The high luteolin content in artichoke may facilitate memory formation, particularly when combined with other nootropics.

- Supporting memory. Bioactive ingredients in artichoke may play a critical role in the formation and retention of memories.
- Neuroprotection. Artichoke has demonstrated antioxidant activity.
Overview
Native to the Mediterranean, artichoke (Cynara scolymus) is a species of thistle with a fleshy stalk and a budding flower head. Its flower bud, leaves, and stalk are all edible and have been incorporated into European and Middle Eastern cuisine for ages.
Artichoke has historically been used to manage hyperuricemia and gout, and it has more recently been considered in some medical practices as a natural way to help promote fat loss, reduce cholesterol levels, and resolve problems with digestion.1 2
The two main active ingredients in artichoke are luteolin (27 –215 mg/kg) and apigenin, both of which are present in various nootropic supplements and have demonstrated health-promoting properties.3 The potent antioxidant capacity of luteolin, which ranks among the highest in vegetables, has spurred belief in its ability to detox the brain and enhance cognitive function.4 5

How Artichoke Might Help the Brain
Inhibiting phosphodiesterase
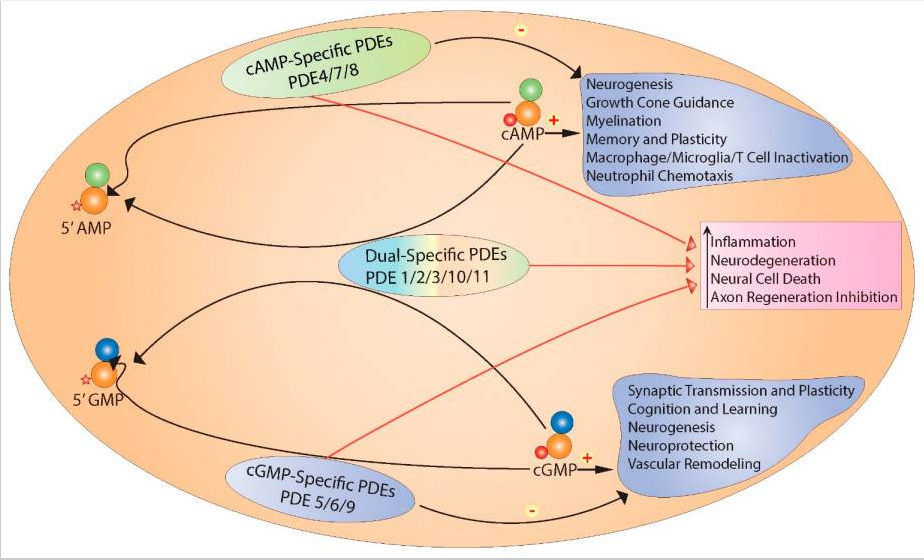
Artichoke, similar to kanna and horny goat weed, contains a high content of luteolin, which is widely recognized as a non-selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase (PDE).6 PDEs are notorious for blocking important brain signaling molecules, such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), from functioning. By inhibiting PDEs, especially PDE-4, artichoke may potentially increase the signaling activity of neurons, which is essential for memory formation and retention.
Further, inhibiting PDEs has also been shown to lead to neuroprotection and repair, which has demonstrated therapeutic effects.7
Artichoke Benefits & Uses for Brain Health
Despite limited clinical evidence, artichoke extract has been used, above all, to improve various functions linked to memory:
- Short-term. Artichoke is believed to enhance the ability to make associations between concepts, which includes performing calculations and logical reasoning.
- Comprehension. Artichoke may boost memory retention and thus bolster the mental ability to comprehend challenging subjects.
Artichoke in the CILTEP nootropic stack
Though there is little clinical evidence backing the nootropic effects of artichoke extracts per se, they have popularly been integrated into a special type of supplemental stack known as CILTEP®, which stands for chemically induced long term potentiation.
The supplement contains artichoke extract, forskolin extract, acetyl-L-carnitine, L-phenylalanine, and vitamin B6, and is theorized to improve focus, learning, and memory, among other benefits, by increasing levels of cAMP and inhibiting PDEs.
Research
Animal Research
Research indicates that artichoke may promote brain health by:
Luteolin, the main bioactive compound in artichoke, has also demonstrated a number of nootropic effects in animal research, including:
- Improving cognitive function in rats10
- Combating cognitive aging and neurodegeneration in mice11
- Ameliorating memory impairment in mice12
- Reducing Alzheimer’s features in mice13
- Enhancing spatial memory in rats14
- Attenuating neuronal cell death in rats15
Human Research
Clinical studies targeting the effect of artichoke extracts on the brain are currently limited.
Artichoke extract (1200 mg) may increase antioxidant activity
In this randomized, double-blind investigation, 22 Polish rowers were given either a placebo or a gelatin capsule containing 400 mg of artichoke extract 3 times a day for 5 weeks while on a consistent rowing regimen. The results showed that total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was significantly higher in the artichoke extract group compared to the placebo.
- The researchers concluded that “consuming artichoke-leaf extract, a natural vegetable preparation of high antioxidant potential, resulted in higher plasma TAC than placebo.”16
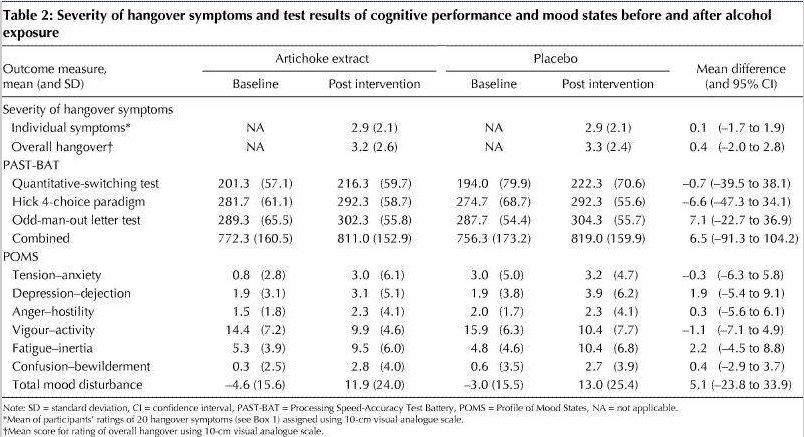
In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation, 15 adults were given either a placebo or 3 artichoke extract capsules at 320 mg each before and after heavy alcohol consumption. No significant differences were noted between the artichoke extract and placebo groups in terms of mood or performance on cognitive tests.
- The researchers concluded that “artichoke extract is not effective in preventing the signs and symptoms of alcohol-induced hangover.”17
Nootropic Dosage
- Clinical research studies have used from 1.2 – 1.92 g of artichoke extract per day.
- Typical artichoke supplements provide from 320 – 1800 mg per daily serving.
Available Forms
- Leaf extract in the form of capsules or tablets
- Powder
- Drops
- Tea

Supplements in Review Says
- Artichoke 500 – 900 mg as a nootropic.
Artichoke may support memory, but research is wanting. Even though artichoke is commonly integrated into nootropic supplements, its isolated impact on cognitive function has yet to receive significant clinical backing. We recommend waiting on using artichoke extracts until more research is conducted.
Try artichoke leaf extracts in CILTEP supplements. Incorporation into the popular CILTEP® stacks may optimize the potential nootropic impact of artichoke extracts as well as be the safest way to take it.
Leave a Reply