endocrine system, culminating in T-synthesis.3 It is a multi-step process involving several glands in the body4:
- First, DAA triggers the hypothalamus to increase the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
- GnRH then signals for the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary.
- Finally, LH stimulates leydig cells in the testes to increase testosterone production.5
With these roles, researchers have said that DAA “seems to play a crucial role in reproduction,” potentially because “it is involved in biosynthesis and the release of sexual hormones.”
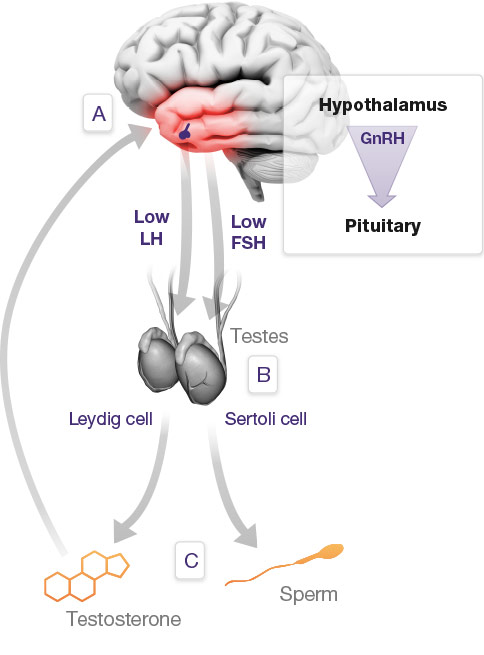
DAA: Part of T-synthesis, every step of the way
DAA appears to be involved in each step of male sex hormone production across the hypothalamic pituitary gonadal axis — from the GnRH that starts the process in the brain, all the way through to the testosterone that finishes it in the testes:
Our take: DAA seems to stimulate and sustain sex hormone production throughout the male endocrine system, enhancing the ultimate measures of male virility: Testosterone and sperm.
Research
Animal Research
D aspartic acid is great at boosting sex hormones:
- A direct correlation between DAA and testosterone levels was identified in mallard testes.6
- DAA was found to increase the activity of aromatase, which converts T into the female hormone estradiol, in boar testes.7
- DAA was shown to migrate to the pituitary gland and testes of male rats, leading to a8:
- 1.6X boost in LH
- 3X boost in testosterone
- 2.9X boost in progesterone (female hormone)
- DAA may actually increase testosterone synthesis while simultaneously decreasing estrogen levels in rodents by9:
- Reducing the expression of estrogen receptors
- Decreasing aromatase levels
A few of these animal studies back the idea that DAA boosts sex hormones across-the-board, affecting both male and female hormones. Although the combined DAA benefits to T and LH appear to outweigh the female progesterone boost, spiking female hormones can still skew testosterone-to-estrogen ratios and disrupt manly balance, if only slightly.
This begs the question: How effective might DAA’s effects be if its corresponding female hormone-boost could be reduced? Accordingly, a potential solution to optimize masculinity may be to combine DAA with female hormone blockers, such as:
- Luteolin, which is believed to block the aromatase enzyme from converting testosterone into estrogen.
- Stinging nettle, another potential aromatase inhibitor.
- Agaricus bisporus, which contains linolenic acids that may also inhibit aromatase.
- Boron, which is theorized to favor an increase in testosterone relative to estradiol.
Human Research
The number of clinical studies with DAA is limited because DAA’s presence in humans is a new discovery. Nonetheless, there are a couple of promising studies that stand out.
DAA (3.12 g) may boost T levels in males
This placebo-controlled study on DAA and testosterone simultaneously evaluated humans and rats. 23 men were given either a placebo or 10 mL of DADAVIT® containing 3.12 grams of D-aspartic acid, which is a liquid supplement that blended plain “unbound” DAA with vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and folic acid. Rats were given a plain DAA liquid formula. The D-aspartic acid formula was found to significantly increase the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone in male humans and rats taking DADAVIT® compared to the control.
- The researchers concluded that “in humans and rats, sodium D-aspartate induces an enhancement of LH and testosterone release.”10
DAA may boost sperm count by 160%
In this study, 30 male patients with fertility problems took DAA every day for 90 days, and the men were tested for sperm count, sperm motility, and the success rate of partner pregnancy. DAA supplementation apparently increased sperm count by 160%, enhanced sperm motility, and resulted in more of their partners getting pregnant. Low testosterone seems to have a strong link to low sperm count.
- The researchers concluded that “treatment of sub-fertile patients with sodium D-aspartate improved the number and the motility of the spermatozoa and consequently improved the rate of pregnancies of their partners.”11
DAA (3 g) seems to have little impact on T levels when coupled with resistance training
In this placebo-controlled investigation, resistance-trained men were given 3 grams of either a placebo or DAA 4 times a week for 28 days during standard training. In both groups, body composition and muscle strength similarly increased, while testosterone, luteinizing hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, and estradiol levels were unchanged.
- The researchers concluded that “D-ASP supplementation is ineffective in up-regulating the activity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis and has no anabolic or ergogenic effects in skeletal muscle.”12
DAA might enhance T-levels but data is inconclusive
In this review, 23 animal and 4 human studies were evaluated and analyzed. The results indicate that though DAA was found to enhance testosterone levels in some studies, it was also shown to have no significant effect in others. The limited number of available studies provide inconsistent information.
- The researchers concluded that “there is an urgent need for more and well-designed human clinical trials with larger sample sizes and longer duration to investigate putative effects of D-Asp on testosterone concentrations.”13
The Unsolved Mystery of DADAVIT®
DADAVIT®, used in the human & rat study previously mentioned, was a trademarked supplement developed by the Italian drug firm Pharmaguida. It combined DAA with vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and folic acid with the intention of boosting male fertility. Despite impressive testosterone benefits shown in human research, DADAVIT® rapidly disappeared off the face of the earth with few, if any, remaining records of its existence. You might be able to mimic DADAVIT®’s “lost formula” by taking DAA with B-vitamins, but the exact ratio and forms Pharmaguida used are still a mystery today.
Dosage for Testosterone
- Successful clinical studies have used from 2.66 – 3.12 grams of DAA in its harder-to-absorb “unbound” form.
- Typical DAA supplements come in daily servings of 3 grams.
- D-AA-CC supplements are a little harder to come by and are offered as 1 – 2 gram servings.
Available Forms
There are two primary forms of DAA, which are most commonly available as capsules or a scoopable powder that can be added to protein shakes or liquids:
- DAA (D-Aspartic Acid). Plain, “unbound” DAA is the cheapest, most basic form. It’s also harder for the body to absorb.
- D-AA-CC (D-Aspartic Acid Calcium Chelate). An advanced form of DAA “bound” to calcium chelate, which is more comfortable to digest and easier to absorb. Note: A lower dose of unbound DAA might actually be more potent and have fewer adverse side effects than bound DAA due to its increased bioavailability.
Supplements in Review Says
- D-AA-CC 1 – 2 g daily for testosterone.
DAA seems to be a flat-out sex hormone enhancer. We recommend DAA for its dynamic T-boosting activity. It even made our list for top testosterone supplements for 2017. The D-AA-CC form is preferred, although you really can’t go wrong with DAA in any form.
Remember how DAA boosts female sex hormones, too? Look for T booster formulas that combine DAA with female hormone blockers such as luteolin. Formulations like these might synergize to unlock DAA’s full T-boosting potential.
Leave a Reply