With ever-increasing access to food and the rise of the sedentary lifestyle, it’s not surprising that obesity has quickly grown into a global health crisis. With 1.9 billion overweight or obese adults, obesity is now one of the leading preventable causes of death worldwide.1 In the United States alone, more than 2 out of every 3 adults are overweight or obese.
With these staggering statistics in mind, it’s not hard to imagine millions of people turning to fat loss supplements every year. But which supplements actually work? And how? In this guide, we’re going to discuss the science behind fat loss and fat burners.
Fat 101
However, the problem is that our modern lives are vastly different from our ancestors, since we have access to a reliable supply of food and a far less active lifestyle. This can result in eating more calories than you’re burning, which will lead to fat gain.
A healthy body fat percentage can range anywhere from: 2
- Age 20-39: 8-20% for men and 21-33% for women
- Age 40-59: 11-22% for men and 23-34% for women
- Age 60-79: 13-25% for men and 24-36% for women
What are Fat Burners?
Fat burners are dietary supplements that promote the loss of body fat through the effects of bioactive plant compounds, minerals, and other substances. Although the term implies that these supplements work by promoting the “burning” of body fat, fat burners can also work through other methods such as reducing the amount of dietary fat absorbed by the body.
How Fat Loss Supplements Work
Fat loss supplements can exert their effects through a variety of mechanisms. The four most common biological methods for reducing body fat are:
- Increasing fat oxidation (the “burning” of fat for energy)
- Decreasing appetite
- Decreasing fat or carbohydrate absorption
- Decreasing adipogenesis (fat cell formation)
While these methods are quite different from one another, the end result is still the same – less body fat. Most fat-burning compounds work through a combination of one or more of these mechanisms. Let’s look at each of these in detail:
Boosting Fat Oxidation
Fat oxidation is a natural process through which fat is oxidized or “burned” in a cell’s mitochondria to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This process serves as the second major source of energy after carbohydrates, and its relationship with fat storage determines whether you maintain, lose, or gain body fat.
In other words, if the rate of fat oxidation is higher than the rate at which you’re storing new fat, you will gradually lose fat.
There are multiple ways to improve fat oxidation, such as:
- Physical activity (endurance exercise in particular)
- Increasing thermogenesis (the body’s heat production)
- Increasing metabolic rate (the rate at which calories are burned)
Caffeine is a popular example of a fat burner that works by increasing fat oxidation.
Suppressing Appetite
Rather than tackling fat directly, some fat burners work by reducing your desire to eat. Similar to the balance between fat oxidation and fat storage, the balance between how many calories you take in and how many you burn determines whether you’re going to maintain, lose, or gain weight. As such, reducing appetite can put you in a negative energy balance and promote fat loss.
A good example of a supplement with this bio-activity is synephrine – the active ingredient of bitter orange. Synephrine is believed to stimulate alpha one adrenergic receptors that regulate appetite, resulting in a reduced desire to eat. Another popular way of reducing your appetite is fiber supplements, which make you feel more satiated.

Reducing Fat or Carbohydrate Absorption
Another method for promoting fat loss is reducing the digestion and absorption of dietary fats or carbohydrates. Similar to reducing your appetite, this results in fewer calories being taken into the body. Compounds that work this way are sometimes called fat or carb blockers.
For example, the catechins in green tea can inhibit enzymes that help with digesting fat, such as pancreatic lipase. As a result, your body takes in fewer calories from the fats in your diet.
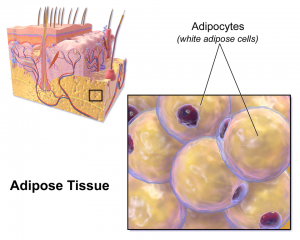
Inhibiting Adipogenesis
Adipogenesis is s complex process through which specialized cells ultimately turn into adipocytes – fat cells. Impeding this process is the most complex way of promoting fat loss. This mechanism is used by the South American herb yerba mate, which believed to suppress the gene expression of Ppar-γ and C/ebp-α – factors that promote adipogenesis.
Types of Fat Burners
Fat loss supplements can be made from a variety of sources. Check out our fat burners list for a closer look at the most popular fat loss supplements.
Plants

Because of this, plant-derived products are typically standardized to contain a certain amount of the active ingredient.
Vitamins, Minerals, and Amino Acids
Some vitamins, minerals, and amino acids are also used in weight loss supplements, but they are typically added to enhance the main active ingredients rather than acting on their own.
This is because these nutrients seem to have more general effects that might support healthy fat metabolism rather than direct fat-burning effects. Examples of this category include chromium picolinate, vitamin B12, l-carnitine, and CoQ10 – a vitamin-like compound.
Fats
It may sound strange, but some fat-containing compounds might actually have some weight loss benefits. Coconut oil, alpha lipoic acid (ALA), and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) are a couple of good examples.
Synthetic Drugs
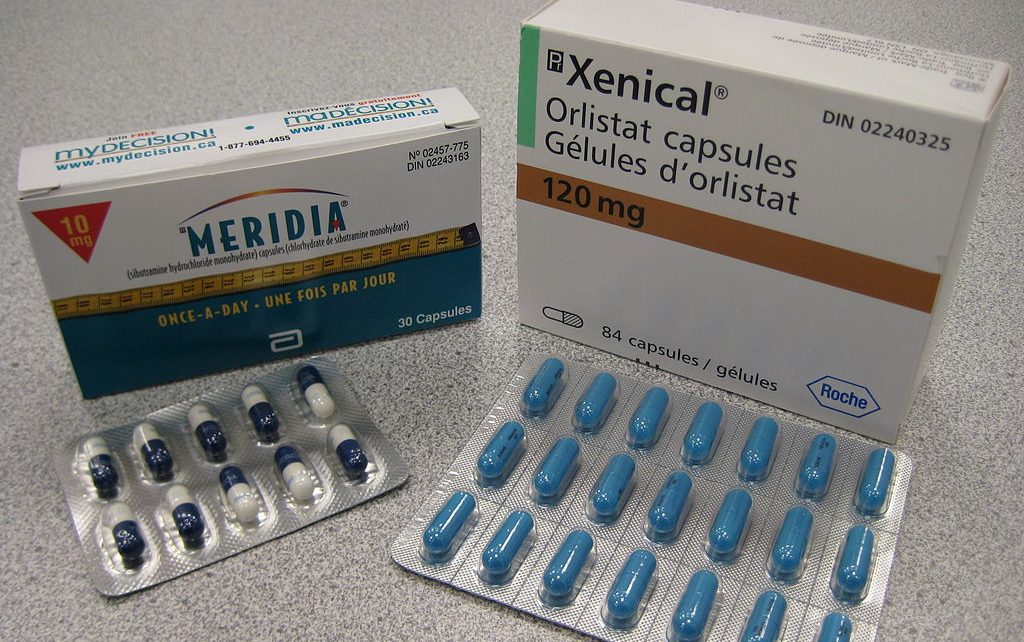
As the case with many health conditions, the pharmaceutical industry has created synthetic drugs that can help promote weight loss. The best example of a synthetic weight loss drug is Orlistat, which works by reducing absorption of fat in the intestine.
Fat Burner Side Effects
Most compounds used in fat loss products are fairly safe and can only lead to minor side effects. Caffeine, for instance, can cause nervousness, irritability, headaches, dehydration, and abnormal heartbeat, especially if taken in large doses.
Having said that, there are two things to watch out for. First, there are controversial fat loss compounds such as ephedrine, which can potentially lead to serious side effects that include elevated blood pressure, heart palpitations and seizures. Second are supplements that combine multiple ingredients which could worsen the side effects.
The bottom line, however, is that most fat burners – be they single or multi-ingredient products – are generally safe.
What is the Best Fat Burner?
Most fat loss supplements – and especially those that use multiple ingredients – have seen little clinical research, which makes it difficult to judge their usefulness.
Having said that, in terms of sheer efficacy, the Asian herb ephedra and its active constituent ephedrine seems to be one of the most potent fat burners. According to a review of more than 50 clinical trials, ephedrine results in an average weight loss of 0.9 kg (2 lb) per month.3 However, ephedrine was banned by the FDA in 2004 because of its potentially dangerous side effects.

Other solid, research-backed options include green coffee bean extract and alpha lipoic acid. Orlistat might also be a good choice, especially considering that it is an FDA-approved weight loss drug.
What is the best Fat Loss Formula?
While single-ingredient supplements can certainly be effective, multi-ingredient formulas are usually more popular. We recommend a supplement that combines green tea extract, green coffee bean extract, and caffeine as the main ingredients. For example, a supplement such as Vintage Burn is a solid option.
Conclusion

Fat loss supplements are extremely popular and there is some scientific evidence that they work. However, barring a massive scientific breakthrough, the effects of currently-available fat burners are fairly small.
Even the most potent fat loss supplement is still a drop in the bucket when compared to the effects of tried-and-true dieting and exercise. As such, fat loss supplements should be seen as a way to improve the weight loss achieved by a low-calorie diet and working out, rather than a standalone magic pill.
